
Organic And Biological Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781305081079
Author: STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher: Cengage Learning,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 15, Problem 15.57EP
Interpretation Introduction
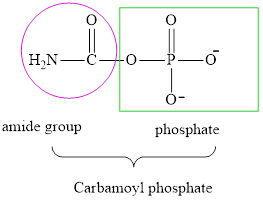
Interpretation: To determine the chemical reactants needed to produce the compound carbamoyl phosphate.
Concept introduction: Carbamoyl phosphate is an intermediate or one of the fuel for the urea cycle. Ammonium ion produced via oxidative deamination reaction is converted into the carbamoyl phosphate which then enters the urea cycle.
The carbamoyl phosphate formation reaction is carried out in the mitochondrial matrix. Carbamoyl is the prefix used to represent an amide group. Thus carbamoyl phosphate is a molecule that contains a phosphate group attached to an amide
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.
Draw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide:
H-
-OH
H-
OH
H-
-OH
CH₂OH
Answer the question in the first photo
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
Ch. 15.1 - Which of the following statements about dietary...Ch. 15.1 - Dietary protein materials as they leave the...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15.1 - Which of the following is not a proteolytic...Ch. 15.2 - The dominant use for the amino acids of the amino...Ch. 15.2 - The most abundant amino acid in the amino acid...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15.3 - The reactants in a transamination reaction are a....Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.3 - Prob. 3QQ
Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 4QQCh. 15.3 - Prob. 5QQCh. 15.3 - Prob. 6QQCh. 15.4 - Prob. 1QQCh. 15.4 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.4 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15.4 - Prob. 4QQCh. 15.4 - Prob. 5QQCh. 15.4 - In the urea cycle, the urea-producing step...Ch. 15.5 - Which of the following statements concerning the...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.5 - Which of the following statements concerning the...Ch. 15.5 - Prob. 4QQCh. 15.6 - Prob. 1QQCh. 15.6 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.6 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15.7 - Prob. 1QQCh. 15.7 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.7 - In the degradation of heme, which of the following...Ch. 15.7 - In the degradation of heme, the iron atom present...Ch. 15.8 - In degradation of the sulfur-containing amino acid...Ch. 15.8 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.8 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15.8 - Prob. 4QQCh. 15.9 - Prob. 1QQCh. 15.9 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.9 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15.10 - Transamination reactions require the cofactor PLP...Ch. 15.10 - Prob. 2QQCh. 15.10 - Prob. 3QQCh. 15 - Prob. 15.1EPCh. 15 - Indicate whether each of the following aspects of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.3EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.4EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.5EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.6EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.7EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.8EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.9EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.10EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.11EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.12EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.13EPCh. 15 - Indicate whether each of the following statements...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.15EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.16EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.17EPCh. 15 - What are the four major uses for amino acids...Ch. 15 - With the help of Table 26-1, classify each of the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.20EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.21EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.22EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.23EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.24EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.25EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.26EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.27EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.28EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.29EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.30EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.31EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.32EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.33EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.34EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.35EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.36EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.37EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.38EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.39EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.40EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.41EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.42EPCh. 15 - Draw the structure of the -keto acid produced from...Ch. 15 - Draw the structure of the -keto acid produced from...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.45EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.46EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.47EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.48EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.49EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.50EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.51EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.52EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.53EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.54EPCh. 15 - What is a carbamoyl group?Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.56EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.57EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.58EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.59EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.60EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.61EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.62EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.63EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.64EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.65EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.66EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.67EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.68EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.69EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.70EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.71EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.72EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.73EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.74EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.75EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.76EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.77EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.78EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.79EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.80EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.81EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.82EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.83EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.84EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.85EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.86EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.87EPCh. 15 - What is the starting material for the biosynthesis...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.89EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.90EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.91EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.92EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.93EPCh. 15 - What are the structural differences between...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.95EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.96EPCh. 15 - Which bile pigment is responsible for the yellow...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.98EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.99EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.100EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.101EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.102EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.103EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.104EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.105EPCh. 15 - Indicate whether each of the following statements...Ch. 15 - Prob. 15.107EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.108EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.109EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.110EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.111EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.112EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.113EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.114EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.115EPCh. 15 - Prob. 15.116EP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ggggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forwardExplain the concepts of hemiacetal and acetal.arrow_forwardBriefly describe a nucleophilic addition.arrow_forward
- Is nucleophilic acyl substitution an SN1 or SN2 reaction?arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. NH2 F3C CF3 NH OMe NH2-NH2, ACOH Aarrow_forwardPhotochemical smog is formed in part by the action of light on nitrogen dioxide. The wavelength of radiation absorbed by NO2 in this reaction is 197 nm.(a) Draw the Lewis structure of NO2 and sketch its π molecular orbitals.(b) When 1.56 mJ of energy is absorbed by 3.0 L of air at 20 °C and 0.91 atm, all the NO2 molecules in this sample dissociate by the reaction shown. Assume that each absorbed photon leads to the dissociation (into NO and O) of one NO2 molecule. What is the proportion, in parts per million, of NO2 molecules in this sample? Assume that the sample behaves ideally.arrow_forward
- Correct each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the skeletal ("line") structure it would have if it were dissolved in a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO Explanation Check NH, 2 W O :□ G ©2025 M unter Accessibilityarrow_forwardAn expression for the root mean square velocity, vrms, of a gas was derived. Using Maxwell’s velocity distribution, one can also calculate the mean velocity and the most probable velocity (mp) of a collection of molecules. The equations used for these two quantities are vmean=(8RT/πM)1/2 and vmp=(2RT/M)1/2 These values have a fixed relationship to each other.(a) Arrange these three quantities in order of increasing magnitude.(b) Show that the relative magnitudes are independent of the molar mass of the gas.(c) Use the smallest velocity as a reference for establishing the order of magnitude and determine the relationship between the larger and smaller values.arrow_forwardThe reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forward
- One liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning


General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry In Focus
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305084476
Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.
Publisher:Cengage Learning