
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To determine whether oxaloacetate is associated with (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, or (3) the urea cycle.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.73EP
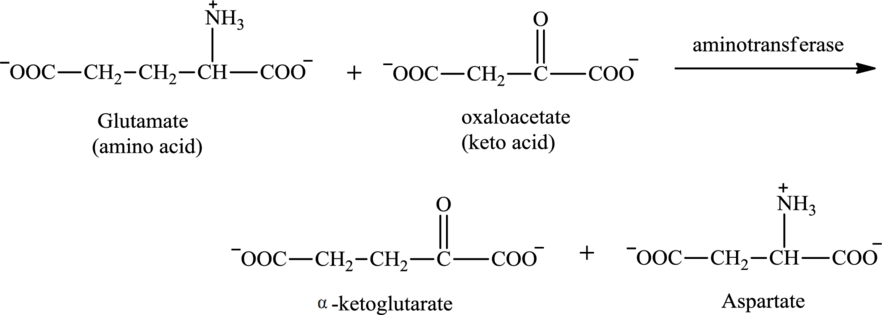
Oxaloacetate is associated with the transamination reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of oxaloacetate is:
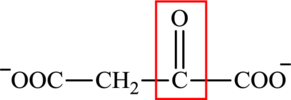
Oxaloacetate contains both a carbonyl group and a carboxyl
(b)
Interpretation: To determine whether arginine is associated with (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, or (3) the urea cycle.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide.
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.73EP
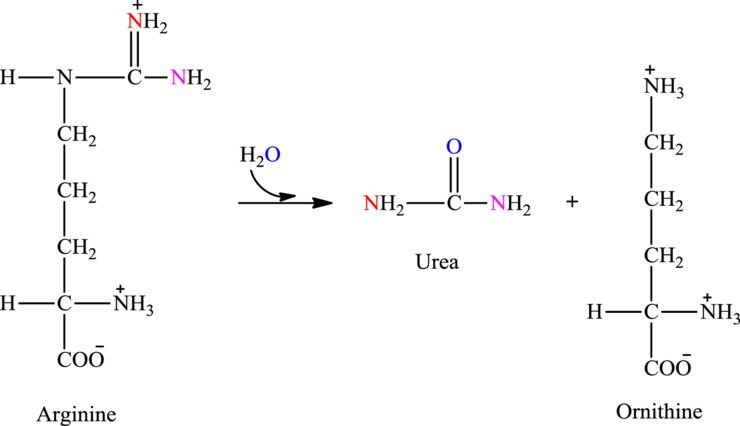
Arginine is associated with the urea cycle.
Explanation of Solution
In step 3 of the urea cycle, catalyst argininosuccinate lyase catalyzes the cleavage of argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate. Arginine formed step 3 reacts with water and undergo hydrolysis in step 4.
Hydrolysis of arginine produce urea and also regenerates the starting fuel ornithine.
(c)
Interpretation: To determine whether
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide.
(c)
Answer to Problem 15.73EP
Water
Explanation of Solution
Water is one of the reactants in oxidative deamination reaction. For example, glutamate is an
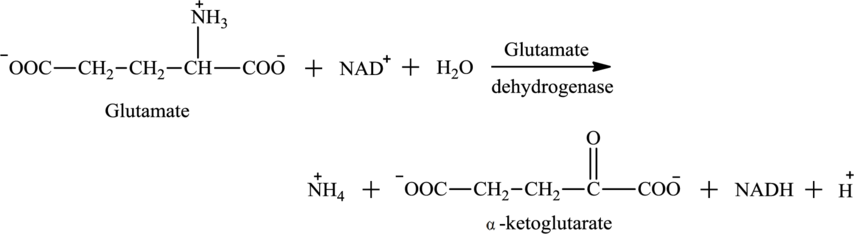
Water is also associated with the urea cycle. Ammonium ion produced from oxidative deamination reaction, carbon dioxide, water, and two ATP molecules reacts to form carbamoyl phosphate. Carbamoyl phosphate is fuel for the urea cycle. The
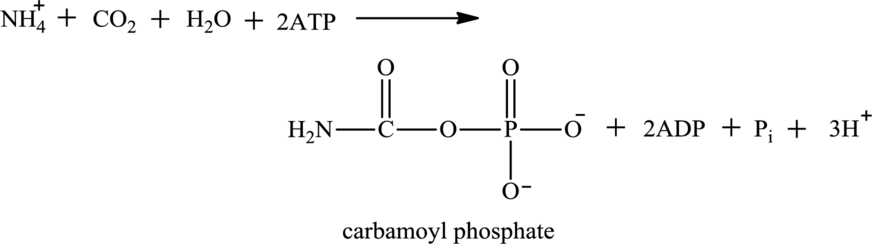
(d)
Interpretation: To determine whether ATP is associated with (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, or (3) the urea cycle.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide.
(d)
Answer to Problem 15.73EP
ATP is associated with the urea cycle.
Explanation of Solution
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that is defined as the energy currency of life and provides energy to carry out the
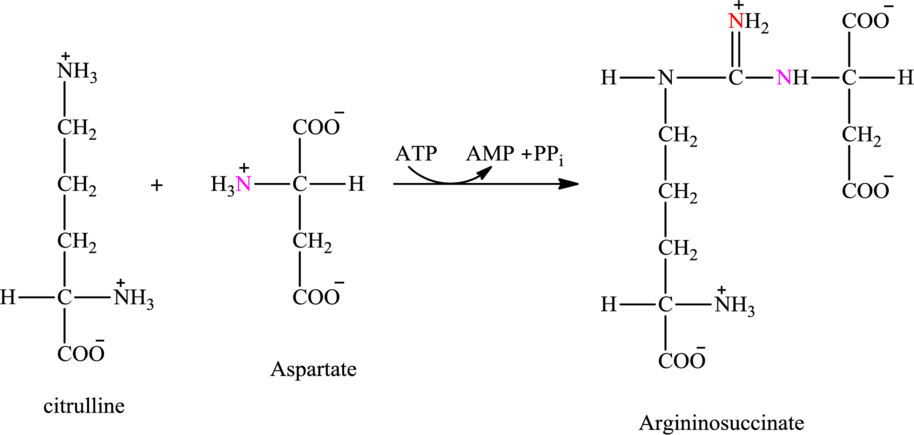
Step 2 of the urea cycle involves a condensation reaction of citrulline with aspartate to produce argininosuccinate. The reaction is carried out with the expenditure of ATP molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- 2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forward
- Instructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forwardC. NaOMe, Br Brarrow_forward
- Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co




