
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 52P
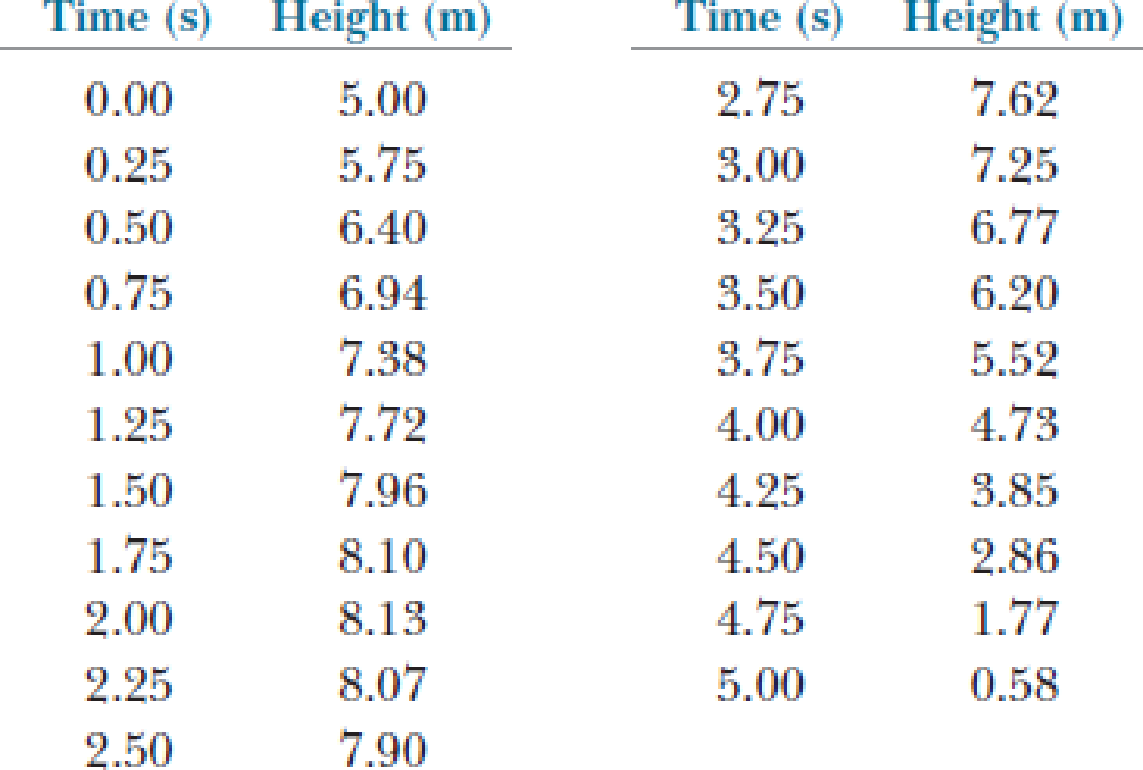
Astronauts on a distant planet toss a rock into the air. With the aid of a camera that takes pictures at a steady rate, they record the rock’s height as a function of time as given in the following table. (a) Find the rock’s average velocity in the time interval between each measurement and the next. (b) Using these average velocities to approximate instantaneous velocities at the midpoints of the time intervals, make a graph of velocity as a function of time. (c) Does the rock move with constant acceleration? If so, plot a straight line of best fit on the graph and calculate its slope to find the acceleration.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
*
Coulomb's Law Example
Three charges are positioned as seen below. Charge
1 is +2.0 μC and charge 2 is +8.0μC, and charge 3 is -
6.0MC.
What is the magnitude and the direction of the force
on charge 2 due to charges 1 and 3?
93
kq92
F
==
2
r13 = 0.090m
91
r12 = 0.12m
92
Coulomb's Constant: k = 8.99x10+9 Nm²/C²
✓
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Chapter 2 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Ch. 2.1 - Under which of the following conditions is the...Ch. 2.2 - Are members of the highway patrol more interested...Ch. 2.4 - Using Active Figure 2.8, match each vxt graph on...Ch. 2.4 - If a car is traveling eastward and slowing down,...Ch. 2.5 - Which of the following statements is true? (a) If...Ch. 2.7 - A ball is thrown upward. While the ball is in...Ch. 2 - One drop of oil falls straight down onto the road...Ch. 2 - When applying the equations of kinematics for an...Ch. 2 - Prob. 3OQCh. 2 - Prob. 4OQ
Ch. 2 - When the pilot reverses the propeller in a boat...Ch. 2 - A pebble is dropped from rest from the top of a...Ch. 2 - A student at the top of a building of height h...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8OQCh. 2 - As an object moves along the x axis, many...Ch. 2 - You drop a ball from a window located on an upper...Ch. 2 - A skateboarder starts from rest and moves down a...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown straight up in the air. For which...Ch. 2 - A hard rubber ball, not affected by air resistance...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14OQCh. 2 - If a car is traveling eastward, can its...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2CQCh. 2 - (a) Can the equations of kinematics (Eqs....Ch. 2 - Prob. 4CQCh. 2 - Prob. 5CQCh. 2 - Prob. 6CQCh. 2 - Prob. 7CQCh. 2 - You throw a ball vertically upward so that it...Ch. 2 - Two cars are moving in the same direction in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 1PCh. 2 - Prob. 2PCh. 2 - Prob. 3PCh. 2 - A person walks first at a constant speed of 5.00...Ch. 2 - A positiontime graph for a particle moving along...Ch. 2 - The position of a particle moving along the x axis...Ch. 2 - Find the instantaneous velocity of the particle...Ch. 2 - Prob. 8PCh. 2 - A hare and a tortoise compete in a race over a...Ch. 2 - An object moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - A particle moves along the x axis according to the...Ch. 2 - A student drives a moped along a straight road as...Ch. 2 - A particle starts from rest and accelerates as...Ch. 2 - A glider of length 12.4 cm moves on an air track...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.15 shows a graph of vx versus t for the...Ch. 2 - Draw motion diagrams for (a) an object moving to...Ch. 2 - Prob. 17PCh. 2 - The minimum distance required to stop a car moving...Ch. 2 - Prob. 19PCh. 2 - Prob. 20PCh. 2 - Prob. 21PCh. 2 - Prob. 22PCh. 2 - The driver of a car slams on the brakes when he...Ch. 2 - In the particle under constant acceleration model,...Ch. 2 - A truck on a straight road starts from rest,...Ch. 2 - A particle moves along the x axis. Its position is...Ch. 2 - A speedboat travels in a straight line and...Ch. 2 - In a classic clip on Americas Funniest Home...Ch. 2 - Prob. 29PCh. 2 - A baseball is hit so that it travels straight...Ch. 2 - Prob. 31PCh. 2 - It is possible to shoot an arrow at a speed as...Ch. 2 - A student throws a set of keys vertically upward...Ch. 2 - At time t = 0, a student throws a set of keys...Ch. 2 - A ball is thrown directly downward with an initial...Ch. 2 - Prob. 36PCh. 2 - Prob. 37PCh. 2 - Prob. 38PCh. 2 - A steam catapult launches a jet aircraft from the...Ch. 2 - An object is at x = 0 at t = 0 and moves along the...Ch. 2 - Colonel John P. Stapp, USAF, participated in...Ch. 2 - A woman is reported to have fallen 144 ft from the...Ch. 2 - A ball starts from rest and accelerates at 0.500...Ch. 2 - A glider of length moves through a stationary...Ch. 2 - Prob. 45PCh. 2 - The Acela is an electric train on the...Ch. 2 - Liz rushes down onto a subway platform to find her...Ch. 2 - A commuter train travels between two downtown...Ch. 2 - Prob. 49PCh. 2 - A motorist drives along a straight road at a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 51PCh. 2 - Astronauts on a distant planet toss a rock into...Ch. 2 - Prob. 53PCh. 2 - A hard rubber ball, released at chest height,...Ch. 2 - A man drops a rock into a well. (a) The man hears...Ch. 2 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 2 - Two objects, A and B, are connected by a rigid rod...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please help with this question asap!!! in detailarrow_forwardplease answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward
- 7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forwardганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY