
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin niacin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.115EP
B vitamin niacin is involved as a cofactor in the process of oxidative deamination and in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate requires dehydrogenase enzyme. It is an oxidoreductase enzyme and works with either
The oxidative deamination reaction of glutamate amino acid is as follows:
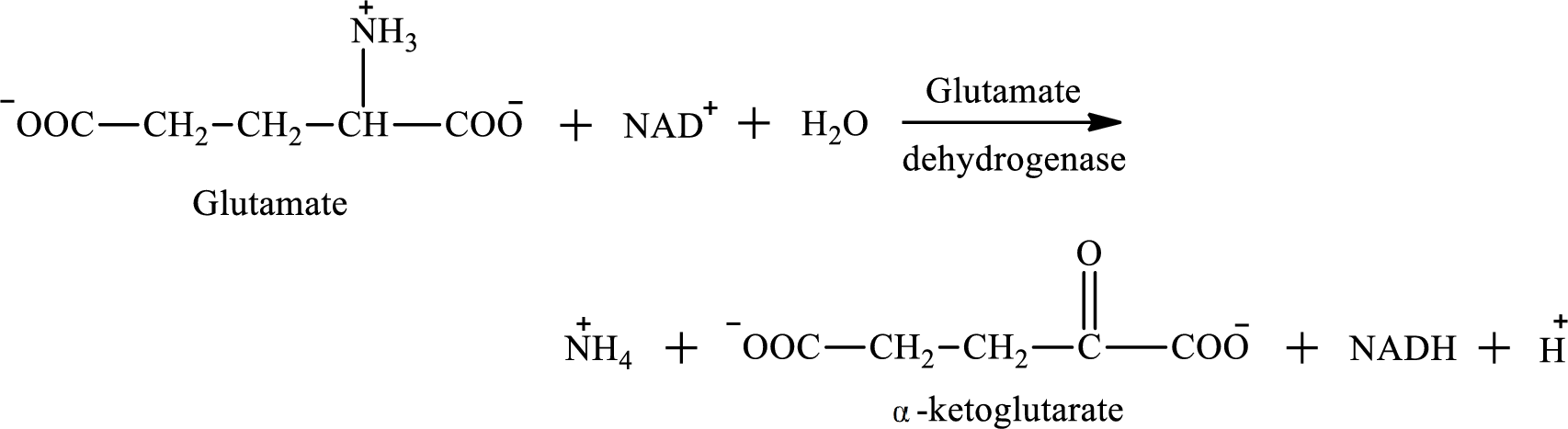
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
(b)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin folate is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.115EP
B vitamin folate is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme tetrahydrofolate
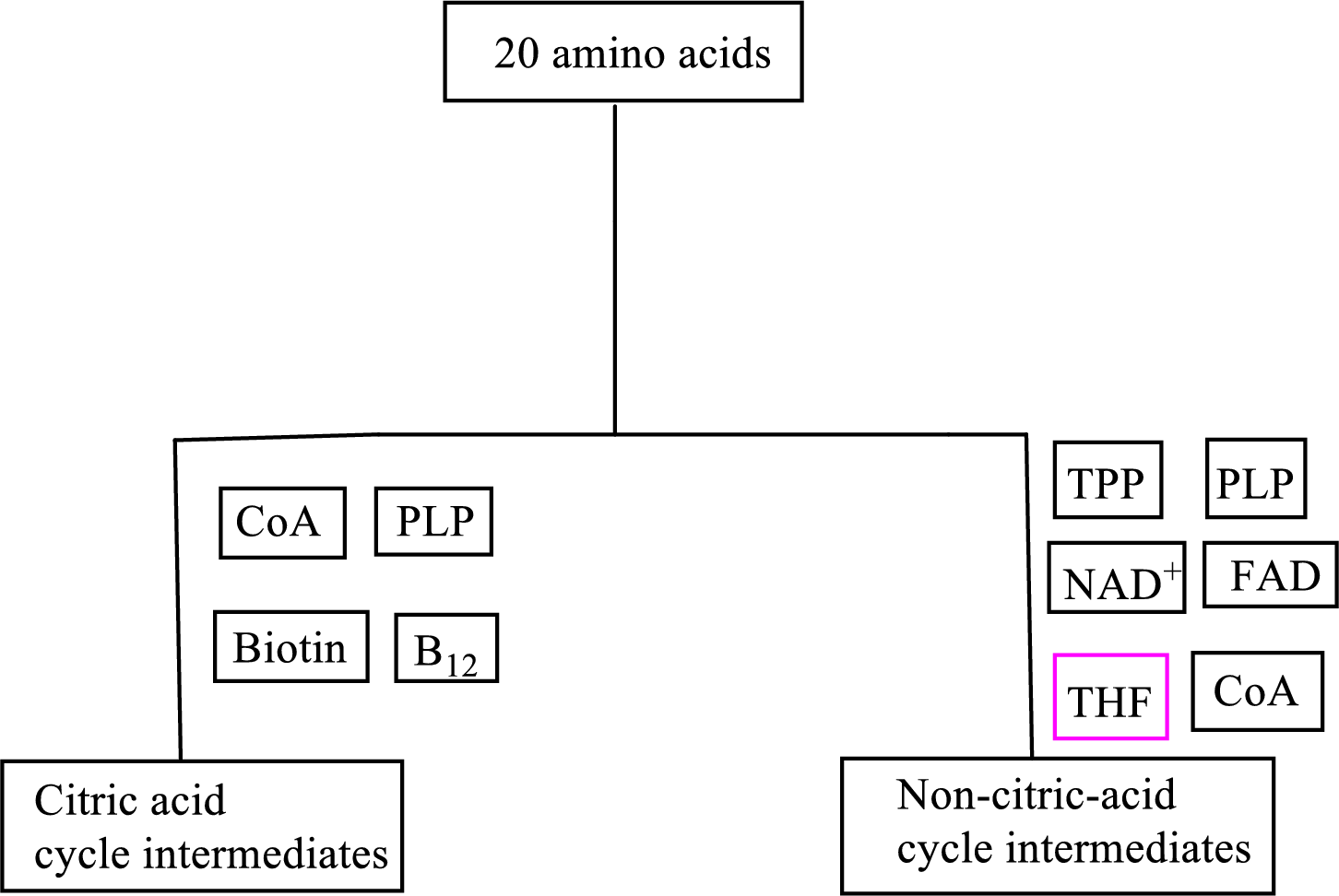
(c)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin biotin is involved as a cofactor in the processes of (1) transamination, (2) oxidative deamination, (3) urea cycle, (4) carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates, or (5) carbon skeleton degradation to non-CAC intermediates.
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(c)
Answer to Problem 15.115EP
B vitamin biotin is involved as a cofactor in carbon skeleton degradation to CAC intermediates.
Explanation of Solution
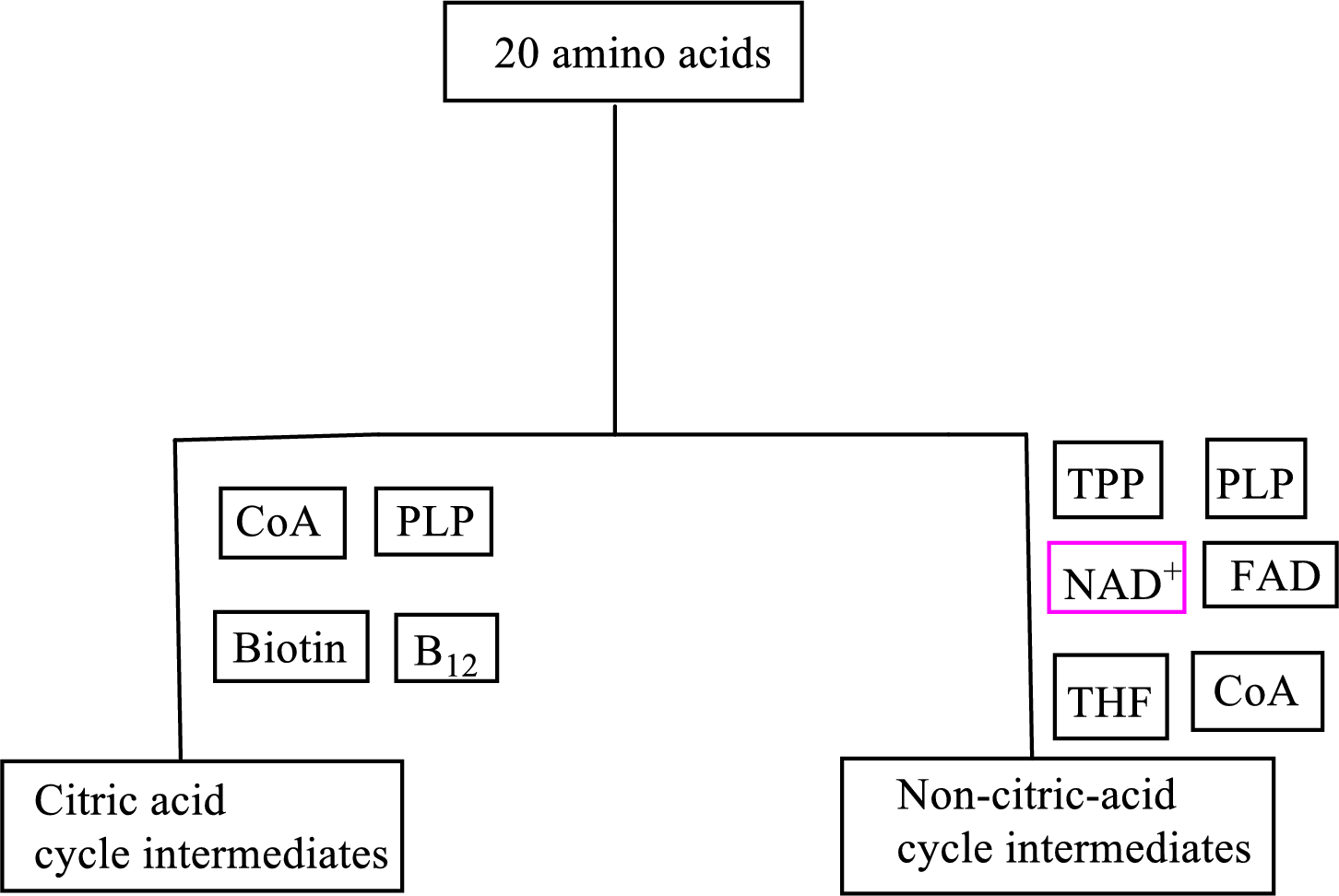
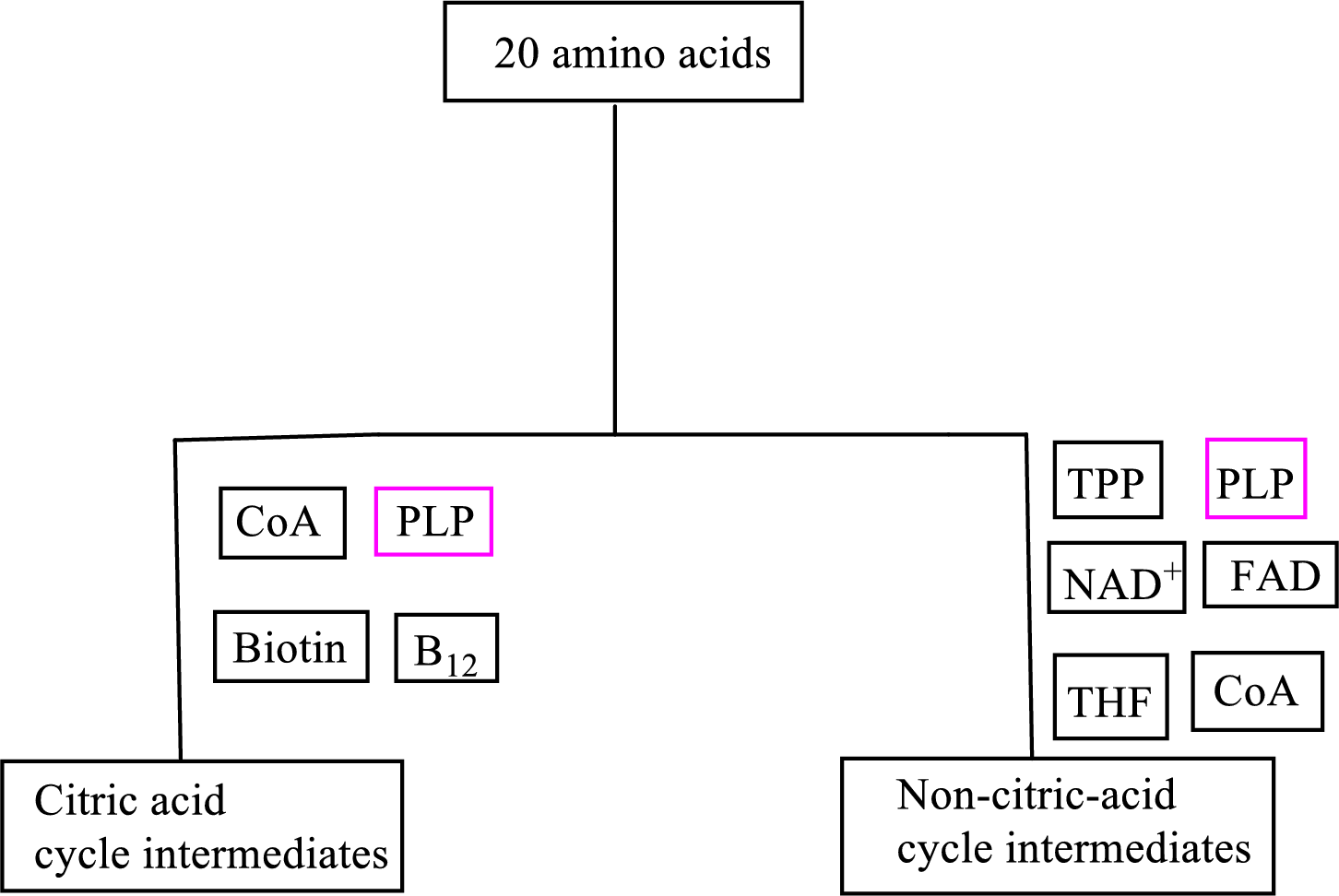
Biotin is involved in the carbon skeleton degradation pathway to CAC intermediates. An overview of the B vitamin participations in the degradation pathways for the carbon skeletons of the 20 standard amino acids is as follows:
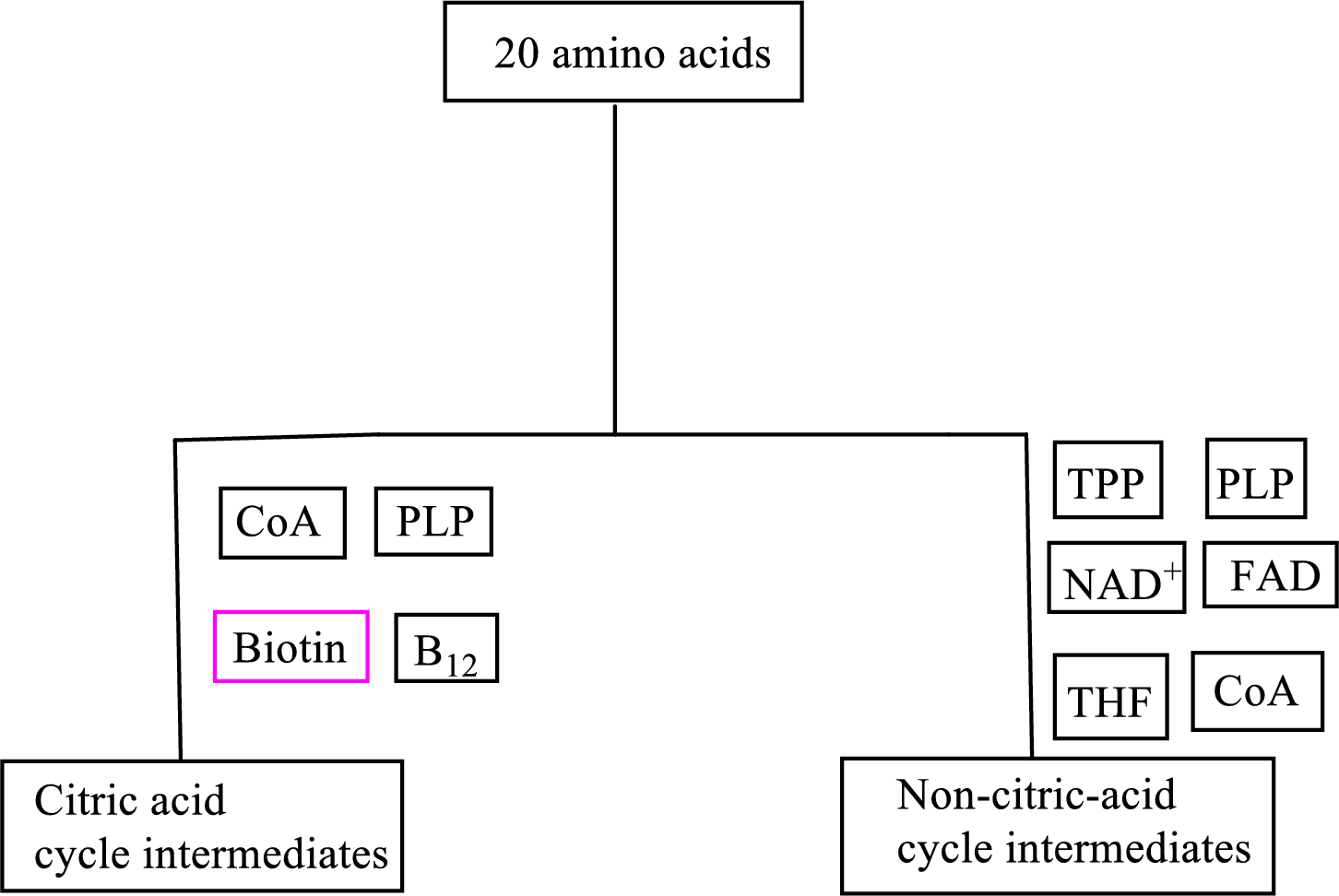
(d)
Interpretation:
To indicate whether B vitamin
Concept introduction:
Cofactors are non-protein organic compounds that are used along with the enzymes and help to carry forward the reaction. The coenzymes containing B-vitamin serve as temporary carriers of atoms or functional groups in the redox and group transfer reactions associated with the metabolism of ingested food in order to obtain energy from the food.
Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
A biochemical reaction in which an
A urea cycle is a cyclic biochemical pathway that involves the production of urea using ammonium ions and aspartate molecules as nitrogen sources. The reactants in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate are ammonium ion, water, and carbon dioxide. The desired product of the urea cycle is urea.
There are 20 standard amino acids. Each amino acid has a different carbon skeleton and has a different degradation pathway for its carbon skeleton.
(d)
Answer to Problem 15.115EP
Explanation of Solution
Coenzyme
Transamination reaction involves a simple transfer of amino groups but the overall reaction occurs in several steps and also requires
Coenzyme
An overview of the B vitamin participations in the degradation pathways for the carbon skeletons of the 20 standard amino acids is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- 8. What is the major product of the following reaction? KMnO4 b a TOH OH OH C d OH "OH HO OH OHarrow_forwardChoose the right answerarrow_forward3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward
- 7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forwardWhat is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride below?arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following questions using the data I included. 1&2arrow_forwardAssign all the Protons in HNMRarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





