
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Interpret the chemical formula of the ideal perovskite material. Perovskite material contains the element Y, Ba, Cu and O elements. They are superconductors at temperature above that of liquid nitrogen were recently discovered.
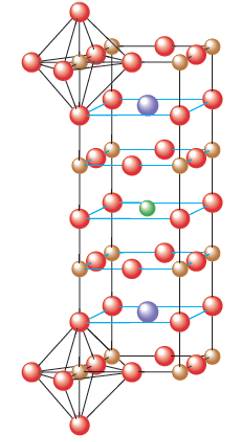
Concept Introduction:
Solids are composed of certain repeating basic units which are called as unit cells. These units represents the arrangement of atoms in a certain manner that repeats itself throughout the solid and make the crystal lattice.
Each solid has a different type of unit cell and crystal lattice that makes it unique from other solids. The atoms are arranged in unit cells.
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of ideal perovskite material needs to be interpreted as given in fig (b). Perovskite material contains the element Y, Ba, Cu and O elements. They are superconductors at temperature above that of liquid nitrogen were recently discovered.
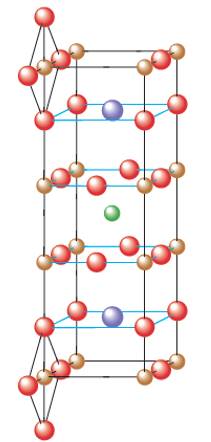
Concept Introduction:
Solids are composed of certain repeating basic units which are called as unit cells. These units represents the arrangement of atoms in a certain manner that repeats itself throughout the solid and make the crystal lattice.
Each solid has a different type of unit cell and crystal lattice that makes it unique from other solids. The atoms are arranged in unit cells.
(c)
Interpretation: The empirical formula of the structure needs to be determined which is given in fig (b) for ideal perovskite material as given in fig (b). Perovskite material contains the element Y, Ba, Cu and O elements. They are superconductors at temperature above that of liquid nitrogen were recently discovered.
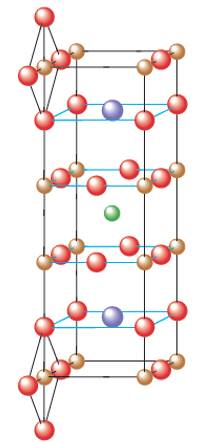
Concept Introduction:
Solids are composed of certain repeating basic units which are called as unit cells. These units represents the arrangement of atoms in a certain manner that repeats itself throughout the solid and make the crystal lattice.
Each solid has a different type of unit cell and crystal lattice that makes it unique from other solids. The atoms are arranged in unit cells.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- 4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardIII O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward
- 3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





