
Concept explainers
17-73 Alcohols can be prepared by the acid-catalyzed hydration of
(a) Ethanol
(b) Cyclohexanol
(c) 2-Propanol
(d) 1-Phenylethanol
(a)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of ethanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
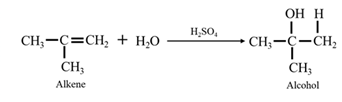
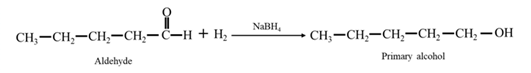
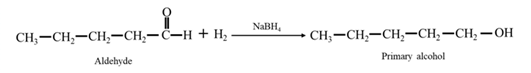
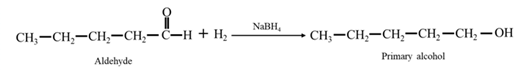
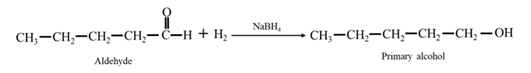
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
Answer to Problem 17.73P
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
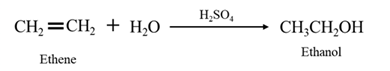
By Reduction of ethanal:
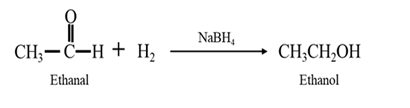
Explanation of Solution
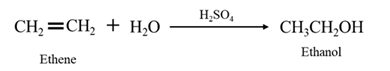
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
When ethene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives ethanol.
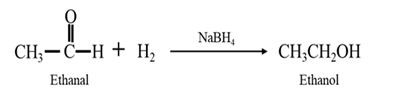
By Reduction of ethanal: When ethanal is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives ethanol.
(b)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of cyclohexanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
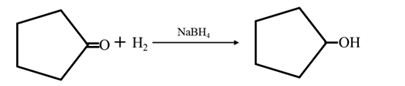
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
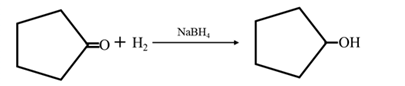
Answer to Problem 17.73P
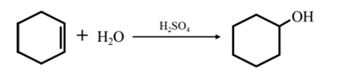
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
By Reduction of ethanal:
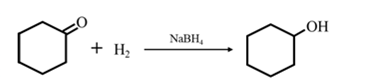
Explanation of Solution
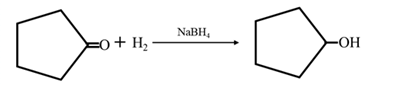
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane: When cyclohexene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives cyclohexanol.
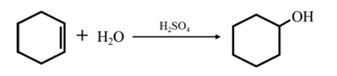
By Reduction of ethanal: When cyclohexanone is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives cyclohexanol.
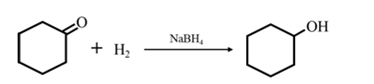
(c)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of 2-propanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
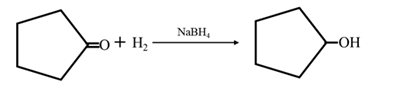
Answer to Problem 17.73P
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
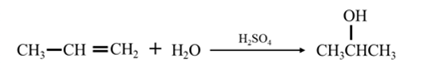
By Reduction of ethanal:
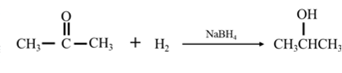
Explanation of Solution
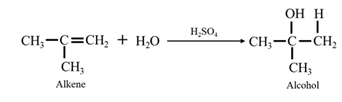
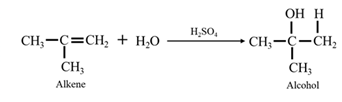
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane: When propene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives 2-propanol.
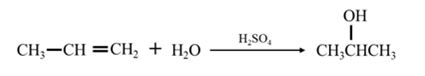
By Reduction of ethanal: When acetone is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives 2-propanol.
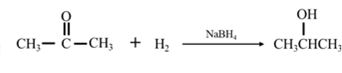
(d)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of 1-phenylethanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
Answer to Problem 17.73P
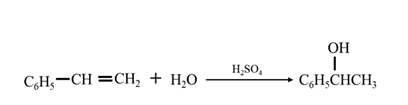
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
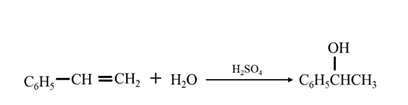
By Reduction of ethanal:
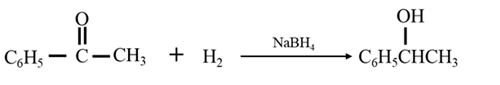
Explanation of Solution
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane: When 1-phenylethene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives 1-phenylethanol.
By Reduction of ethanal: When acetophenone is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives 1-phenylethanol.
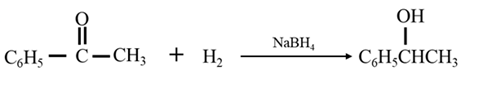
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Using line angle formulas, draw thestructures of and name four alkanes that have total of 7carbons, one of which is tertiary.Please explain this in detail and can you also explain how to approach a similar problem like this as well?arrow_forwardUsing dashed line wedge projections drawthe indicated compounds and indicate whether thecompound you have drawn is R or S.(a) The two enantiomers of 2-chlorobutane. Can you please explain your steps and how you would approach a similar problem. Thank you!arrow_forward5) There are no lone pairs shown in the structure below. Please add in all lone pairs and then give the hybridization scheme for the compound. (8) 10,11 7) 1.2.3 H 4 | 14 8) COC 12 13 H 16 15 H7 9) - 5.6 C 8 H 10) H 1). 2) 3)_ 11) 12) 13) 4)_ 14) 5) 15) 16) 6)arrow_forward
- The sum of the numbers in the name of isA. 11; B. 13; C. 10; D. 12; E. none of the other answers iscorrect. I believe the awnser should be E to this problem but the solution to this problem is D 12. I'm honestly unsure how that's the solution. If you can please explain the steps to this type of problem and how to approach a problem like this it would be greatly appreciated!arrow_forwardConsider the following data for phosphorus: g atomic mass 30.974 mol electronegativity 2.19 kJ electron affinity 72. mol kJ ionization energy 1011.8 mol kJ heat of fusion 0.64 mol You may find additional useful data in the ALEKS Data tab. Does the following reaction absorb or release energy? 2+ + (1) P (g) + e → P (g) Is it possible to calculate the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (1) using only the data above? If you answered yes to the previous question, enter the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (1): Does the following reaction absorb or release energy? 00 release absorb Can't be decided with the data given. yes no ☐ kJ/mol (²) P* (8) + + + e →>> P (g) Is it possible to calculate the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (2) using only the data above? If you answered yes to the previous question, enter the amount of energy absorbed or released by reaction (2): ☐ release absorb Can't be decided with the data given. yes no kJ/mol аarrow_forwardThe number of hydrogens in an alkyne that has a main chain of 14carbons to which are attached a cyclobutyl ring, a benzene ring, an–OH group, and a Br is A. 34; B. 35; C. 36; D. 24; E. 43arrow_forward
- Hello! I have a 500 Hz H-NMR for 1,5-bis-(4-methoxyphenyl)-penta-1,4-dien-3-one. I need to label the signals with the corresponding H's. Then, find out if the two alkenes are cis or trans by calculating the J values. I believe that I have the H-NMR labeled correctly, but not sure if I got the J values correct to determine if the two alkenes in the compound will make the compound cis or trans.arrow_forwardWhat is the only possible H-Sb-H bond angle in SbH3?arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


