
VECTOR MECH...,DYNAMICS(LOOSE)-W/ACCESS
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260265521
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.1, Problem 17.49P
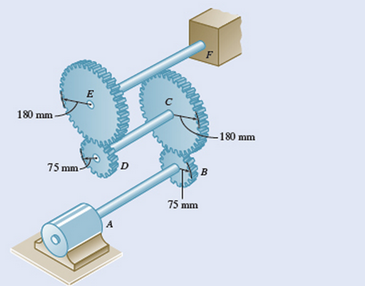
Three shafts and four gears are used to form a gear train that will transmit 7.5 kW from the motor at A to a machine tool at F. (Bearings for the shafts are omitted from the sketch.) Knowing that the frequency of the motor is 30 Hz, determine the magnitude of the couple that is applied to shaft (a) AB, (b) CD, (c) EF.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
5.112 A mounting bracket for electronic components is formed from sheet
metal with a uniform thickness. Locate the center of gravity of the
bracket.
0.75 in.
3 in.
༧
Fig. P5.112
1.25 in.
0.75 in.
y
r = 0.625 in.
2.5 in.
1 in.
6 in.
x
4-105. Replace the force system acting on the beam by an equivalent resultant force and couple
moment at point B.
A
30 in.
4 in.
12 in.
16 in.
B
30%
3 in.
10 in.
250 lb
260 lb
13
5
12
300 lb
Sketch and Describe a hatch coaming and show how the hatch coamings are framed in to ships strucure?
Chapter 17 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,DYNAMICS(LOOSE)-W/ACCESS
Ch. 17.1 - A round object of mass m and radius r is released...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ2PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ3PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ4PCh. 17.1 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.1 - A 200-kg flywheel is at rest when a constant 300 N...Ch. 17.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform disks of the same material are...Ch. 17.1 - Two disks of the same material are attached to a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.5P
Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.6PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.7PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.8PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.9PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.10PCh. 17.1 - Each of the gears A and B has a mass of 10 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Solve Prob. 17.11, assuming that the 6 N m couple...Ch. 17.1 - The gear train shown consists of four gears of the...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.14PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.15PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.16PCh. 17.1 - The 15-kg rear hatch of a vehicle opens as shown...Ch. 17.1 - A slender 9-lb rod can rotate in a vertical plane...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.19PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.20PCh. 17.1 - A collar with a mass of 1 kg is rigidly attached...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.22PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.23PCh. 17.1 - The 30-kg turbine disk has a centroidal radius of...Ch. 17.1 - A 100-kg solid cylindrical disk, 800 mm in...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.26PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.27PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.28PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.29PCh. 17.1 - A half-cylinder with mass m and radius r is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.31PCh. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - A bar of mass m=5 kg is held as shown between four...Ch. 17.1 - The 1.5-kg uniform slender bar AB is connected to...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.36PCh. 17.1 - A 5-m-long ladder has a mass of 15 kg and is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.38PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.39PCh. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - Each of the two rods shown is of length L=1 m and...Ch. 17.1 - The 4-kg rod AB is attached to a collar of...Ch. 17.1 - If in Prob. 17.43 the angular velocity of the...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC are of mass 3 kg and 8...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC weigh 2.4 kg and 4 kg,...Ch. 17.1 - The 80-mm-radius gear shown has a mass of 5 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.48PCh. 17.1 - Three shafts and four gears are used to form a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.50PCh. 17.1 - The drive belt on a vintage sander transmits 12 hp...Ch. 17.2 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.2 - A 1-m-long uniform slender bar AB has an angular...Ch. 17.2 - The 350-kg flywheel of a small hoisting engine has...Ch. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is placed on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.F3PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.52PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.53PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.54PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.55PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.56PCh. 17.2 - A disk of constant thickness, initially at rest,...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.58PCh. 17.2 - A cylinder of radius r and weight W with an...Ch. 17.2 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a centroidal...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.61PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.62PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.63PCh. 17.2 - A tape moves over the two drums shown. Drum A...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.65PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.66PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.67PCh. 17.2 - Consider a rigid body initially at rest and...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.69PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.70PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.71PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.72PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.73PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.74PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.75PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.76PCh. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.78PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.79PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.80PCh. 17.2 - Two 10-lb disks and a small motor are mounted on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.82PCh. 17.2 - A 1.6-kg tube AB can slide freely on rod DE, which...Ch. 17.2 - In the helicopter shown, a vertical tail propeller...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.85PCh. 17.2 - The 4-kg uniform disk B is attached to the shaft...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.87PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.88PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.89PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.90PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.91PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.92PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.93PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.94PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.95PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB ofmass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F5PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F6PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.96PCh. 17.3 - A bullet weighing 0.08 lb is fired with a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.98PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.99PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.100PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.101PCh. 17.3 - A 45-g bullet is fired with a velocity of 400 m/s...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.103PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.104PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB of mass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.106PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.107PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.108PCh. 17.3 - Determine the height h at which the bullet of...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender bar of length L=200 mm and mass...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod of length L is dropped onto...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB has a mass m, a length L,...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.113PCh. 17.3 - The trapeze/lanyard air drop (t/LAD) launch is a...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rectangular block shown is moving...Ch. 17.3 - The 40-kg gymnast drops from her maximum height of...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.117PCh. 17.3 - A uniformly loaded square crate is released from...Ch. 17.3 - A 1-oz bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 17.3 - For the beam of Prob. 17.119, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - The plank CDEhas a mass of 15 kg and rests on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.122PCh. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.125PCh. 17.3 - A 2-kg solid sphere of radius r=40 mm is dropped...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass mA=2 kg and radius r=40 mm rolls...Ch. 17.3 - A large 3-lb sphere with a radius r=3 in. is...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.131PCh. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass m and radius r rolls without...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.133PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.134PCh. 17 - A uniform disk, initially at rest and of constant...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.136RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.137RPCh. 17 - You are asked to analyze a catcher for a small...Ch. 17 - A uniform slender rod is placed at corner B and is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.140RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.141RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.142RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.143RPCh. 17 - A square block of mass m is falling with a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.145RPCh. 17 - A 1.8-lb javelin DE impacts a 10-lb slender rod...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sketch and describe hatch coamings. Describe structrual requirements to deck plating to compensate discontinuity for corners of a hatch. Show what is done to the deck plating when the decks are cut away and include the supporting members.arrow_forwardAn Inclining experiment done on a ship thats 6500 t, a mass of 30t was moved 6.0 m transvesly causing a 30 cm deflection in a 6m pendulum, calculate the transverse meta centre height.arrow_forwarda ship 150 m long and 20.5 m beam floats at a draught of8 m and displaces 19 500 tonne. The TPC is 26.5 and midshipsection area coefficient 0.94. Calculate the block, prismatic andwaterplane area coefficients.arrow_forward
- A vessel loads 680 t fuel between forward and aft deep tanks. centre of gravity of forward tank is 24m forward of ships COG. centre to centre between tanks is 42 m. how much in each tank to keep trim the samearrow_forwardBeam of a vessel is 11% its length. Cw =0.72. When floating in SW of relative denisity 1.03, TPC is 0.35t greater than in freshwater. Find the length of the shiparrow_forwardAn inclining experiment was carried out on a ship of 4000tonne displacement, when masses of 6 tonne were moved transverselythrough 13.5 m. The deflections of a 7.5 m pendulurnwere 81, 78, 85, 83, 79, 82, 84 and 80 mm respectively.Caiculate the metacentric height.arrow_forward
- A ship of 10 000 tonne displacement has a waterplanearea of 1300 m2. The ship loads in water of 1.010 t/m3 andmoves into water of 1.026 t/m3. Find the change in meandraughtarrow_forwardA ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water.arrow_forwardA ship has 300 tonne of cargo in the hold, 24 m forward ofmidships. The displacement of the vessel is 6000 tonne and its centre of gravity is 1.2 m forward of midships.Find the new position of the centre of gravity if this cargo ismoved to an after hold, 40 m from midshipsarrow_forward
- Sketch and describe how ships are supported in dry dock. When and where does the greatest amount of stresses occur?arrow_forwardSketch and desribe a balanced rudder and how it is suspendedarrow_forwardA ship 140 m long and 18 m beam floats at a draught of9 m. The immersed cross-sectionai areas at equai intervais are 5,60, 116, 145, 152, 153, 153, 151, 142, 85 and 0 m2 respectively.Calculate:(a) displacement(b) block coefficient(c) midship section area coefficient(d) prismatic coefficient.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Power Transmission; Author: Terry Brown Mechanical Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVm4LNVp1vA;License: Standard Youtube License