
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 2VCQ
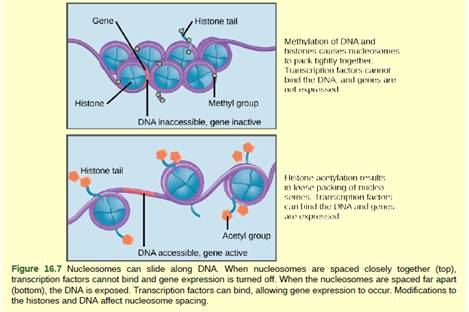
Figure 16.7 In females, one of the two X chromosomes is inactivated during embryonic development because of epigenetic changes to the chromatin. What impact do you think these changes would have on nucleosome packing?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question #3:
In the KeyGene paper, the authors state that it would be useful if pollen from an apomict would
transmit apomixis-inducing genes to the female in the cross (assuming the pollen is viable). Assuming
there was just one gene conferring gametophytic obligate apomixis, and that the two parents are
inbreds, what would be the consequences of such a cross if:
a) The apomixis was a dominant trait? Indicate the genotypes and phenotypes (apomict or non-
apomict) of the parents, F1 and F2 generations. Remember to include the expected genotypic
and phenotypic ratios (or percentages) in the F1 and F2 generations, and to position the female
first (left side) in the parental cross.
b) The apomixis was a recessive trait? Indicate the genotypes and phenotypes (apomict or non-
apomict) of the parents, F1 and F2 generations. Remember to include the expected genotypic
and phenotypic ratios (or percentages) in the F1 and F2 generations, and to position the female
first (left side) in the…
Question #5:
Assume that two genes are identified that confer gametophytic facultative apomixis in soybean. The
genes show independent assortment. Recessive alleles at both loci are required for the facultative
apomixis. Facultative apomixis is triggered when the temperature at pollination is above 20 degrees C.
At temperatures below 20 degrees C, all reproduction is sexual, independent of genotype.
A facultative apomict male, capable of producing viable pollen, was crossed with a sexually
reproducing female. Assuming the parents are completely inbred, what are the predicted phenotypic
ratios (apomict: non-apomict) for the F1, F2, and DH (F1-derived) generations at each of the following
temperatures*:
a) 15°C?
b) 25°C?
*for full credit, show crosses and genotypes where appropriate. Remember to position the
female first (left side) in the cross.
Type your answer here:
a. What percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent.
b. What will happen to elimination of the drug in the previous question if the system is saturated? explain and show any math involved
Chapter 16 Solutions
Biology 2e
Ch. 16 - Figure 16.5 In E. coli, the tip operon is on by...Ch. 16 - Figure 16.7 In females, one of the two X...Ch. 16 - Figure 16.13 An increase in phosphorylation levels...Ch. 16 - Control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells...Ch. 16 - Post-translational control refers to: regulation...Ch. 16 - How does the regulation of gene expression support...Ch. 16 - If glucose is absent, but so is lactose, the lac...Ch. 16 - Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. Therefore, the...Ch. 16 - The a/a operon is an inducible operon that...Ch. 16 - What are epigenetic modifications? the addition of...
Ch. 16 - Which of the following are true of epigenetic...Ch. 16 - The binding of _____ is required for transcription...Ch. 16 - What will result from the binding of a...Ch. 16 - A scientist compares the promoter regions of two...Ch. 16 - Which of the following are involved in post...Ch. 16 - Binding of an RNA binding protein will the...Ch. 16 - An unprocessed pre-mRNA has the following...Ch. 16 - IS. Alternative splicing has been estimated to...Ch. 16 - Post-translational modifications of proteins can...Ch. 16 - A scientist mutates elF-2 to eliminate its GTP...Ch. 16 - Cancer causing genes are called transformation...Ch. 16 - Targeted therapies are used in patients with a set...Ch. 16 - Name two differences between prokaryotic and...Ch. 16 - Describe how controlling gene expression will...Ch. 16 - Describe how transcription in prokaryotic cells...Ch. 16 - What is the difference between a repressible and...Ch. 16 - In cancer cells, alteration to epigenetic...Ch. 16 - A scientific study demonstrated that rat mothering...Ch. 16 - Some autoimmune diseases show a positive...Ch. 16 - A mutation within the promoter region can alter...Ch. 16 - What could happen if a cell had too much of an...Ch. 16 - A scientist identifies a potential transcription...Ch. 16 - Describe how RBPs can prevent miRNAs from...Ch. 16 - How can external stimuli alter...Ch. 16 - Protein modification can alter gene expression in...Ch. 16 - Alternative forms of a protein can be beneficial...Ch. 16 - Changes in epigenetic modifications alter the...Ch. 16 - A scientist discovers a virus encoding a Protein X...Ch. 16 - New drugs are being developed that decrease DNA...Ch. 16 - How can understanding the gene expression pattern...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. ___ Mitosis 2. ___ Meiosis 3. __ Homologous chromosomes 4. __ Crossing over 5. __ Cytokinesis A. Cytoplasmic...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
How do you think a cell performing cellular respiration rids itself of the resulting CO2?
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
For the generic equilibrium HA(aq) ⇌ H + (aq) + A- (aq), which of these statements is true?
The equilibrium con...
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Identify each of the following characteristics as belonging to cervical, thoracic, or lumbar vertebrae; the sac...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
1. If an object is not moving, does that mean that there are no forces acting on it? Explain.
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If you wanted to reduce the difference between peak and trough levels that occur with repeated administration of a drug, how would you adjust the dose and dose interval without changing the plateau concentration (plateau is the average of peak and trough levels)? Select your answers for both dose and interval. Hint: It may be helpful to think about this problem using an example such as food. How would you eat if you wanted to maintain very steady hunger/satiety levels without changing your total caloric intake? Options: A. Dose; Increase dose B. Dose; Decrease dose C. Dose; Do not change dose D. Interval; Increase the interval between doses (give the drug less frequently) E. Interval; Decrease the interval between doses (give the drug more frequently) F. Interval; Do not change the intervalarrow_forwardWhat percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. Show the matharrow_forwardBriefly explain the 6 domain of interprofessional collaboration: Role clarification, Team functioning, Interprofessional communication, Patient/client/family/community-centered care, Interprofessional conflict resolution, Collaborative leadership. Provide a specific negative events that nursing student would observe in a clinical setting for each domain.arrow_forward
- what is an intermittent water course and what kind of fish habitat it would providearrow_forwardwhy are native freshwater mussels are an important part of great lakes ecosystemarrow_forwardwhat morphological features differentiate the lamprey species and other species in the great lakesarrow_forward
- There are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour fish or mussel species that are native to the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forward
- four physial characteristics of a fish or a mussel that would help you identify it to a speciesarrow_forwarddescribe what you would do in this situation, you are working ona. river and it will take 20 minutes by boat to get back to the field truck, you are 1 hour from finishing the field work on the last day of field trip. you hear thunder int he dsitnace, what did you do?arrow_forwardunu grow because auxin is still produced in the tip to Another of Boysen and Jensen's experiments included the use of mica, explain why one of the shoots was able to show phototropism and the other was not. Mica Wafer Ligh c. They then t but this time permeable n shoot. Why phototropis Light Mica Wafer Coleoptile tips Tips removed: agar Explain why the shoo direction after the ag the cut shoot, even tarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
QCE Biology: Introduction to Gene Expression; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7hydUtCIJk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY