
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977237
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 17.146RP
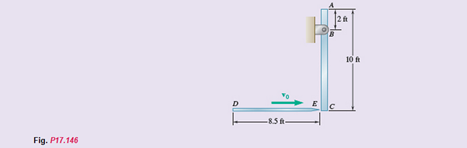
A 1.8-lb javelin DE impacts a 10-lb slender rod ABC with a horizontal velocity of
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Study Area
Document Sharing
User Settings
Access Pearson
mylabmastering.pearson.com
P Pearson MyLab and Mastering
The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a
nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material.
The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle
penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1)
Part A
P Course Home
b My Questions | bartleby
Review
Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it
strikes the first barrel.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
1 of 1
36
μΑ
S =
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
?
Next >
Water is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Saturated vapor enters the turbine at 12 MPa, and the
condenser pressure is 8 kPa. The mass flow rate of steam entering the turbine is 50 kg/s.
Determine:
(a) the net power developed, in kW.
(b) the rate of heat transfer to the steam passing through the boiler, in kW.
(c) the percent thermal efficiency.
(d) the mass flow rate of condenser cooling water, in kg/s, if the cooling water undergoes a temperature
increase of 18°C with negligible pressure change in passing through the condenser.
4. The figure below shows a bent pipe with the external loading FA
228 lb, and M₁ = M₂ = 1 kip-ft. The force Fernal loading FA = 300 lb, FB:
parallel to the y-axis, and
and yc = 60°.
= 125 lb, Fc
=
acts parallel to the x-z plane, the force FB acts
Cartesian resultan Coordinate direction angles of Fc are ac = 120°, ẞc = 45°,
a. Compute the resultant force vector of the given external loading and express it in
EST
form.
b. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the origin, O,
and express it in Cartesian vector form. Use the vector method while computing the
moments of forces.
c. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the line OA
and express it in Cartesian vector form.
:00 PM EST
k
ghoufran@buffaternal du
2 ft
M₁
A
40°
FA
M2
C
18 in
1 ft
Fc
25
houfran@bald.edu - Feb 19,
3 ft
FB
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 17.1 - A round object of mass m and radius r is released...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ2PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ3PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ4PCh. 17.1 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.1 - A 200-kg flywheel is at rest when a constant 300 N...Ch. 17.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform disks of the same material are...Ch. 17.1 - Two disks of the same material are attached to a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.5P
Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.6PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.7PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.8PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.9PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.10PCh. 17.1 - Each of the gears A and B has a mass of 10 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Solve Prob. 17.11, assuming that the 6 N m couple...Ch. 17.1 - The gear train shown consists of four gears of the...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.14PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.15PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.16PCh. 17.1 - The 15-kg rear hatch of a vehicle opens as shown...Ch. 17.1 - A slender 9-lb rod can rotate in a vertical plane...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.19PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.20PCh. 17.1 - A collar with a mass of 1 kg is rigidly attached...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.22PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.23PCh. 17.1 - The 30-kg turbine disk has a centroidal radius of...Ch. 17.1 - A 100-kg solid cylindrical disk, 800 mm in...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.26PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.27PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.28PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.29PCh. 17.1 - A half-cylinder with mass m and radius r is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.31PCh. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - A bar of mass m=5 kg is held as shown between four...Ch. 17.1 - The 1.5-kg uniform slender bar AB is connected to...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.36PCh. 17.1 - A 5-m-long ladder has a mass of 15 kg and is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.38PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.39PCh. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - Each of the two rods shown is of length L=1 m and...Ch. 17.1 - The 4-kg rod AB is attached to a collar of...Ch. 17.1 - If in Prob. 17.43 the angular velocity of the...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC are of mass 3 kg and 8...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC weigh 2.4 kg and 4 kg,...Ch. 17.1 - The 80-mm-radius gear shown has a mass of 5 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.48PCh. 17.1 - Three shafts and four gears are used to form a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.50PCh. 17.1 - The drive belt on a vintage sander transmits 12 hp...Ch. 17.2 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.2 - A 1-m-long uniform slender bar AB has an angular...Ch. 17.2 - The 350-kg flywheel of a small hoisting engine has...Ch. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is placed on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.F3PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.52PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.53PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.54PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.55PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.56PCh. 17.2 - A disk of constant thickness, initially at rest,...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.58PCh. 17.2 - A cylinder of radius r and weight W with an...Ch. 17.2 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a centroidal...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.61PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.62PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.63PCh. 17.2 - A tape moves over the two drums shown. Drum A...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.65PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.66PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.67PCh. 17.2 - Consider a rigid body initially at rest and...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.69PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.70PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.71PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.72PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.73PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.74PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.75PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.76PCh. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.78PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.79PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.80PCh. 17.2 - Two 10-lb disks and a small motor are mounted on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.82PCh. 17.2 - A 1.6-kg tube AB can slide freely on rod DE, which...Ch. 17.2 - In the helicopter shown, a vertical tail propeller...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.85PCh. 17.2 - The 4-kg uniform disk B is attached to the shaft...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.87PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.88PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.89PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.90PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.91PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.92PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.93PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.94PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.95PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB ofmass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F5PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F6PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.96PCh. 17.3 - A bullet weighing 0.08 lb is fired with a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.98PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.99PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.100PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.101PCh. 17.3 - A 45-g bullet is fired with a velocity of 400 m/s...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.103PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.104PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB of mass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.106PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.107PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.108PCh. 17.3 - Determine the height h at which the bullet of...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender bar of length L=200 mm and mass...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod of length L is dropped onto...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB has a mass m, a length L,...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.113PCh. 17.3 - The trapeze/lanyard air drop (t/LAD) launch is a...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rectangular block shown is moving...Ch. 17.3 - The 40-kg gymnast drops from her maximum height of...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.117PCh. 17.3 - A uniformly loaded square crate is released from...Ch. 17.3 - A 1-oz bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 17.3 - For the beam of Prob. 17.119, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - The plank CDEhas a mass of 15 kg and rests on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.122PCh. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.125PCh. 17.3 - A 2-kg solid sphere of radius r=40 mm is dropped...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass mA=2 kg and radius r=40 mm rolls...Ch. 17.3 - A large 3-lb sphere with a radius r=3 in. is...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.131PCh. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass m and radius r rolls without...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.133PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.134PCh. 17 - A uniform disk, initially at rest and of constant...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.136RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.137RPCh. 17 - You are asked to analyze a catcher for a small...Ch. 17 - A uniform slender rod is placed at corner B and is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.140RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.141RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.142RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.143RPCh. 17 - A square block of mass m is falling with a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.145RPCh. 17 - A 1.8-lb javelin DE impacts a 10-lb slender rod...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation: Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) . a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K? b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe? c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40)arrow_forwardAuto Controls Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The 150-lb skater passes point A with a speed of 6 ft/s. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine his speed when he reaches point B. Neglect friction. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. με ? VB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the normal force exerted on him by the track at this point. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ☐ о Α NB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forward
- mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. The crate is originally at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is μk = 0.2. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of 8.1 m/s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 500 N 1 of 1 Α S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ■Review Next >arrow_forwardThe differential equation of a DC motor can be described by the following equation Find the transfer function between the applied voltage ( Va)and the motor speed (thetadot m). What is the steady state speed of the motor after a voltage (Va = 10V) has been applied. Find the transfer function between the applied voltage (Va) and the shaft angle (thetadot m) .arrow_forwardStudy Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review The sports car has a mass of 2.5 Mg and accelerates at 6 m/s², starting from rest. (Figure 1) If the drag resistance on the car due to the wind is FD = (10v) N, where v is the velocity in m/s, determine the power supplied to the engine when t = 5 s. The engine has a running efficiency of € = 0.66. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 о Α ? P = Value Units Submit Request Answer Return to Assignment Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Study Area mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Document Sharing User Settings The car in (Figure 1) having a mass of 2 Mg is originally traveling at 2 m/s. Assume 0 = 22°. Figure 1 of 1 Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby ■Review Determine the distance it must be towed by a force F = 4 kN in order to attain a speed of 6 m/s. Neglect friction and the mass of the wheels. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Α ? S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardDerive the Laplace transform of the following functions. Use the definition of Laplace transform. f(t)=sin4t and f(t)=cos2t Auto Controlsarrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Marbles having a mass of 5 g fall from rest at A through the glass tube and accumulate in the can at C. (Figure 1) Figure Aarrow_forwardVC Vc B S TDC -BDC S TQ Tp = Pg A (asne) [1+ % CUSA] At what position (in degrees after top dead center) would you want the peak pressure of combustion to occur to create the maximum torque on the crankshaft? For a 100mm piston digimeter acting on a connecting. rod with a length of 80mm use the equation above to calculate the torque (NIM) on the crankshaft at this crank position for an engine that develops a peak pressure of 135 bararrow_forwardAccess Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Study Area Document Sharing User Settings The man having a weight of 180 lb is able to run up a 18-ft-high flight of stairs shiwn in (Figure 1) in 4 s. Figure 1 of 1 R mylabmastering.pearson.com Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Determine the power generated. Express your answer in horsepower to three significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ. Η vec P = Submit Request Answer Part B ? hp How long would a 100-W light bulb have to burn to expend the same amount of energy? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HÅ ? t = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Review Next >arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY