
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16.2, Problem 16.108P
Gear C has a mass of 5 kg and a centroidal radius of gyration of 75 mm. The uniform bar AB has a mass of 3 kg and gear D is stationary. If the system is released from rest in the position shown, determine (a) the angular acceleration of gear C, (b) the acceleration of point B.
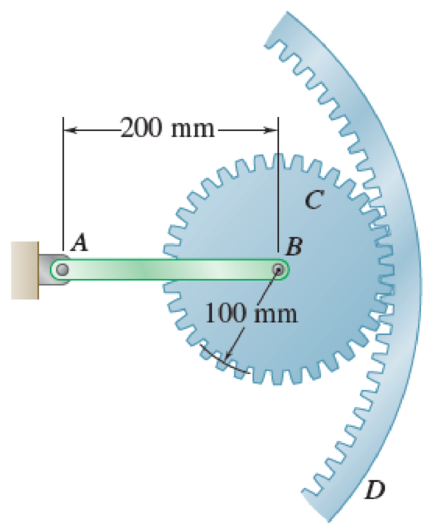
Fig. P16.108
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 6
What kind of problem would arise if components of the strain tensor were defined
as v
please show steps, thanks
You design a pin joint. The pin is made of a material with the yield strength of 325
MPa and ultimate strength of 500 MPa. The maximum allowed stress in service is
expressed as a tensor
0
100 0
σ
100
0
0 MPa
0
0
Evaluate the safety factor SF for stress in this design.
Write answer unitless rounding to 2 decimal places and enter decimals even if those
are zeros.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two pendulums, A and B, with the masses and...Ch. 16.1 - Two solid cylinders, A and B, have the same mass m...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.1FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.2FBPCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.3FBPCh. 16.1 - The 400-lb crate shown is lowered by means of two...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - A 60-lb uniform thin panel is placed in a truck...Ch. 16.1 - 16.3 Knowing that the coefficient of static...
Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.4PCh. 16.1 - A uniform rod BC of mass 4 kg is connected to a...Ch. 16.1 - A 2000-kg truck is being used to lift a 400-kg...Ch. 16.1 - The support bracket shown is used to transport a...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.8PCh. 16.1 - A 20-kg cabinet is mounted on casters that allow...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.9, assuming that the casters are...Ch. 16.1 - 16.11 A completely filled barrel and its contents...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.12PCh. 16.1 - The retractable shelf shown is supported by two...Ch. 16.1 - Bars AB and BE, each with a mass of 4 kg, are...Ch. 16.1 - At the instant shown, the tensions in the vertical...Ch. 16.1 - Three bars, each of mass 3 kg, are welded together...Ch. 16.1 - Members ACE and DCB are each 600 mm long and are...Ch. 16.1 - 16.18 A prototype rotating bicycle rack is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.19PCh. 16.1 - The coefficients of friction between the 30-lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.21PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.22PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in translation, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - For a rigid body in centroidal rotation, show that...Ch. 16.1 - It takes 10 min for a 2.4-Mg flywheel to coast to...Ch. 16.1 - The rotor of an electric motor has an angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.27PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.28PCh. 16.1 - The 100-mm-radius brake drum is attached to a...Ch. 16.1 - The 180-mm-radius disk is at rest when it is...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.30, assuming that the direction of...Ch. 16.1 - In order to determine the mass moment of inertia...Ch. 16.1 - The flywheel shown has a radius of 20 in., a...Ch. 16.1 - Each of the double pulleys shown has a mass moment...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.35PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.36PCh. 16.1 - Gear A weighs 1 lb and has a radius of gyration of...Ch. 16.1 - The 25-lb double pulley shown is at rest and in...Ch. 16.1 - A belt of negligible mass passes between cylinders...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.40PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass of 6 kg and an initial angular...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.42PCh. 16.1 - Disk A has a mass mA = 4 kg, a radius rA = 300 mm,...Ch. 16.1 - Disk B is at rest when it is brought into contact...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.45PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.46PCh. 16.1 - For a rigid body in plane motion, show that the...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.48PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.49PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.50PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.51PCh. 16.1 - A 250-lb satellite has a radius of gyration of 24...Ch. 16.1 - A rectangular plate of mass 5 kg is suspended from...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.54PCh. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - A drum with a 200-mm radius is attached to a disk...Ch. 16.1 - The 12-lb uniform disk shown has a radius of r =...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.58PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.59PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.60PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.61PCh. 16.1 - Two uniform cylinders, each of weight W = 14 lb...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.63PCh. 16.1 - Prob. 16.64PCh. 16.1 - A uniform slender bar AB with a mass m is...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.66PCh. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - 16.66 through 16.68A thin plate of the shape...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m is projected along...Ch. 16.1 - Solve Prob. 16.69, assuming that the sphere is...Ch. 16.1 - A bowler projects an 8-in.-diameter ball weighing...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 16.72PCh. 16.1 - A uniform sphere of radius r and mass m is placed...Ch. 16.1 - A sphere of radius r and mass m has a linear...Ch. 16.2 - A cord is attached to a spool when a force P is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.6CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7CQCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.5FBPCh. 16.2 - Two identical 4-lb slender rods AB and BC are...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.7FBPCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.8FBPCh. 16.2 - Show that the couple I of Fig. 16.15 can be...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.76PCh. 16.2 - 16.77 In Prob. 16.76, determine (a) the distance r...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender rod of length L = 36 in. and...Ch. 16.2 - In Prob. 16.78, determine (a) the distance h for...Ch. 16.2 - An athlete performs a leg extension on a machine...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.81PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.82PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.83PCh. 16.2 - A uniform rod of length L and mass m is supported...Ch. 16.2 - 16.84 and 16.85 A uniform rod of length L and mass...Ch. 16.2 - An adapted launcher uses a torsional spring about...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.87PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.88PCh. 16.2 - The object ABC consists of two slender rods welded...Ch. 16.2 - A 3.5-kg slender rod AB and a 2-kg slender rod BC...Ch. 16.2 - A 9-kg uniform disk is attached to the 5-kg...Ch. 16.2 - Derive the equation MC=IC for the rolling disk of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.93PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.94PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.95PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.96PCh. 16.2 - A 40-kg flywheel of radius R = 0.5 m is rigidly...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.98PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.99PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.100PCh. 16.2 - 16.98 through 16.101 A drum of 60-mm radius is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.102PCh. 16.2 - 16.102 through 16.105 A drum of 4-in. radius is...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.104PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.105PCh. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - 16.106 and 16.107A 12-in.-radius cylinder of...Ch. 16.2 - Gear C has a mass of 5 kg and a centroidal radius...Ch. 16.2 - Two uniform disks A and B, each with a mass of 2...Ch. 16.2 - A single-axis personal transport device starts...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - A hemisphere of weight W and radius r is released...Ch. 16.2 - The center of gravity G of a 1.5-kg unbalanced...Ch. 16.2 - A small clamp of mass mB is attached at B to a...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.115PCh. 16.2 - A 4-lb bar is attached to a 10-lb uniform cylinder...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform rod AB with a mass m and a length of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.118PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.119PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.120PCh. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 6-kg uniform rod AB rests on the...Ch. 16.2 - End A of the 8-kg uniform rod AB is attached to a...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform rod ABD is attached to the crank...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The 3-lb uniform rod BD is connected to crank AB...Ch. 16.2 - The test rig shown was developed to perform...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.127 for = 90. 16.127The test rig...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-kg uniform slender bar BD is attached to bar...Ch. 16.2 - The motion of the uniform slender rod of length L...Ch. 16.2 - At the instant shown, the 20-ft-long, uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.132PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.133PCh. 16.2 - The hatchback of a car is positioned as shown to...Ch. 16.2 - The 6-kg rod BC connects a 10-kg disk centered at...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.136PCh. 16.2 - In the engine system shown, l = 250 mm and b = 100...Ch. 16.2 - Solve Prob. 16.137 when = 90. 16.137In the engine...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - The 4-lb uniform slender rod AB, the 8-lb uniform...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two rotating rods in the vertical plane are...Ch. 16.2 - Two disks, each with a mass m and a radius r, are...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform slender bar AB of mass m is suspended as...Ch. 16.2 - A uniform rod AB, of mass 15 kg and length 1 m, is...Ch. 16.2 - The uniform slender 2-kg bar BD is attached to the...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.147PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.148PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.149PCh. 16.2 - Prob. 16.150PCh. 16.2 - (a) Determine the magnitude and the location of...Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 16.152PCh. 16 - A cyclist is riding a bicycle at a speed of 20 mph...Ch. 16 - 16.154 The forklift truck shown weighs 2250 lb and...Ch. 16 - The total mass of the Baja car and driver,...Ch. 16 - Identical cylinders of mass m and radius r are...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.157RPCh. 16 - The uniform rod AB of weight W is released from...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.159RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.160RPCh. 16 - A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without...Ch. 16 - Prob. 16.162RPCh. 16 - Prob. 16.163RPCh. 16 - The Geneva mechanism shown is used to provide an...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
What output will the following lines of code display on the screen? cout "The works of Wolfgang\ninclude the f...
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. A single crystal of aluminum is oriented for a tensile test such that its slip plane normal makes an angle of 28.1° with the tensile axis. Three possible slip directions make angles of 62.4°, 72.0°, and 81.1° with the same tensile axis. (a) Which of these three slip directions is most favored? (b) If plastic deformation begins at a tensile stress of σ x = 1.95 MPa (280 psi), determine the critical resolved shear stress for aluminium. (c) If this single crystalspecimen is loaded under the new stress state: σ x =1.2 MPa σ y = -0.8 MPa, and τ xy = 0.6 MPa, howmuch is the resolve the shear stress along the most favored slip direction?arrow_forwardPlease explain how to do each part and tell me if my drawing is correct. thank youarrow_forward4. Determine which of the following flow fields represent a possible incompressible flow? (a) u= x²+2y+z; v=x-2y+z;w= -2xy + y² + 2z a (b) V=U cose U coso 1 (9) [1-9] Usino |1 (4)] [+] V=-Usin 1+1arrow_forward
- 3. Determine the flow rate through the pipe line show in the figure in ft³/s, and determine the pressures at A and C, in psi. 5' B C 12° 20' D 6"d 2nd- Water Aarrow_forward5. A flow is field given by V = x²₁³+xy, and determine 3 ·y³j- (a) Whether this is a one, two- or three-dimensional flow (b) Whether it is a possible incompressible flow (c) Determine the acceleration of a fluid particle at the location (X,Y,Z)=(1,2,3) (d) Whether the flow is rotational or irrotational flow?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwarddraw the pneumatic circuit to operate a double-acting cylinder with: 1. Extension: Any of two manual conditions plus cylinder fully retracted, → Extension has both meter-in and meter-out, 2. Retraction: one manual conditions plus cylinder fully extended, → Retraction is very fast using quick exhaust valve.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Expert solution plsarrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY