
(a)
The angular momentum of the assembly about point
Answer to Problem 18.15P
The angular momentum of the assembly about point
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of each L-shaped arm is
The below figure represents x’, y’, and z’ axis parallel to the x, y, and z axis.
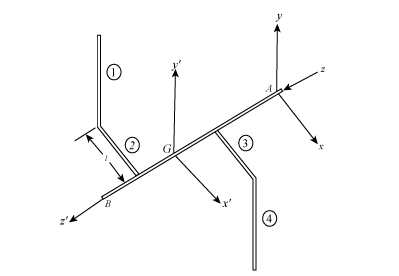
Figure (1)
Write the expression for angular velocity in x’-direction.
Write the expression for angular velocity in y’-direction.
Write the expression for mass of each segment of arm
Here,
Write the expression for angular velocity in z-direction.
Here, speed of assembly is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (1) in x-z direction
Here mass moment of inertia along x-y direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (1) in y-z direction.
Here mass moment of inertia along y-z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (1) in z direction
Here mass moment of inertia along z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (2) in x-z direction.
Here, mass moment of inertia along x-y direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (2) in y-z direction.
Here mass moment of inertia along y-z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (2) in z direction.
Here mass moment of inertia along z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (3) in x-z direction.
Here, mass moment of inertia along x-z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (3) in y-z direction.
Here, mass moment of inertia along y-z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (3) in z direction.
Here mass moment of inertia along z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (4) x-z direction.
Here, mass moment of inertia along x-y direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (4) y-z direction.
Here, mass moment of inertia along y-z direction is
Write the expression for moment of inertia for part (4) z direction.
Here mass moment of inertia along z direction is
Write the expression for total mass moment of inertia in x-y direction.
Write the expression for total mass moment of inertia in y-z direction.
Write the expression for total mass moment of inertia in z direction.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Write the expression for angular momentum in x-z direction.
Substitute
Write the expression for angular momentum in y-z direction.
Substitute
Write the expression for angular momentum in z direction.
Substitute
Write the expression for
Substitute,
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus angular momentum of the assembly about point
(b)
The angle formed by
Answer to Problem 18.15P
The angle formed by
Explanation of Solution
Given information Write the expression for the magnitude of angular momentum in about assembly A
Write the Expression for angle formed by
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus angle formed by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- Consider a round potato being baked in an oven. Would you model the heat transfer to the potato as one, two, or three dimensional? Would the heat transfer be steady or transient? Also, which coordinate system would you use to solve this problem, and where would you place the origin? Explain.arrow_forward0 = 6 a = 25 t = 3 Y b = 30 xarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardreading is 0.4 mas SHOWN. Assume h₁ = 0.4 m, h₂ = 0.5 m. (a) Do you know the specific weight of mercury? (b) Do you know the specific weight of gasoline? (c) Do you know the specific weight of oil? (a) YHg = 133,000 (b) Ygas = 6867 (c) Yoil = 8829 eTextbook and Media Part 2 N/m³ N/m³ N/m³ A+ Gasoline t +B Oil -Mercury Attempts: unlimited Did you calculate the pressure difference between two locations using the correct specific weight? Did you assume that the pressures in fluid are the same in a horizontal plane even though they are in different tubes? Are the calculated pressures in a column of fluid always higher at lower elevations? Did you account for the fact that the two horizontal tubes of the U-tube are above the ground? Concepts: The pressure in a fluid is a function of the specific weight of the fluid and the height relative to a reference. Pressure is constant in a horizontal plane of a continuous mass of fluid. (a) What is the initial pressure difference? (PA-PB) (b) What is…arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) "-4y+3y=0 3) "+16y=0 2) y"-16y=0 4) y"-y-6y=0 5) y"+2y=0 7) y"+y=0, (#0) 9) y"-y=0, y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -4 11) y"-4y+3y=0, y(0)=-1, 13) y'(0) = -5 "+2y+2y=0 15) y"-9y=0 17) y"-4y=0 6) y"-2y+2y=0 8) "+4y+5y=0 10) y"-9y=0, y(0) = 2, y'(0) = 0 12) y"-3y+2y= 0, y(0)=-1, y'(0) = 0 14) 4y+4y+y=0 16) "+6y+12y=0 18) 4y+4y+17y=0arrow_forward
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





