
Concept explainers
a) 1 mol Br2 in CH2Cl2
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene reacts with one mole of bromine in CH2Cl2 are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes are treated with bromine in CH2Cl2 undergo both 1,2 and 1,4 addition of bromine to yield different products.
To give:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene reacts with one mole of bromine in CH2Cl2.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene reacts with one mole of bromine in CH2Cl2 are 3,6-dibromocyclohexene and 3,4-dibromocyclohexene.

Explanation of Solution
1,3-cyclohexadiene is a conjugated diene. When treated with one mole of bromine in CH2Cl2 it yields 3,6-dibromocyclohexene by 1,4 addition and 3,4-dibromocyclohexene by 1,2 addition reaction.
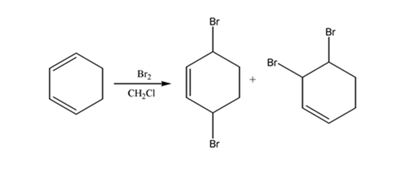
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene reacts with one mole of bromine in CH2Cl2 are 3,6-dibromocyclohexene and 3,4-dibromocyclohexene.

b) O3 followed by Zn
Interpretation:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with ozone followed by zinc is to be given.
Concept introduction:
To give:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with ozone followed by zinc is to be given.
Answer to Problem 27AP
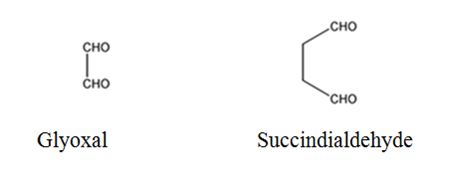
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with ozone followed by zinc are glyoxal and succindialdehyde.
Explanation of Solution
Ozone adds to both the double bonds in 1,3-cyclohexadiene to form an ozonide. When treated with Zn and acetic acid the ozonide breaks to yield carbonyl compounds. The carbons that have oxygen in the products are joined through double bonds in the reactant.
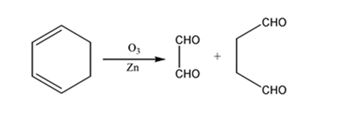
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with ozone followed by zinc are glyoxal and succindialdehyde.

c) 1 mol HCl in ether
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of HCl in ether is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes when treated with one mole of HCl in ether undergo both 1,2 and 1,4 addition of HCl to yield different products. With unsubstituted cyclic conjugated 1,3-dienes a single product is produced in both types of addition.
To give:
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of HCl is to be given.
Answer to Problem 27AP
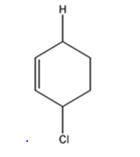
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of HCl is 3-chlorocyclohexene.
Explanation of Solution
Both 1,2 and 1,4 addition of HCl to 1,3-cyclohexadiene leads to the formation of the same product, 3-chlorocyclohexene, as it is an unsubstituted conjugated 1,3-diene.
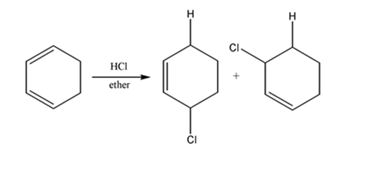
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of HCl is 3-chlorocyclohexene.
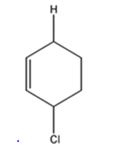
d) 1 mol DCl in ether
Interpretation:
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of DCl are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Conjugated dienes when treated with one mole of DCl in ether undergo both 1,2 and 1,4 addition of DCl to yield different products.
To give:
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of DCl.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of DCl are 3-chloro-4-deuteratedcyclohexene and 3-chloro-6-deuteratedcyclohexene.
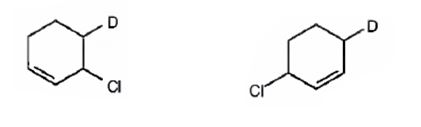
Explanation of Solution
1,3-cyclohexadiene is a conjugated diene. When treated with one mole of DCl it yields 3-chloro-4-deuteratedcyclohexen by 1,2 addition 3-chloro-6-deuteratedcyclohexene by 1,4 addition reaction.
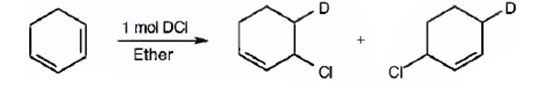
The products expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with one mole of DCl are 3-chloro-4-deuteratedcyclohexene and 3-chloro-6-deuteratedcyclohexene.

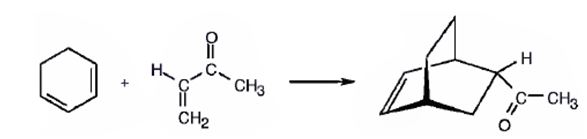
e) 3-Buten-2-one (H2C=CHCOCH3)
Interpretation:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with 3-buten-2-one is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In Diels-Alder reaction, a dienophile reacts with a diene to yield a cyclic adduct. The reaction takes place through 1,4 addition of the dienophile into the diene through a cyclic transition state. During the reaction the diene and dienophile orient themselves on top of one another and so an endo product results.
To give:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with 3-buten-2-one.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with 3-buten-2-one is
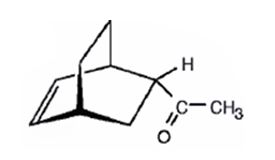
Explanation of Solution
The diene, 1,3-cyclohexadiene and the dienophile 3-buten-2-one arrange themselves one on the top of the other and react through the formation of a cyclic six member transition state to yield the endo product.
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with 3-buten-2-one is
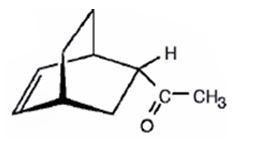
f) Excess OsO4, followed by NaHSO3
Interpretation:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with excess OsO4 and then with NaHSO3 is to be given.
Concept introduction:
The reaction given involves hydroxylation of the double bonds in the diene. When a diene is treated with OsO4, a single step addition of OsO4 to each of the double bonds takes place to give a cyclic osmate. The cyclic osmate gets cleaved when treated with NaHSO3 yields a tetraol.
To give:
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with excess OsO4 and then with NaHSO3.
Answer to Problem 27AP
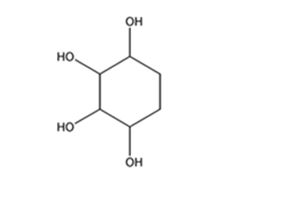
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with excess OsO4 and then with NaHSO3 is cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetraol.
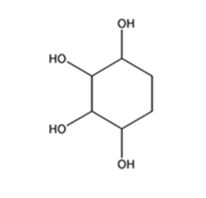
Explanation of Solution
When 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with excess OsO4 the addition of OsO4 takes place to both the double bonds in it. The addition occurs with syn stereochemistry to yield a cyclic osmate. The cyclic osmate then gets cleaved when treated with NaHSO3 to yield the tetraol.
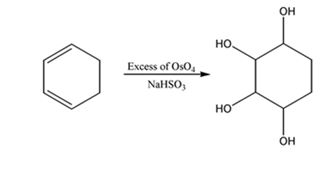
The product expected to be formed when 1,3-cyclohexadiene is treated with excess OsO4 and then with NaHSO3 is cyclohexane-1,2,3,4-tetraol.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration methodarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds faster at temperatures above -48. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) ✓ AS is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below 114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate below 135. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is C This reaction is exothermic and proceeds faster at temperatures above -43. °C. (pick one) AS is (pick one) v Х 5 ? 18 Ararrow_forwardion. A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the perchlorate (CIO) io : :0: : Cl : - - : :0: ك Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure. atom central O formal charge ☐ top O ☐ right O ☐ bottom O ☐ Cl ☐arrow_forward
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Yes. Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Cl- : 2: :Z: :Z: N—N : 0: C C1: O CO No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0". ☑arrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions ΔΗ is (pick one) A This reaction is faster above 103. °C than below. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous only above -9. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) C The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous. AS is (pick one) 18 Ararrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below 41. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 94. °C. AS is (pick one) This reaction is always spontaneous, but ΔΗ is (pick one) C proceeds slower at temperatures below −14. °C. AS is (pick one) Х 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ B 1 1arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + H CH3CH2OH HCI Drawingarrow_forwardplease explain this in simple termsarrow_forwardK Most Reactive Na (3 pts) Can the metal activity series (shown on the right) or a standard reduction potential table explain why potassium metal can be prepared from the reaction of molten KCI and Na metal but sodium metal is not prepared from the reaction of molten NaCl and K metal? Show how (not). Ca Mg Al с Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Least Reactivearrow_forward
- (2 pts) Why is O2 more stable as a diatomic molecule than S2?arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic phosphite (PO¾³¯) a anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. C I A [ ]¯arrow_forwardDecide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. :0: Cl C C1: 0=0: : 0 : : 0 : H C N No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* Yes. ☐ No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0".arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





