
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977237
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 17.3, Problem 17.99P
To determine
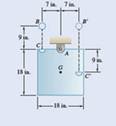
Calculate the velocity of panel center G after the impact. Wooden panel is hinged to pin support at A. When metal sphere falls in a hemispherical cup C. Assuming perfect plastic impact .Refer figure for details.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Complete the following problems. Show your work/calculations, save as.pdf and upload to the
assignment in Blackboard.
missing information to present a completed program. (Hint: You may have to look up geometry
for the center drill and standard 0.5000 in twist drill to know the required depth to drill).
1. What are the x and y dimensions for the center position of holes 1,2, and 3 in the part shown in
Figure 26.2 (below)?
6.0000
Zero
reference
point
7118
1.0005
1.0000
1.252
Bore
6.0000
.7118
Cbore
0.2180 deep
(3 holes)
2.6563 1.9445
Figure 26.2
026022 (8lot and Drill Part)
(Setup Instructions---
(UNITS: Inches
(WORKPIECE NAT'L SAE 1020 STEEL
(Workpiece: 3.25 x 2.00 x0.75 in. Plate
(PRZ Location 054:
'
XY 0.0 - Upper Left of Fixture
TOP OF PART 2-0
(Tool List
( T02 0.500 IN 4 FLUTE FLAT END MILL
#4 CENTER DRILL
Dashed line indicates-
corner of original stock
( T04
T02
3.000 diam. slot
0.3000 deep.
0.3000 wide
Intended toolpath-tangent-
arc entry and exit sized to
programmer's judgment…
A program to make the part depicted in Figure 26.A has been created, presented in figure 26.B, but some information still needs to be filled in. Compute the tool locations, depths, and other missing information to present a completed program. (Hint: You may have to look up geometry for the center drill and standard 0.5000 in twist drill to know the required depth to drill).
We consider a laminar flow induced by an impulsively started infinite flat
plate. The y-axis is normal to the plate. The x- and z-axes form a plane parallel
to the plate. The plate is defined by y = 0. For time t <0, the plate and the flow
are at rest. For t≥0, the velocity of the plate is parallel to the 2-coordinate;
its value is constant and equal to uw. At infinity, the flow is at rest. The flow
induced by the motion of the plate is independent of z.
(a) From the continuity equation, show that v=0 everywhere in the flow and
the resulting momentum equation is
მu
Ət
Note that this equation has the form of a diffusion equation (the same form as
the heat equation).
(b) We introduce the new variables T, Y and U such that
T=kt, Y=k/2y, U = u
where k is an arbitrary constant. In the new system of variables, the solution
is U(Y,T). The solution U(Y,T) is expressed by a function of Y and T and the
solution u(y, t) is expressed by a function of y and t. Show that the functions are
identical.…
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Ch. 17.1 - A round object of mass m and radius r is released...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ2PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ3PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.CQ4PCh. 17.1 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.1 - A 200-kg flywheel is at rest when a constant 300 N...Ch. 17.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform disks of the same material are...Ch. 17.1 - Two disks of the same material are attached to a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.5P
Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.6PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.7PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.8PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.9PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.10PCh. 17.1 - Each of the gears A and B has a mass of 10 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Solve Prob. 17.11, assuming that the 6 N m couple...Ch. 17.1 - The gear train shown consists of four gears of the...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.14PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.15PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.16PCh. 17.1 - The 15-kg rear hatch of a vehicle opens as shown...Ch. 17.1 - A slender 9-lb rod can rotate in a vertical plane...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.19PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.20PCh. 17.1 - A collar with a mass of 1 kg is rigidly attached...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.22PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.23PCh. 17.1 - The 30-kg turbine disk has a centroidal radius of...Ch. 17.1 - A 100-kg solid cylindrical disk, 800 mm in...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.26PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.27PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.28PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.29PCh. 17.1 - A half-cylinder with mass m and radius r is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.31PCh. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W=14 lb and...Ch. 17.1 - A bar of mass m=5 kg is held as shown between four...Ch. 17.1 - The 1.5-kg uniform slender bar AB is connected to...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.36PCh. 17.1 - A 5-m-long ladder has a mass of 15 kg and is...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.38PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.39PCh. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - The mechanism shown is one of two identical...Ch. 17.1 - Each of the two rods shown is of length L=1 m and...Ch. 17.1 - The 4-kg rod AB is attached to a collar of...Ch. 17.1 - If in Prob. 17.43 the angular velocity of the...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC are of mass 3 kg and 8...Ch. 17.1 - The uniform rods AB and BC weigh 2.4 kg and 4 kg,...Ch. 17.1 - The 80-mm-radius gear shown has a mass of 5 kg and...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.48PCh. 17.1 - Three shafts and four gears are used to form a...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.50PCh. 17.1 - The drive belt on a vintage sander transmits 12 hp...Ch. 17.2 - Slender bar A is rigidly connected to a massless...Ch. 17.2 - A 1-m-long uniform slender bar AB has an angular...Ch. 17.2 - The 350-kg flywheel of a small hoisting engine has...Ch. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is placed on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.F3PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.52PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.53PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.54PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.55PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.56PCh. 17.2 - A disk of constant thickness, initially at rest,...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.58PCh. 17.2 - A cylinder of radius r and weight W with an...Ch. 17.2 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a centroidal...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.61PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.62PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.63PCh. 17.2 - A tape moves over the two drums shown. Drum A...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.65PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.66PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.67PCh. 17.2 - Consider a rigid body initially at rest and...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.69PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.70PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.71PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.72PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.73PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.74PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.75PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.76PCh. 17.2 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.78PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.79PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.80PCh. 17.2 - Two 10-lb disks and a small motor are mounted on a...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.82PCh. 17.2 - A 1.6-kg tube AB can slide freely on rod DE, which...Ch. 17.2 - In the helicopter shown, a vertical tail propeller...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.85PCh. 17.2 - The 4-kg uniform disk B is attached to the shaft...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.87PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.88PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.89PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.90PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.91PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.92PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.93PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.94PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.95PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB ofmass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F5PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.F6PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.96PCh. 17.3 - A bullet weighing 0.08 lb is fired with a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.98PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.99PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.100PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.101PCh. 17.3 - A 45-g bullet is fired with a velocity of 400 m/s...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.103PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.104PCh. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB of mass m is at rest on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.106PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.107PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.108PCh. 17.3 - Determine the height h at which the bullet of...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender bar of length L=200 mm and mass...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod of length L is dropped onto...Ch. 17.3 - A uniform slender rod AB has a mass m, a length L,...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.113PCh. 17.3 - The trapeze/lanyard air drop (t/LAD) launch is a...Ch. 17.3 - The uniform rectangular block shown is moving...Ch. 17.3 - The 40-kg gymnast drops from her maximum height of...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.117PCh. 17.3 - A uniformly loaded square crate is released from...Ch. 17.3 - A 1-oz bullet is fired with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 17.3 - For the beam of Prob. 17.119, determine the...Ch. 17.3 - The plank CDEhas a mass of 15 kg and rests on a...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.122PCh. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - A slender rod AB is released from rest in the...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.125PCh. 17.3 - A 2-kg solid sphere of radius r=40 mm is dropped...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Member ABC has a mass of 2.4 kg and is attached to...Ch. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass mA=2 kg and radius r=40 mm rolls...Ch. 17.3 - A large 3-lb sphere with a radius r=3 in. is...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.131PCh. 17.3 - Sphere A of mass m and radius r rolls without...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.133PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.134PCh. 17 - A uniform disk, initially at rest and of constant...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.136RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.137RPCh. 17 - You are asked to analyze a catcher for a small...Ch. 17 - A uniform slender rod is placed at corner B and is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.140RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.141RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.142RPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.143RPCh. 17 - A square block of mass m is falling with a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.145RPCh. 17 - A 1.8-lb javelin DE impacts a 10-lb slender rod...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part A: Suppose you wanted to drill a 1.5 in diameter hole through a piece of 1020 cold-rolled steel that is 2 in thick, using an HSS twist drill. What values if feed and cutting speed will you specify, along with an appropriate allowance? Part B: How much time will be required to drill the hole in the previous problem using the HSS drill?arrow_forward1.1 m 1.3 m B 60-mm diameter Brass 40-mm diameter Aluminum PROBLEM 2.52 - A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB and BC is restrained at both ends. Portion AB is made of brass (E₁ = 105 GPa, α = 20.9×10°/°C) and portion BC is made of aluminum (Ę₁ =72 GPa, α = 23.9×10/°C). Knowing that the rod is initially unstressed, determine (a) the normal stresses induced in portions AB and BC by a temperature rise of 42°C, (b) the corresponding deflection of point B.arrow_forward30 mm D = 40 MPa -30 mm B C 80 MPa PROBLEM 2.69 A 30-mm square was scribed on the side of a large steel pressure vessel. After pressurization, the biaxial stress condition at the square is as shown. For E = 200 GPa and v=0.30, determine the change in length of (a) side AB, (b) side BC, (c) diagnonal AC.arrow_forward
- Please solve in detail this problem thank youarrow_forward0,5 mm 450 mm 350 mm Bronze A = 1500 mm² E = 105 GPa प 21.6 × 10-PC Aluminum A = 1800 mm² £ = 73 GPa = a 23.2 × 10-PC PROBLEM 2.58 Knowing that a 0.5-mm gap exists when the temperature is 24°C, determine (a) the temperature at which the normal stress in the aluminum bar will be equal to -75 MPa, (b) the corresponding exact length of the aluminum bar.arrow_forward0.5 mm 450 mm -350 mm Bronze Aluminum A 1500 mm² A 1800 mm² E 105 GPa E 73 GPa K = 21.6 X 10 G < = 23.2 × 10-G PROBLEM 2.59 Determine (a) the compressive force in the bars shown after a temperature rise of 82°C, (b) the corresponding change in length of the bronze bar.arrow_forward
- The truss shown below sits on a roller at A and a pin at E. Determine the magnitudes of the forces in truss members GH, GB, BC and GC. State whether they are in tension or compression or are zero force members.arrow_forwardA weight (W) hangs from a pulley at B that is part of a support frame. Calculate the maximum possible mass of the weight if the maximum permissible moment reaction at the fixed support is 100 Nm. Note that a frictionless pin in a slot is located at C.arrow_forwardIt is the middle of a winter snowstorm. Sally and Jin take shelter under an overhang. The loading of the snow on top of the overhang is shown in the figure below. The overhang is attached to the wall at points A and B with pin supports. Another pin is at C. Determine the reactions of the pin supports at A and B. Express them in Cartesian vector form.arrow_forward
- Recall that the CWH equation involves two important assumptions. Let us investigate how these assumptions affect the accuracy of state trajectories under the control inputs optimized in (a) and (b). (c.1): Discuss the assumptions about the chief and deputy orbits that are necessary for deriving CWH.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2.50 1.8 m The concrete post (E-25 GPa and a = 9.9 x 10°/°C) is reinforced with six steel bars, each of 22-mm diameter (E, = 200 GPa and a, = 11.7 x 10°/°C). Determine the normal stresses induced in the steel and in the concrete by a temperature rise of 35°C. 6c " 0.391 MPa 240 mm 240 mm 6₁ = -9.47 MPaarrow_forwardFor some viscoelastic polymers that are subjected to stress relaxation tests, the stress decays with time according to a(t) = a(0) exp(-4) (15.10) where σ(t) and o(0) represent the time-dependent and initial (i.e., time = 0) stresses, respectively, and t and T denote elapsed time and the relaxation time, respectively; T is a time-independent constant characteristic of the material. A specimen of a viscoelastic polymer whose stress relaxation obeys Equation 15.10 was suddenly pulled in tension to a measured strain of 0.5; the stress necessary to maintain this constant strain was measured as a function of time. Determine E (10) for this material if the initial stress level was 3.5 MPa (500 psi), which dropped to 0.5 MPa (70 psi) after 30 s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Material Properties 101; Author: Real Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHZALtqAjeM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY