
Concept explainers
a)
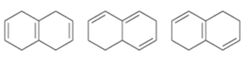
Interpretation:
The molecules given are to be arranged from shortest to longest wavelength on the basis their wavelength of maximum absorption in UV spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Extended conjugation shifts the UV absorption maxima to higher wavelengths. For example, the UV absorption maxima for 1,3-butadiene is 217 nm and that of 1,3,5-hexatriene is 258nm.
To arrange:
The molecules given from shortest to longest wavelength on the basis their wavelength of maximum absorption in UV spectroscopy.
b)
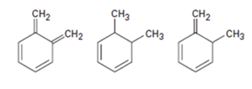
Interpretation:
The molecules given are to be arranged from shortest to longest wavelength on the basis their wavelength of maximum absorption in UV spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Extended conjugation shifts the UV absorption maxima to higher wavelengths. For example, the UV absorption maxima for 1,3-butadiene is 217 nm and that of 1,3,5-hexatriene is 258nm.
To arrange:
The molecules given from shortest to longest wavelength on the basis their wavelength of maximum absorption in UV spectroscopy.
c)
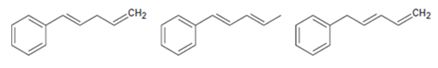
Interpretation:
The molecules given are to be arranged from shortest to longest wavelength on the basis their wavelength of maximum absorption in UV spectroscopy.
Concept introduction:
Extended conjugation shifts the UV absorption maxima to higher wavelengths. For example, the UV absorption maxima for 1,3-butadiene is 217 nm and that of 1,3,5-hexatriene is 258nm.
To arrange:
The molecules given from shortest to longest wavelength on the basis their wavelength of maximum absorption in UV spectroscopy.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 20.35 Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and specify the configuration of compound B. EtO₂C 250°C C14H2004 CO₂Et 1. Oso, then NaHSO3 2. HIO4 C14H2006 A Barrow_forward20.21 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HCI to cyclopentadiene. 20.22 Draw structural formulas for the two constitutional isomers with the molecular for- mula C₂H,Br, formed by adding one mole of Br, to cyclopentadiene.arrow_forwardAdd substituents to draw the conformer below (sighting down the indicated bond), then rotate the back carbon to provide the conformation that will be capable of an E2 elimination. R/S stereochemistry is graded. + I I H CH3 Ph Досн Br OCH 3 Drawing Q H Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Tap a node to see suggestions. H H H H H Undo Reset Remove Done Rotatearrow_forward
- 20.17 Predict the structure of the major product formed by 1,2-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene. 3-Methylenecyclohexene 20.18 Predict the major product formed by 1,4-addition of HBr to 3-methylenecyclohexene.arrow_forward+ Draw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Br Drawing Strong Base H Q Atoms, Bonds Charges and Rings Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Remove Done 語 Reset Undo + Drag To Panarrow_forwardDraw a vicinal alkyl bromide that would produce the following alkene in an E2 elimination. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Drawing Į Strong Base H Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset 謂 Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + Br CH3 Q Strong Base Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges Undo Reset H "Br H N Br. Remove Done .N. Drag To Panarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the product of this elementary step in an elimination mechanism. Include all lone pairs and charges as appropriate. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore byproducts. + Br: .. 8 0.01 M NaOH heat Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges and Lone Pairs Draw or tap a new bond to see suggestions. Undo Reset Remove Done + Drag To Panarrow_forward+ Draw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. Ph CH2CH3 H H3C H Br DBN [૪] Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings H | OH Charges ―00 H. C | Undo Reset Br I Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Reaction A Now the production A ΠIn the product of reaction i 12 Dear the product of actionarrow_forwardMacmillan Learnin When an unknown amine reacts with an unknown acid chloride, an amide with a molecular mass of 163 g/mol (M* = 163 m/z) is formed. In the infrared spectrum, important absorptions appear at 1661, 750 and 690 cm-1. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra are provided. Draw the structure of the product as the resonance contributor lacking any formal charges. 13C NMR DEPT 90 200 160 120 80 40 0 200 160 120 80 DEPT 135 200 160 120 80 40 0 Draw the unknown amide. 40 40 0arrow_forwardDraw the major product karmed when I reach with the epoxide. Use walge dah bonds, including hydrogen al alcach genic center, to show the chemistry of the product Beeldraw any hydrogen akams on coxygen where applicablearrow_forward

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



