
Concept explainers
Draw the predominant form of the following amino acids at physiological pH (7.4):
- a. Lysine
- b. Arginine
- c. tyrosine
(a)
Interpretation:
The predominant form of lysine at physiological
Concept introduction:
Acid-base properties of Amino acids:
Every amino acid has a carbonyl group and an amino group, and each group can exist in an acidic form or a basic form, depending on
The compound exists primarily in the acidic form in solutions that are more acidic than their
At
Answer to Problem 29P
The predominant form of lysine at physiological
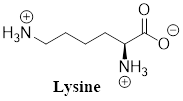
Explanation of Solution
The predominant form of glutamine at physiological

(b)
Interpretation:
The predominant form of arginine at physiological
Concept introduction:
Acid-base properties of Amino acids:
Every amino acid has a carbonyl group and an amino group, and each group can exist in an acidic form or a basic form, depending on
The compound exists primarily in the acidic form in solutions that are more acidic than their
At
Answer to Problem 29P
The predominant form of lysine at physiological
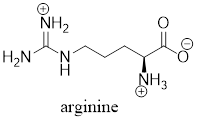
Explanation of Solution
The predominant form of lysine at physiological
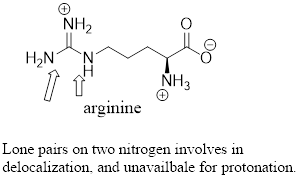
(c)
Interpretation:
The predominant form of tyrosine at physiological
Concept introduction:
Acid-base properties of Amino acids:
Every amino acid has a carbonyl group and an amino group, and each group can exist in an acidic form or a basic form, depending on
The compound exists primarily in the acidic form in solutions that are more acidic than their
At
Answer to Problem 29P
The predominant form of tyrosine at physiological
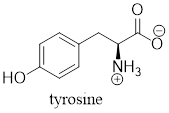
Explanation of Solution
The predominant form of tyrosine at physiological

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Briefly explain chemical potential.arrow_forwardReason whether it is possible to determine changes in the Galvani potential difference at the metal-solution interface.arrow_forwardObtain the standard potential at 25°C of the Cu* I Cu | Pt electrode from the standard potentials E° Cu²+/Cu = 0.341 V and E Cu²+ /Cu+ = 0.153 V.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
