
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
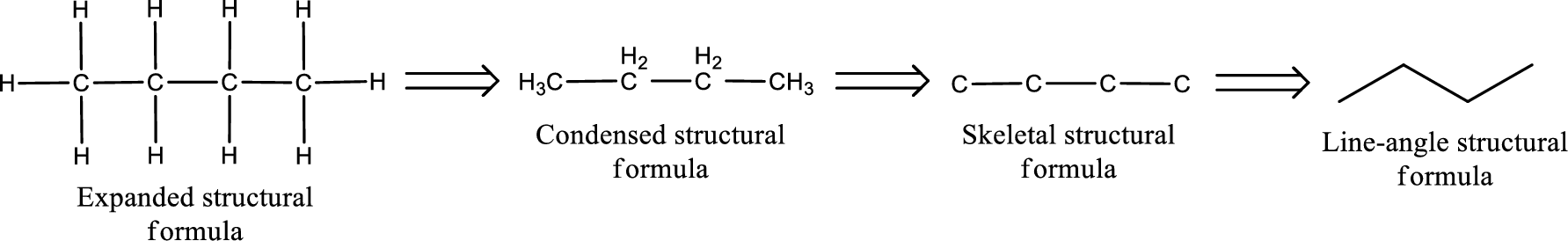
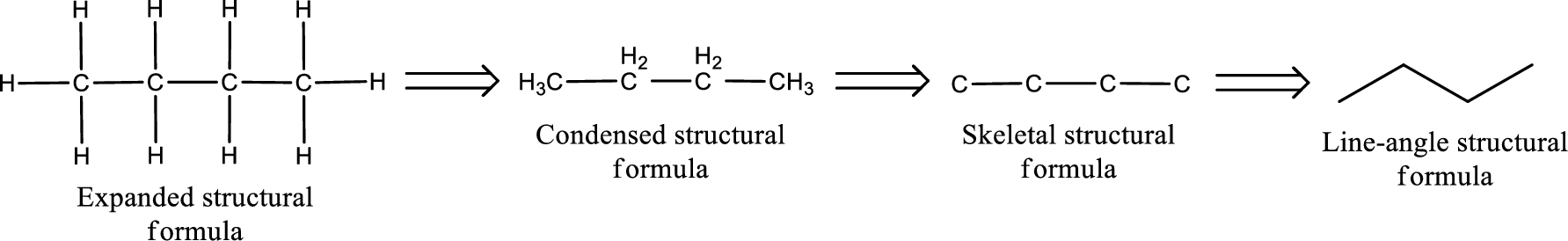
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15.22EP
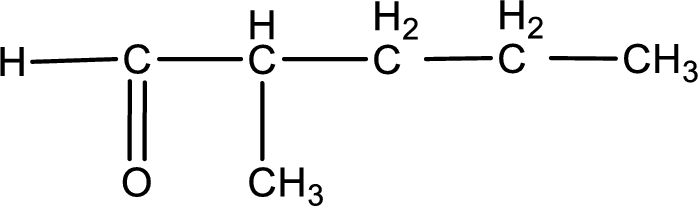
The structural formula for 2-methylpentanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 2-methylpentanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is pentane and it contains five carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,

From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituent is a methyl group on second carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
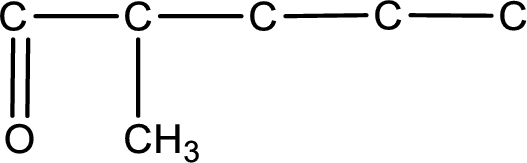
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
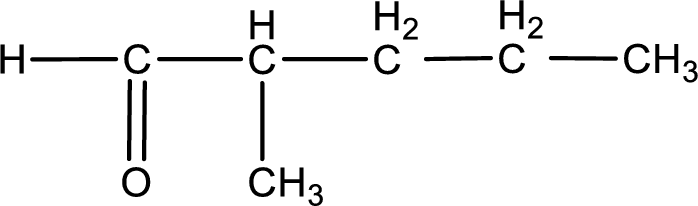
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
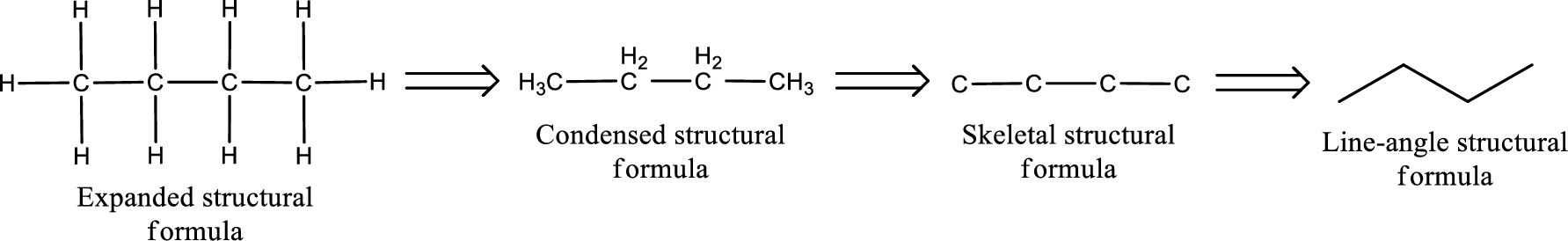
(b)
Answer to Problem 15.22EP
The structural formula for 4-ethylhexanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 4-ethylhexanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is hexane and it contains six carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,
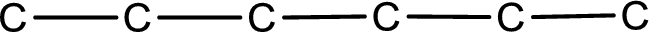
From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituent is an ethyl group on fourth carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
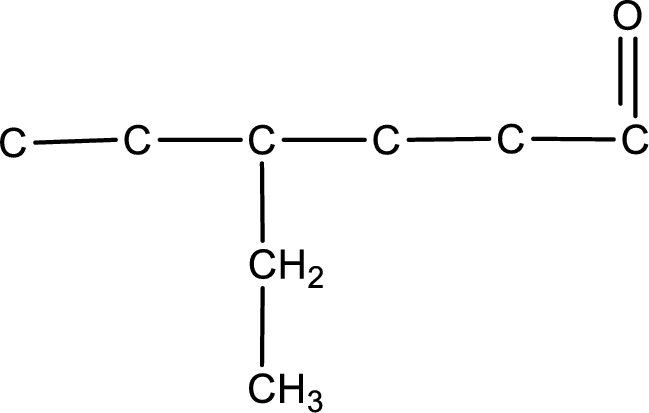
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
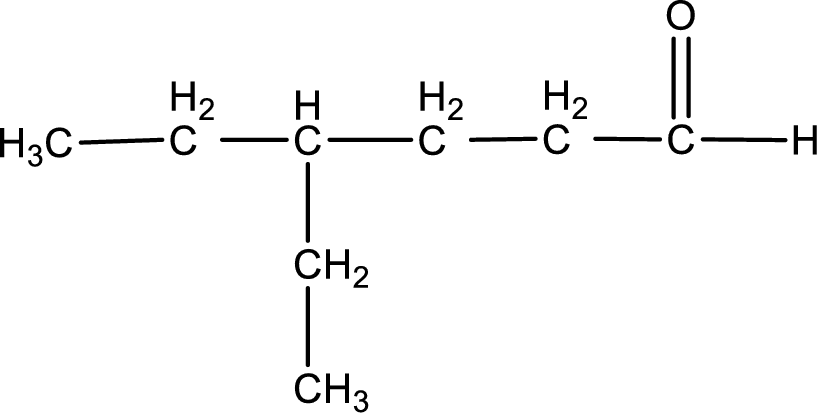
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(c)
Answer to Problem 15.22EP
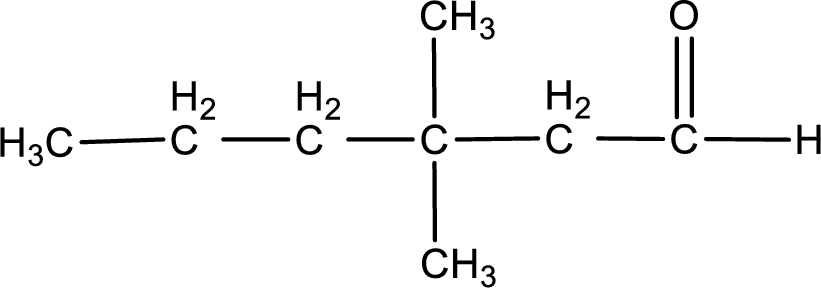
The structural formula for 3,3-dimethylhexanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 3,3-dimethylhexanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is hexane and it contains six carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,
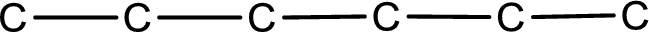
From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituents are two methyl groups on third carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
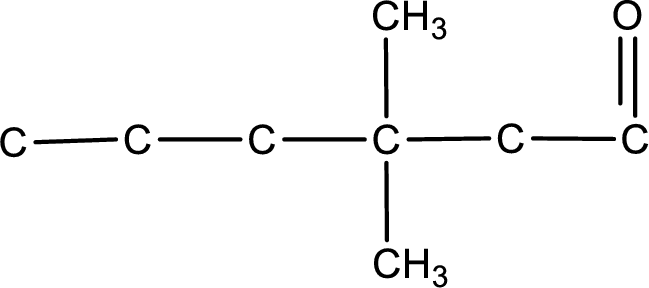
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
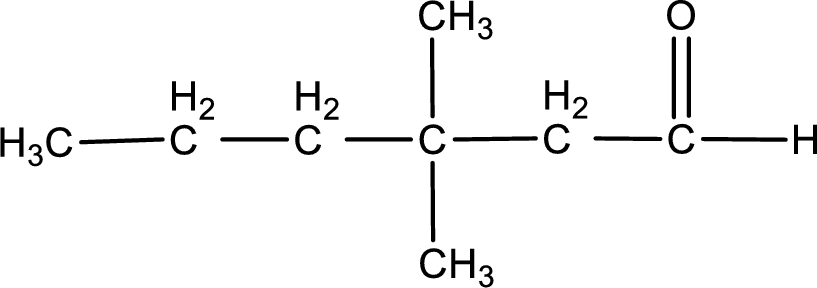
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the given aldehyde has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the aldehyde can be drawn from the IUPAC name. In the IUPAC name, the parent chain of carbon atom can be identified and then the substituents present in it can also be identified. With these information, the structure for the given compound can be drawn. In an aldehyde the counting has to be always from the carbonyl carbon that is given the number 1.
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- • Expanded structural formula
- • Condensed structural formula
- • Skeletal structural formula
- • Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(d)
Answer to Problem 15.22EP
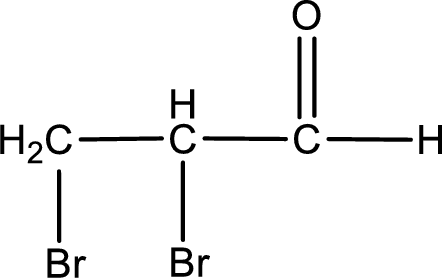
The structural formula for 2,3-dibromopropanal is,
Explanation of Solution
The given name of the compound is 2,3-dibromopropanal. From the name it is understood that the parent carbon chain is propane and it contains three carbon atoms. The parent chain can be drawn as shown below,
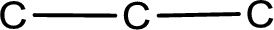
From the name of the given aldehyde, the substituents that are present can be identified. In this case, the substituents are two bromine atoms, each on second carbon atom and third carbon atom. The first carbon atom has to be the carbonyl carbon atom as the given compound is an aldehyde.
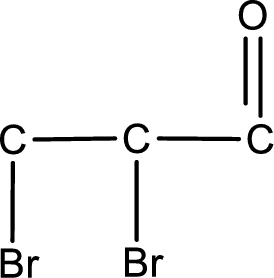
Carbon atom has a valence of four. Hence, carbon atom can form four covalent bonds. The remaining bonds are satisfied by hydrogen atom. The structure is obtained as shown below,
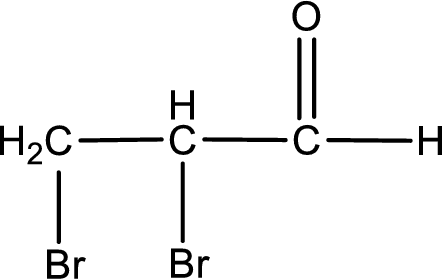
Structural formula for the given aldehyde is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning


