
Concept explainers
17-30 Answer true or false.
(a) The reduction of an
(b) The reduction of a
(c) The oxidation of an aldehyde gives a
(d) The oxidation of a primary alcohol gives a ketone.
(e) Tollens’ reagent can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
(f) Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, reduces an aldehyde to a primary alcohol.
(g) The addition of one molecule of alcohol to the carbonyl group of a ketone gives a hemiacetal.
(h) The reaction of an aldehyde with two molecules of alcohol gives an acetal, plus a molecule
of water.
(j) The formation of hemiacetals and acetals is reversible.
(j) The cyclic hemiacetal formed from 4-hydroxy-pentanal has two stereocenters and can exist as
a mixture of 22 = 4 stereoisomers.
(a)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reduction of an aldehyde always gives an alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction is the addition of a hydrogen atom to a compound.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
In aldehydes, the functional group is
Oxidation of aldehydes forms primary alcohol. For example, reduction of pentanal gives 1-pentanol.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reduction of ketones always gives a secondary alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Reduction is the addition of a hydrogen atom to a compound.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Reduction of ketones, hydrogen is added to the carbonyl carbon and gives secondary alcohol.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The oxidation of aldehydes gives a carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Oxidation is the process in which oxygen is added to the molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation of aldehydes, oxygen is added to the carbonyl group and form carboxylic acid.

Therefore, the given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The oxidation of primary alcohol gives ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. Oxidation is the process in which oxygen is added to the molecule.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation of primary alcohol first converted into aldehyde and followed by carboxylic acids.
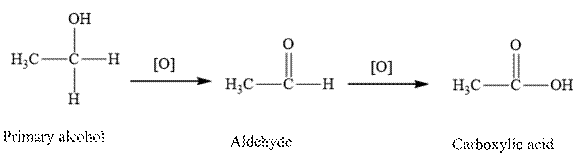
Therefore, the given statement is false.
(e)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Tollen’s reagent can be used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Tollen’s reagent is a mild oxidizing agent.
Tollen’s reagent is reacts with the aldehyde group of a compound. The carbonyl group acts as a reducing agent and reduces the silver ion of the Tollen’s regent to silver metal.
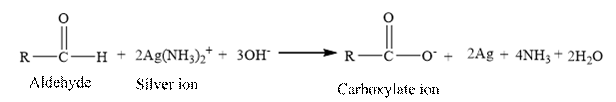
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes undergo oxidation easily, even with mild oxidizing agents and give carboxylic acid.
Ketone does not undergo oxidation with mild oxidizing agent due to selectivity of aldehyde and ketone for oxidation is used to differentiate an aldehyde and a ketone. Therefore, aldehyde and ketones are distinguished by using Tollen’s regent.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(f)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Sodium borohydride,
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. The aldehydes undergoes a reduction reaction where in the addition of hydrogen occurs at the double bond between the oxygen and the carbon of the carbonyl group present in the aldehyde.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
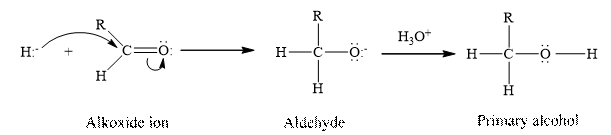
(g)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The addition of one molecule of alcohol to the carbonyl group of a ketone gives a hemiacetal.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In Hemiacetal, carbon is added to hydroxyl group and alkoxy group.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
When a molecule of alcohol is added to a ketone, the hydrogen of the alcohol is added o the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group, while the alkoxy group of the alcohol is added to the carbon of the carbonyl group. Hence ketone forms hemiacetal when the reacts with one molecule of alcohol.
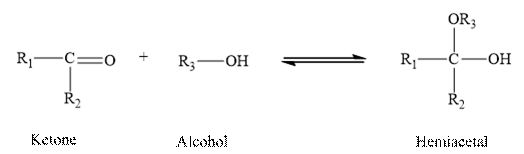
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The reaction of an aldehyde with two molecules of alcohol gives an acetal, plus a molecule of water.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In acetal, carbon is bonded to two alkoxy groups.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Two molecules of an alcohol are added to an aldehyde to form hemiacetal. And it is unstable and it reacts with another molecule of an alcohol in the presence of an acid forms acetal and water.
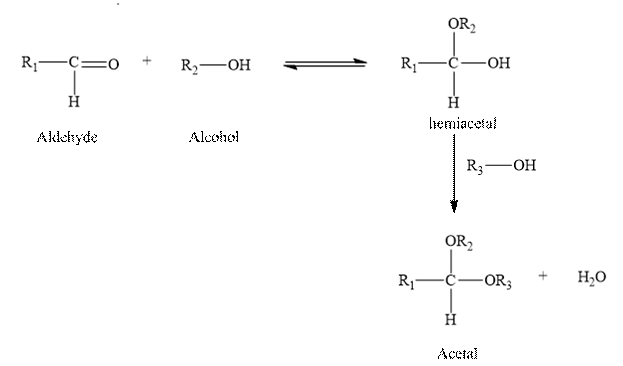
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The formation of hemiacetals and acetal is reversible.
Concept Introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group as a functional group. In Hemiacetal, carbon is added to hydroxyl group and alkoxy group. In acetal, carbon is added to a two alkoxy groups.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
By using large excess of alcohol hemiacetals and acetals are reversible by the removal of water molecules. To shift the equilibrium towards the left side by the hydrolysis of the acetal to the aldehyde or ketone and alcohol.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The cyclic hemiacetal formed from 4-hydroxypentanal has two stereocentres and can exists as a mixture of
Concept Introduction:
A stereocentre is a carbon atom with four different groups bonded to it. The stereocentres of molecule can be calculated by using
n= stereocentre.
Answer to Problem 17.30P
The given statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The cyclic hemiacetal; obtained from 4-hydroxypentanal has two stereocenters.
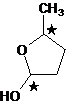
4- hydroxypentanal has two stereocenters, therefore it have 4 stereoisomers.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Use the literature Ka value of the acetic acid, and the data below to answer these questions. Note: You will not use the experimental titration graphs to answer the questions that follow. Group #1: Buffer pH = 4.35 Group #2: Buffer pH = 4.70 Group #3: Buffer pH = 5.00 Group #4: Buffer pH = 5.30 Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, the buffer pH provided and the literature pKa value of acetic acid to perform the following: a) calculate the ratios of [acetate]/[acetic acid] for each of the 4 groups buffer solutions above. b) using the calculated ratios, which group solution will provide the best optimal buffer (Hint: what [acetate]/[acetic acid] ratio value is expected for an optimal buffer?) c) explain your choicearrow_forwardHow would you prepare 1 liter of a 50 mM Phosphate buffer at pH 7.5 beginning with K3PO4 and 1 M HCl or 1 M NaOH? Please help and show calculations. Thank youarrow_forwardDraw the four most importantcontributing structures of the cation intermediate thatforms in the electrophilic chlorination of phenol,(C6H5OH) to form p-chlorophenol. Put a circle aroundthe best one. Can you please each step and also how you would approach a similar problem. Thank you!arrow_forward
- A 100mM lactic acid/lactate buffer was found to have a lactate to lactic acid ratio of 2 and a pH of 4.2. What is the pKa of lactic acid? Can you please help show the calculations?arrow_forwardUsing line angle formulas, draw thestructures of and name four alkanes that have total of 7carbons, one of which is tertiary.Please explain this in detail and can you also explain how to approach a similar problem like this as well?arrow_forwardUsing dashed line wedge projections drawthe indicated compounds and indicate whether thecompound you have drawn is R or S.(a) The two enantiomers of 2-chlorobutane. Can you please explain your steps and how you would approach a similar problem. Thank you!arrow_forward
- 5) There are no lone pairs shown in the structure below. Please add in all lone pairs and then give the hybridization scheme for the compound. (8) 10,11 7) 1.2.3 H 4 | 14 8) COC 12 13 H 16 15 H7 9) - 5.6 C 8 H 10) H 1). 2) 3)_ 11) 12) 13) 4)_ 14) 5) 15) 16) 6)arrow_forwardThe sum of the numbers in the name of isA. 11; B. 13; C. 10; D. 12; E. none of the other answers iscorrect. I believe the awnser should be E to this problem but the solution to this problem is D 12. I'm honestly unsure how that's the solution. If you can please explain the steps to this type of problem and how to approach a problem like this it would be greatly appreciated!arrow_forwardConsider the following data for phosphorus: g atomic mass 30.974 mol electronegativity 2.19 kJ electron affinity 72. mol kJ ionization energy 1011.8 mol kJ heat of fusion 0.64 mol You may find additional useful data in the ALEKS Data tab. Does the following reaction absorb or release energy? 2+ + (1) P (g) + e → P (g) Is it possible to calculate the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (1) using only the data above? If you answered yes to the previous question, enter the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (1): Does the following reaction absorb or release energy? 00 release absorb Can't be decided with the data given. yes no ☐ kJ/mol (²) P* (8) + + + e →>> P (g) Is it possible to calculate the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (2) using only the data above? If you answered yes to the previous question, enter the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (2): ☐ release absorb Can't be decided with the data given. yes no kJ/mol аarrow_forward
- The number of hydrogens in an alkyne that has a main chain of 14carbons to which are attached a cyclobutyl ring, a benzene ring, an–OH group, and a Br is A. 34; B. 35; C. 36; D. 24; E. 43arrow_forwardHello! I have a 500 Hz H-NMR for 1,5-bis-(4-methoxyphenyl)-penta-1,4-dien-3-one. I need to label the signals with the corresponding H's. Then, find out if the two alkenes are cis or trans by calculating the J values. I believe that I have the H-NMR labeled correctly, but not sure if I got the J values correct to determine if the two alkenes in the compound will make the compound cis or trans.arrow_forwardWhat is the only possible H-Sb-H bond angle in SbH3?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

