
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.1, Problem 1P
- a. Explain why, when the imidazole ring of histidine is protonated, the double-bonded nitrogen is the nitrogen that accepts the proton. (Hint: Localized electrons are more apt to be protonated than delocalized electrons.)
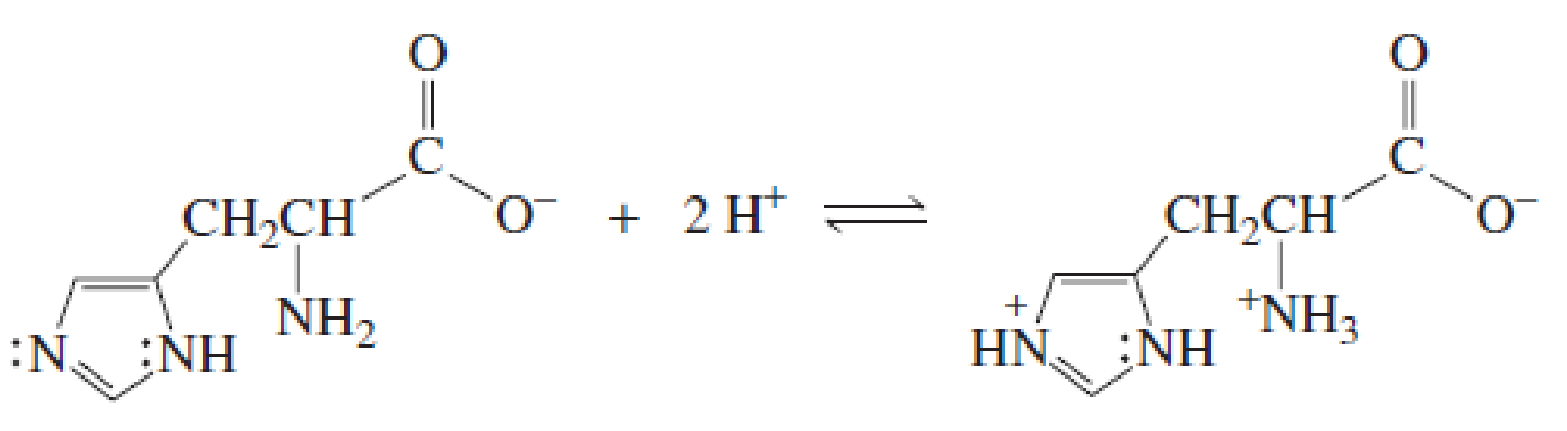
- b. Explain why, when the guanidino group of arginine is protonated, the double-bonded nitrogen is the nitrogen that accepts the proton.
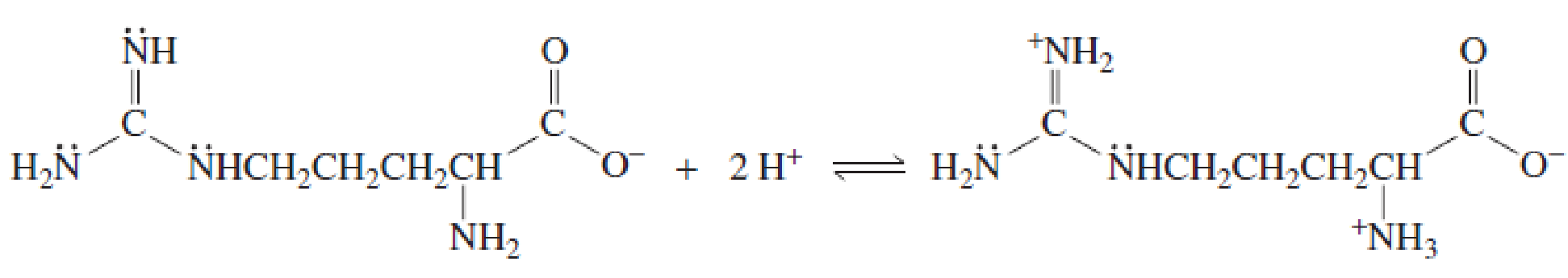
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
None
None
None
Chapter 17 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 17.1 - a. Explain why, when the imidazole ring of...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 17.4 - Calculate the pI of each of the following amino...Ch. 17.4 - a. Which amino acid has the lowest pI value? b....Ch. 17.5 - What aldehyde is formed when valine is treated...Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 10PCh. 17.5 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 17.6 - Prob. 13PCh. 17.6 - What amino acid would be formed using the...Ch. 17.6 - What amino acid would be formed when the aldehyde...Ch. 17.7 - Pig liver esterase is an enzyme that catalyzes the...Ch. 17.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 17.8 - Prob. 18PCh. 17.8 - Prob. 19PCh. 17.8 - Prob. 20PCh. 17.10 - Prob. 21PCh. 17.10 - Prob. 22PCh. 17.10 - Why does cyanogen bromide not cleave on the C-side...Ch. 17.10 - Prob. 24PCh. 17.10 - Prob. 26PCh. 17.12 - Prob. 27PCh. 17.13 - a. Which would have the greatest percentage of...Ch. 17 - Draw the predominant form of the following amino...Ch. 17 - What is the pI of serine?Ch. 17 - Prob. 31PCh. 17 - Prob. 32PCh. 17 - Which would have a higher percentage of negative...Ch. 17 - Draw the form of aspartate that predominates at...Ch. 17 - Prob. 35PCh. 17 - A professor was preparing a manuscript for...Ch. 17 - a. Why is the pKa of the glutamate side chain...Ch. 17 - Prob. 38PCh. 17 - Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide...Ch. 17 - Prob. 40PCh. 17 - Prob. 41PCh. 17 - Three peptides were obtained from a trypsin...Ch. 17 - Prob. 43PCh. 17 - After the polypeptide shown here was treated with...Ch. 17 - The disulfide bridges of a polypeptide were...Ch. 17 - -Amino acids can be prepared by treating an...Ch. 17 - Reaction of a polypeptide with carboxypeptidase A...Ch. 17 - Prob. 48PCh. 17 - Prob. 49PCh. 17 - Show how valine can be prepared by a. a Strecker...Ch. 17 - Prob. 51PCh. 17 - Why is proline never found in an -helix?Ch. 17 - Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide...Ch. 17 - Prob. 55PCh. 17 - A chemist wanted to test his hypothesis that the...Ch. 17 - A normal polypeptide and a mutant of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nonearrow_forwardDraw the structure of the product of the reaction given the IR and MS data. Spectral analysis of the product reveals: MS: M 150, M-15, M-43 CH.COCI AICI, IR: 3150-3000 cm, 2950-2850 cm and 1700 cmarrow_forwardPart II. Identify whether the two protons in blue are homotopic, enantiopic, diasteriotopic, or heterotopic. a) HO b) Bri H HH c) d) H H H Br 0arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardChoose the option that is decreasing from biggest to smallest. Group of answer choices: 100 m, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100000 um, 10000000 nm 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100 m 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100 m 100 m, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100000 um, 10000000 nmarrow_forwardQ1. (a) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH3. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement. (b) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH4*. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement.arrow_forward
- Part II. count the expected number of signals in the 1H-NMR spectrum of these compounds HO 0 одев * Cl -cl "D"arrow_forwardPart I. Create a splitting tree diagram to predict the multiplet pattern of proton Hb in the compound below: 3 (Assume that "Jab >>> ³JbC) Ha Hb He он Ha NH2 Ha HCarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Biomolecules - Protein - Amino acids; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySNVPDHJ0ek;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY