
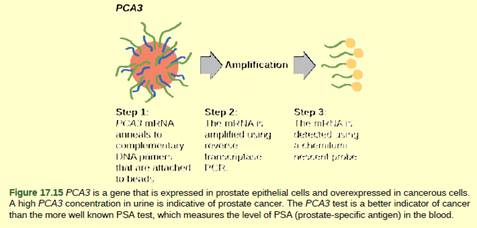
Figure 17.15 In 2011, the United States Preventative Services Task Force recommended against using the PSA test to screen healthy men for prostate cancer. Their recommendation is based on evidence that screening does not reduce the risk of death from prostate cancer. Prostate cancer often develops very slowly and does not cause problems, while the cancer treatment can have severe side effects. The PCA3 test is considered to be more accurate, but screening may still result in men who would not have been harmed by the cancer itself suffering side effects from treatment. What do you think? Should all healthy men be screened for prostate cancer using the PCA3 or PSA test? Should people in general be screened to find out if they have a genetic risk for cancer or other diseases?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Biology 2e
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- How many milligrams of zinc did you consume on average per day over the 3 days? (See the Actual Intakes vs. Recommended Intakes Report with all days checked.) Enter the number of milligrams of zinc rounded to the first decimal place in the box below. ______ mg ?arrow_forwardthe direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forwardthe direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forward
- Did your intake of vitamin C meet or come very close to the recommended amount? yes noarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about hydration is true? Absence of thirst is a reliable indication that an individual is adequately hydrated. All of these statements are true. Although a popular way to monitor hydration status, weighing yourself before and after intensive physical activity is not a reliable method to monitor hydration. Urine that is the color of apple juice indicates dehydration. I don't know yetarrow_forwardThree of the many recessive mutations in Drosophila melanogaster that affect body color, wing shape, or bristle morphology are black (b) body versus grey in wild type, dumpy (dp), obliquely truncated wings versus long wings in the male, and hooked (hk) bristles versus not hooked in the wild type. From a cross of a dumpy female with a black and hooked male, all of the F1 were wild type for all three of the characters. The testcross of an F1 female with a dumpy, black, hooked male gave the following results: Trait Number of individuals Wild type 169 Black 19 Black, hooked 301 Dumpy, hooked 21 Hooked, dumpy, black 172 Dumpy, black 6 Dumpy 305 Hooked 8 Determine the order of the genes and the mapping distance between genes. Determine the coefficient of confidence for the portion of the chromosome involved in the cross. How much interference takes place in the cross?arrow_forward
- What happens to a microbes membrane at colder temperature?arrow_forwardGenes at loci f, m, and w are linked, but their order is unknown. The F1 heterozygotes from a cross of FFMMWW x ffmmww are test crossed. The most frequent phenotypes in the test cross progeny will be FMW and fmw regardless of what the gene order turns out to be. What classes of testcross progeny (phenotypes) would be least frequent if locus m is in the middle? What classes would be least frequent if locus f is in the middle? What classes would be least frequent if locus w is in the middle?arrow_forward1. In the following illustration of a phospholipid... (Chemistry Primer and Video 2-2, 2-3 and 2-5) a. Label which chains contain saturated fatty acids and non-saturated fatty acids. b. Label all the areas where the following bonds could form with other molecules which are not shown. i. Hydrogen bonds ii. Ionic Bonds iii. Hydrophobic Interactions 12-6 HICIH HICIH HICHH HICHH HICIH OHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH C-C-C-C-C-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-c-C-C-H HH H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H HO H-C-O H-C-O- O O-P-O-C-H H T HICIH HICIH HICIH HICIH HHHHHHH HICIH HICIH HICIH 0=C HIC -C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-CC-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-H HHHHHHHHH IIIIIIII HHHHHHHH (e-osbiv)arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage LearningLifetime Physical Fitness & WellnessHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337677509Author:HOEGERPublisher:Cengage
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage LearningLifetime Physical Fitness & WellnessHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337677509Author:HOEGERPublisher:Cengage





