
a)
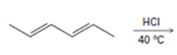
Interpretation:
The major products formed during the addition of one equivalent of HCl to hexa-2, 4-diene along with the mechanism of their formation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes undergo electrophilic addition reactions through the formation of an allyl carbocation. The allyl cation is resonance stabilized and the attack of chloride ion on each of these forms leads to the formation of a mixture of 1, 2- and 1, 4-addition products.
To show:
The major product formed during the addition of one equivalent of HCl to hexa-2, 4-diene along with the mechanism of their formation.
b)
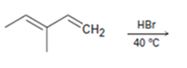
Interpretation:
The major products formed during the addition of one equivalent of HX to 3-methylpenta-1, 3-diene along with the mechanism of their formation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes undergo electrophilic addition reactions through the formation of an allyl carbocation. The allyl cation is resonance stabilized and the attack of chloride ion on each of these forms leads to the formation of a mixture of 1, 2- and 1, 4-addition products.
To show:
The major products formed during the addition of one equivalent of HBr to 3-methylpenta-1, 3-diene along with the mechanism of their formation.
c)
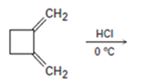
Interpretation:
The major product formed during the addition of one equivalent of HCl to 1, 2-dimethylenecyclobutane, along with the mechanism of their formation is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes undergo electrophilic addition reactions through the formation of an allyl carbocation. The allyl cation is resonance stabilized and the attack of chloride ion on each of these forms leads to the formation of a mixture of 1, 2- and 1, 4-addition products.
To show:
The major product formed during the addition of one equivalent of HCl to 1, 2-dimethylenecyclobutane along with the mechanism of their formation.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- > H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardThe answer is shown. What is the reaction mechanism to arrive at the answer?arrow_forward
- no Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardConsider the following nucleophilic substitution reaction. The compound listed above the arrow is the solvent for the reaction. If nothing is listed over the arrow, then the nucleophile is also the solvent for the reaction. Part 1 of 2 Br CH,CN + I¯ What is the correct mechanism for the reaction? Select the single best answer. @SN2 ○ SN 1 Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Draw the products for the reaction. Include both the major organic product and the inorganic product. If more than one stereoisomer is possible, draw only one stereoisomer. Include stereochemistry where relevant. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X હૈarrow_forward20.33 Think-Pair-Share (a) Rank the following dienes and dienophiles in order of increasing reactivity in the Diels-Alder reaction. (i) CO₂Et (ii) COEt || CO₂Et MeO MeO (b) Draw the product that results from the most reactive diene and most reactive dienophile shown in part (a). (c) Draw a depiction of the orbital overlap involved in the pericyclic reaction that oc- curs between the diene and dienophile in part (b). (d) Is the major product formed in part (b) the endo or exo configuration? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
