
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Interpret the chemical formula of the ideal perovskite material. Perovskite material contains the element Y, Ba, Cu and O elements. They are superconductors at temperature above that of liquid nitrogen were recently discovered.
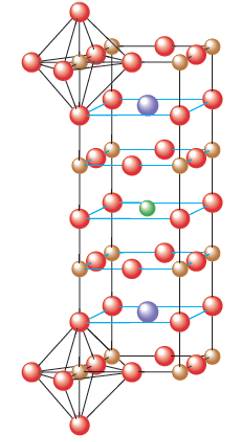
Concept Introduction:
Solids are composed of certain repeating basic units which are called as unit cells. These units represents the arrangement of atoms in a certain manner that repeats itself throughout the solid and make the crystal lattice.
Each solid has a different type of unit cell and crystal lattice that makes it unique from other solids. The atoms are arranged in unit cells.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of ideal perovskite material needs to be interpreted as given in fig (b). Perovskite material contains the element Y, Ba, Cu and O elements. They are superconductors at temperature above that of liquid nitrogen were recently discovered.
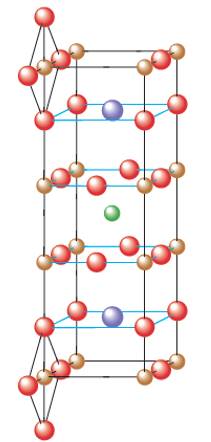
Concept Introduction:
Solids are composed of certain repeating basic units which are called as unit cells. These units represents the arrangement of atoms in a certain manner that repeats itself throughout the solid and make the crystal lattice.
Each solid has a different type of unit cell and crystal lattice that makes it unique from other solids. The atoms are arranged in unit cells.
(c)
Interpretation: The empirical formula of the structure needs to be determined which is given in fig (b) for ideal perovskite material as given in fig (b). Perovskite material contains the element Y, Ba, Cu and O elements. They are superconductors at temperature above that of liquid nitrogen were recently discovered.
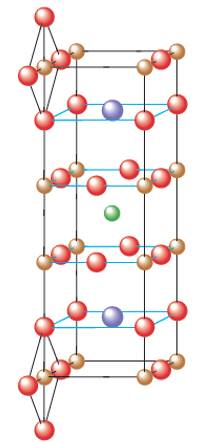
Concept Introduction:
Solids are composed of certain repeating basic units which are called as unit cells. These units represents the arrangement of atoms in a certain manner that repeats itself throughout the solid and make the crystal lattice.
Each solid has a different type of unit cell and crystal lattice that makes it unique from other solids. The atoms are arranged in unit cells.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Given Kp for 2 reactions. Find the Kp for the following reaction: BrCl(g)+ 1/2 I2(g) ->IBr(g) + 1/2 Cl2(g)arrow_forwardFor a certain gas-phase reaction at constant pressure, the equilibrium constant Kp is observed to double when the temperature increases from 300 K to 400 K. Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction, Ah, using this information.arrow_forwardHydrogen bonding in water plays a key role in its physical properties. Assume that the energy required to break a hydrogen bond is approximately 8 kJ/mol. Consider a simplified two-state model where a "formed" hydrogen bond is in the ground state and a "broken" bond is in the excited state. Using this model: • Calculate the fraction of broken hydrogen bonds at T = 300 K, and also at T = 273 K and T = 373 K. • At what temperature would approximately 50% of the hydrogen bonds be broken? • What does your result imply about the accuracy or limitations of the two-state model in describing hydrogen bonding in water? Finally, applying your understanding: • Would you expect it to be easier or harder to vaporize water at higher temperatures? Why? If you were to hang wet laundry outside, would it dry more quickly on a warm summer day or on a cold winter day, assuming humidity is constant?arrow_forward
- (3 pts) Use the Kapustinskii equation to calculate the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2 anddiscuss any differences between this result and that from #4.arrow_forward(3 pts) Silver metal adopts a fcc unit cell structure and has an atomic radius of 144 pm. Fromthis information, calculate the density of silver. Show all work.arrow_forward4. (3 pts) From the information below, determine the lattice enthalpy for MgBr2. Show all work. AH/(kJ mol-¹) Sublimation of Mg(s) +148 lonization of Mg(g) +2187 to Mg2+(g) Vaporization of Br₂(1) +31 Dissociation of Br,(g) +193 Electron gain by Br(g) -331 Formation of MgBr₂(s) -524arrow_forward
- 1. (4 pts-2 pts each part) Consider the crystal structures of NaCl, ZnS, and CsCl (not necessarily shown in this order). a. For one of the three compounds, justify that the unit cell is consistent with stoichiometry of the compound. b. In each of the crystal structures, the cations reside in certain holes in the anions' packing structures. For each compound, what type of holes are occupied by the cations and explain why those particular types of holes are preferred.arrow_forward(2 pts) What do you expect to happen in a Na2O crystal if a Cl− ion replaces one of the O2−ions in the lattice?arrow_forward(2 pts) WSe2 is an ionic compound semiconductor that can be made to be p-type or n-type.What must happen to the chemical composition for it to be p-type? What must happen tothe chemical composition for it to be n-type?arrow_forward
- 8. (2 pts) Silicon semiconductors have a bandgap of 1.11 eV. What is the longest photon wavelength that can promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band in a silicon-based photovoltaic solar cell? Show all work. E = hv = hc/λ h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js c = 3.00 x 108 m/s 1 eV 1.602 x 10-19 Jarrow_forwardA solution containing 100.0 mL of 0.155 M EDTA buffered to pH 10.00 was titrated with 100.0 mL of 0.0152 M Hg(ClO4)2 in a cell: calomel electrode (saturated)//titration solution/Hg(l) Given the formation constant of Hg(EDTA)2-, logKf= 21.5, and alphaY4-=0.30, find out the cell voltage E. Hg2+(aq) + 2e- = Hg(l) E0= 0.852 V E' (calomel electrode, saturated KCl) = 0.241 Varrow_forwardFrom the following reduction potentials I2 (s) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V I2 (aq) + 2e- = 2I- (aq) E0= 0.620 V I3- (aq) + 2e- = 3I- (aq) E0= 0.535 V a) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (aq) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). b) Calculate the equilibrium constant for I2 (s) + I- (aq) = I3- (aq). c) Calculate the solubility of I2 (s) in water.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





