
Concept explainers
A solid, insulating sphere of radius a has a uniform charge density throughout its volume and a total charge Q. Concentric with this sphere is an uncharged,
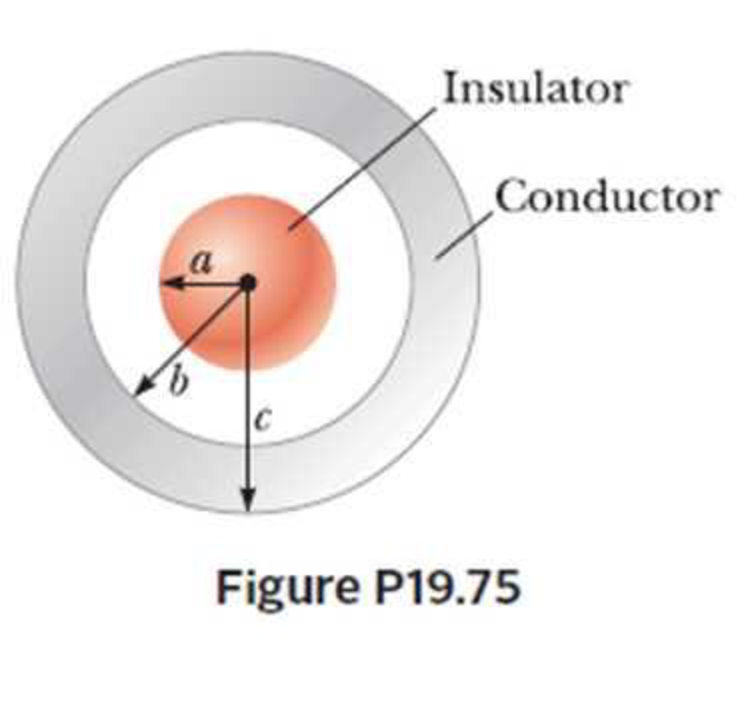
(a)
The charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Answer to Problem 75P
The charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 represents an insulating sphere of radius
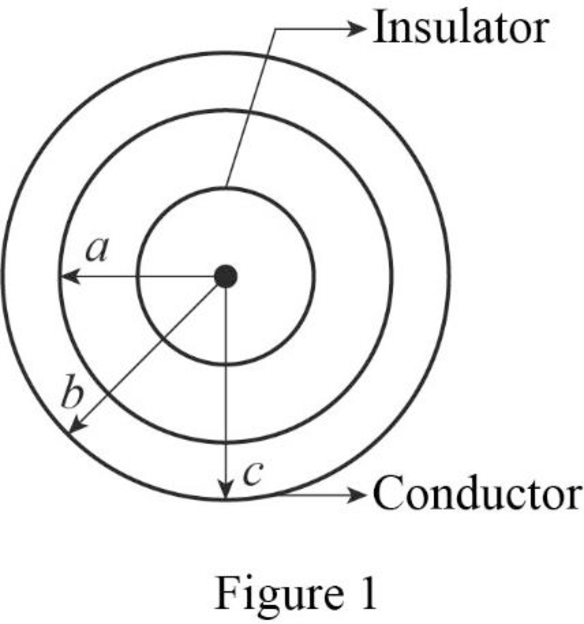
Consider a Gaussian surface of radius
Write the expression for charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Here,
Write the expression for volume enclosed by the Gaussian surface.
Here,
Use equation (II) in (I).
Write the expression for volume charge density for the insulating sphere of radius
Use equation (IV) in (III),to find
Conclusion:
Therefore, the charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
(b)
The electric field in the region
Answer to Problem 75P
The electric field in the region
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for Gauss law.
Here,
Due to spherical symmetry, the element of area
From subpart (a), the charge enclosed in the region
Use equation (V) in (VII), and rearrange.
The above is written as
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electric field in the region
(c)
The charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Answer to Problem 75P
The charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Here,
Conclusion:
Therefore, charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
(d)
The magnitude of electric field in the region
Answer to Problem 75P
The magnitude of electric field in the region
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Here,
Use equation (XI) in (VII).
The above equation is written as
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of electric field in the region
(e)
The magnitude of electric field in the region
Answer to Problem 75P
The magnitude of electric field in the region
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for Gauss law.
The Gaussian surface encloses zero charge in the region
Write the expression for charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface in the region
Here,
Use equation (XIII) in (VI).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of electric field in the region
(f)
The charge on the inner surface of the hollow sphere.
Answer to Problem 75P
The charge on the inner surface of the hollow sphere is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for Gauss law.
Write the expression for charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface.
Here,
Use equation (XIV) in (VI).
The electric field inside the conductor is zero, the charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is zero. The above equation is reduced to
Conclusion:
Therefore, the charge on the inner surface of the hollow sphere is
(g)
The charge on the outer surface of the hollow sphere.
Answer to Problem 75P
The charge on the outer surface of the hollow sphere is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for total charge inside the hollow sphere.
Here,
The total charge inside the conductor is zero, the above equation is reduced to
Rearrange the above equation, to find
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, The charge on the outer surface of the hollow sphere is
(h)
Among the three spherical surfaces having radii
Answer to Problem 75P
The inner surface of radius
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for surface charge density.
Here,
The solid insulating sphere has small surface charge density since its total charge is uniformly distributed throughout its volume.
The inner surface of the hollow cylinder with radius
Conclusion:
Therefore, the inner surface of radius
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- solve for (_) Narrow_forwardTwo boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forwardAll correct but t1 and t2 from part Aarrow_forward
- Three long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I₁ = 3.50 A, I2 = 5.50 A, and I3 = 8.50 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 34.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between (11) and (12) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (A). Solve in Teslas (T). I₁arrow_forwardNumber There are four charges, each with a magnitude of 2.38 μC. Two are positive and two are negative. The charges are fixed to the corners of a 0.132-m square, one to a corner, in such a way that the net force on any charge is directed toward the center of the square. Find the magnitude of the net electrostatic force experienced by any charge. ips que Mi Units estic re harrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forward
- Thank you in advance, image with question is attached below.arrow_forwardQuestion is attached, thank you.arrow_forwardTwo very small spheres are initially neutral and separated by a distance of 0.612 m. Suppose that 4.12 × 1013 electrons are removed from one sphere and placed on the other. (a) What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force that acts on each sphere? (b) Is the force attractive or repulsive?arrow_forward
- Estimate the diameter of the Moon. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon passes in front of the Sun so that during “totality” their apparent sizes match and the Moon blocks light from the Sun shining on the Earth. a) What do you predict the size of the Moon would be if you were to use a pinhole in an aluminum holder, meter stick, and white paper screen to project light from the full Moon through a pinhole onto a screen that is one meter away from the pinhole? b) Describe in detail how you would use this apparatus and your knowledge of pinhole phenomena to estimate the diameter of the Moon. Assume that the distance between the Earth and the Moon is 250,000 miles.arrow_forwardThe following data was collected for a friction experiment in which an object was observed moving at constant speed over a surface. Graph the Applied Force versus the Normal Force and determine the coefficient of friction. Is this value the coefficient of kinetic friction or the coefficient of static friction? Justify your answer. Trial Normal Force Applied Force 1 4.13 1.44 2 6.41 1.68 3 8.94 2.82 4 11.34 3.94 5 13.82 5.05arrow_forward1. Measurements and Linear Regression 1.1 Introduction The objective of this lab assignment is to represent measurement data in graphical form in order to illustrate experimental data and uncertainty visually. It is often convenient to represent experimental data graphically, not only for reporting results but also to compute or measure several physical parameters. For example, consider two physical quantities represented by x and y that are linearly related according to the algebraic relationship, y=mx+b, (1.1) where m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept. In order to assess the linearity between y and x, it is convenient to plot these quantities in a y versus x graph, as shown in Figure 1.1. Datapoints Line of regression Figure 1.1: Best fit line example. Once the data points are plotted, it is necessary to draw a "best fit line" or "regression line" that describes the data. A best fit line is a straight line that is the best approximation of the given set of data, and…arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





