
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321947345
Author: William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14.4, Problem 20E
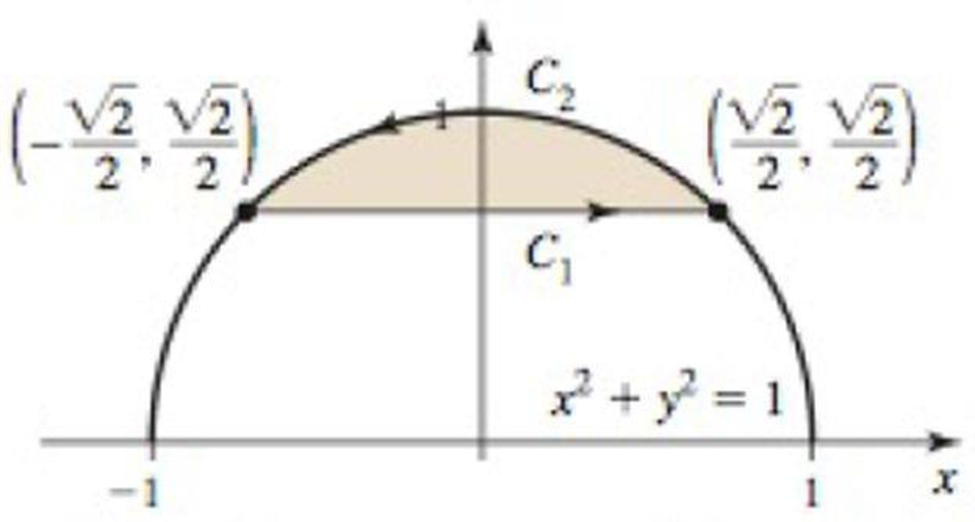
Area of regions Use a line
20. The region shown in the figure
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule06:44
Students have asked these similar questions
Evaluate the triple integral
3'
23
HIG
2
+3
f(x, y, z)dxdydz where f(x, y, z) = x +
2x-y
ม
u =
v =
and w =
2
2
3
Triple Integral
Region R
-2
x
N
2
y
3
Find the volume of the solid bounded below by the circular cone z = 2.5√√√x² + y² and above by the
sphere x² + y²+z² = 6.5z.
Electric charge is distributed over the triangular region D shown below so that the charge density at (x, y)
is σ(x, y) = 4xy, measured in coulumbs per square meter (C/m²). Find the total charge on D. Round
your answer to four decimal places.
1
U
5
4
3
2
1
1
2
5
7
coulumbs
Chapter 14 Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Ch. 14.1 - How is a vector field F = f, g, h used to describe...Ch. 14.1 - Sketch the vector field F = x, y.Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 3ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 4ECh. 14.1 - Interpret the gradient field of the temperature...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...
Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Two-dimensional vector fields Sketch the following...Ch. 14.1 - Matching vector Fields with graphs Match vector...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 17ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 18ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 19ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 20ECh. 14.1 - Three-dimensional vector fields Sketch a few...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 14.1 - Three-dimensional vector fields Sketch a few...Ch. 14.1 - Three-dimensional vector fields Sketch a few...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Gradient fields Find the gradient field F = for...Ch. 14.1 - Equipotential curves Consider the following...Ch. 14.1 - Equipotential curves Consider the following...Ch. 14.1 - Equipotential curves Consider the following...Ch. 14.1 - Equipotential curves Consider the following...Ch. 14.1 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 42ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 43ECh. 14.1 - Design your own vector field Specify the component...Ch. 14.1 - Design your own vector field Specify the component...Ch. 14.1 - Design your own vector field Specify the component...Ch. 14.1 - Design your own vector field Specify the component...Ch. 14.1 - Electric field due to a point charge The electric...Ch. 14.1 - Electric field due to a line of charge The...Ch. 14.1 - Gravitational force due to a mass The...Ch. 14.1 - Flow curves in the plane Let...Ch. 14.1 - Flow curves in the plane Let...Ch. 14.1 - Flow curves in the plane Let...Ch. 14.1 - Flow curves in the plane Let...Ch. 14.1 - Flow curves in the plane Let...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 56ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 57ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 58ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 59ECh. 14.1 - Prob. 60ECh. 14.1 - Cartesian-to-polar vector field Write the vector...Ch. 14.2 - How does a line integral differ from the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 14.2 - If a curve C is given by r(t) = t, t2, what is...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 7ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 9ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 10ECh. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals with arc length as parameter...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 12ECh. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals with arc length as parameter...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 14ECh. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in the plane a.Find a...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 16ECh. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in the plane a.Find a...Ch. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in the plane a.Find a...Ch. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in the plane a.Find a...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 20ECh. 14.2 - Average values Find the average value of the...Ch. 14.2 - Average values Find the average value of the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 23ECh. 14.2 - Average values Find the average value of the...Ch. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in 3Convert the line...Ch. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in 3Convert the line...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 27ECh. 14.2 - Scalar line integrals in 3Convert the line...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 29ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 30ECh. 14.2 - Length of curves Use a scalar line integral to...Ch. 14.2 - Length of curves Use a scalar line integral to...Ch. 14.2 - Line integrals of vector fields in the plane Given...Ch. 14.2 - Line integrals of vector fields in the plane Given...Ch. 14.2 - Line integrals of vector fields in the plane Given...Ch. 14.2 - Line integrals of vector fields in the plane Given...Ch. 14.2 - Line integrals of vector fields in the plane Given...Ch. 14.2 - Line integrals of vector fields in the plane Given...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals Given the force field F, find the...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals Given the force field F, find the...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals Given the force field F, find the...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals Given the force field F, find the...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals in 3 Given the force field F, find...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals in 3 Given the force field F, find...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals in 3 Given the force field F, find...Ch. 14.2 - Work integrals in 3 Given the force field F, find...Ch. 14.2 - Circulation Consider the following vector fields F...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 48ECh. 14.2 - Flux Consider the vector fields and curves in...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 50ECh. 14.2 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.2 - Flying into a headwind An airplane flies in the...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 53ECh. 14.2 - Prob. 54ECh. 14.2 - Changing orientation Let f(x, y) = x and let C be...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 56ECh. 14.2 - Zero circulation fields 57.Consider the vector...Ch. 14.2 - Zero flux fields 58.For what values of a and d...Ch. 14.2 - Zero flux fields 59.Consider the vector field F =...Ch. 14.2 - Work in a rotation field Consider the rotation...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 61ECh. 14.2 - Mass and density A thin wire represented by the...Ch. 14.2 - Mass and density A thin wire represented by the...Ch. 14.2 - Heat flux in a plate A square plate R = {(x, y): 0...Ch. 14.2 - Prob. 65ECh. 14.2 - Flux across curves in a vector field Consider the...Ch. 14.2 - Looking ahead: Area from line integrals The area...Ch. 14.2 - Looking ahead: Area from line integrals The area...Ch. 14.3 - What does it mean for a function to have an...Ch. 14.3 - What are local maximum and minimum values of a...Ch. 14.3 - What conditions must be met to ensure that a...Ch. 14.3 - How do you determine whether a vector field in 3...Ch. 14.3 - Briefly describe how to find a potential function ...Ch. 14.3 - If F is a conservative vector field on a region R,...Ch. 14.3 - If F is a conservative vector field on a region R,...Ch. 14.3 - Give three equivalent properties of conservative...Ch. 14.3 - How do you determine the absolute maximum and...Ch. 14.3 - Explain how a function can have an absolute...Ch. 14.3 - Testing for conservative vector fields Determine...Ch. 14.3 - Testing for conservative vector fields Determine...Ch. 14.3 - Testing for conservative vector fields Determine...Ch. 14.3 - Testing for conservative vector fields Determine...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Designing a function Sketch a graph of a function...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 20ECh. 14.3 - Designing a function Sketch a graph of a function...Ch. 14.3 - Designing a function Sketch a graph of a function...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Finding potential functions Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 28ECh. 14.3 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14.3 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14.3 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14.3 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals of vector fields on closed curves...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals of vector fields on closed curves...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals of vector fields on closed curves...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals of vector fields on closed curves...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals of vector fields on closed curves...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals of vector fields on closed curves...Ch. 14.3 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals Evaluate each line integral using a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 41ECh. 14.3 - Line integrals Evaluate each line integral using a...Ch. 14.3 - Line integrals Evaluate each line integral using a...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 44ECh. 14.3 - Work in force fields Find the work required to...Ch. 14.3 - Work in force fields Find the work required to...Ch. 14.3 - Work in force fields Find the work required to...Ch. 14.3 - Work in force fields Find the work required to...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 49ECh. 14.3 - Prob. 50ECh. 14.3 - Prob. 51ECh. 14.3 - Conservation of energy Suppose an object with mass...Ch. 14.3 - Gravitational potential The gravitational force...Ch. 14.3 - Radial Fields in 3 are conservative Prove that the...Ch. 14.3 - 55.Rotation fields are usually not conservative...Ch. 14.3 - Linear and quadratic vector fields a.For what...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 57ECh. 14.3 - Prob. 58ECh. 14.3 - Prob. 59ECh. 14.3 - Alternative construction of potential functions...Ch. 14.3 - Prob. 61ECh. 14.4 - Explain why the two forms of Greens Theorem are...Ch. 14.4 - Referring to both forms of Greens Theorem, match...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 3ECh. 14.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 14.4 - Prob. 5ECh. 14.4 - Why does a two-dimensional vector field with zero...Ch. 14.4 - Why does a two-dimensional vector field with zero...Ch. 14.4 - Sketch a two-dimensional vector field that has...Ch. 14.4 - Sketch a two-dimensional vector field that has...Ch. 14.4 - Discuss one of the parallels between a...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, circulation form Consider the...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, circulation form Consider the...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, circulation form Consider the...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, circulation form Consider the...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 16ECh. 14.4 - Area of regions Use a line integral on the...Ch. 14.4 - Area of regions Use a line integral on the...Ch. 14.4 - Area of regions Use a line integral on the...Ch. 14.4 - Area of regions Use a line integral on the...Ch. 14.4 - Area of regions Use a line integral on the...Ch. 14.4 - Area of regions Use a line integral on the...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, flux form Consider the following...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 24ECh. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, flux form Consider the following...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, flux form Consider the following...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, flux form Consider the following...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem, flux form Consider the following...Ch. 14.4 - Line integrals Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the...Ch. 14.4 - Line integrals Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 31ECh. 14.4 - Line integrals Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 33ECh. 14.4 - Line integrals Use Greens Theorem to evaluate the...Ch. 14.4 - General regions For the following vector fields,...Ch. 14.4 - General regions For the following vector fields,...Ch. 14.4 - General regions For the following vector fields,...Ch. 14.4 - General regions For the following vector fields,...Ch. 14.4 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.4 - Circulation and flux For the following vector...Ch. 14.4 - Circulation and flux For the following vector...Ch. 14.4 - Circulation and flux For the following vector...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 43ECh. 14.4 - Special line integrals Prove the following...Ch. 14.4 - Special line integrals Prove the following...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 46ECh. 14.4 - Area line integral Show that the value of...Ch. 14.4 - Area line integral In terms of the parameters a...Ch. 14.4 - Stream function Recall that if the vector field F...Ch. 14.4 - Stream function Recall that if the vector field F...Ch. 14.4 - Stream function Recall that if the vector field F...Ch. 14.4 - Stream function Recall that if the vector field F...Ch. 14.4 - Applications 5356. Ideal flow A two-dimensional...Ch. 14.4 - Applications 5356. Ideal flow A two-dimensional...Ch. 14.4 - Applications 5356. Ideal flow A two-dimensional...Ch. 14.4 - Applications 5356. Ideal flow A two-dimensional...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 57ECh. 14.4 - Greens Theorem as a Fundamental Theorem of...Ch. 14.4 - Greens Theorem as a Fundamental Theorem of...Ch. 14.4 - Whats wrong? Consider the rotation field...Ch. 14.4 - Whats wrong? Consider the radial field...Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 62ECh. 14.4 - Flux integrals Assume the vector field F = (f, g)...Ch. 14.4 - Streamlines are tangent to the vector field Assume...Ch. 14.4 - Streamlines and equipotential lines Assume that on...Ch. 14.4 - Channel flow The flow in a long shallow channel is...Ch. 14.5 - Explain how to compute the divergence of the...Ch. 14.5 - Interpret the divergence of a vector field.Ch. 14.5 - What does it mean if the divergence of a vector...Ch. 14.5 - Explain how to compute the curl of the vector...Ch. 14.5 - Interpret the curl of a general rotation vector...Ch. 14.5 - What does it mean if the curl of a vector field is...Ch. 14.5 - What is the value of ( F)?Ch. 14.5 - What is the value of u?Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of vector fields Find the divergence of...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence of radial fields Calculate the...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 18ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 19ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 20ECh. 14.5 - Divergence and flux from graphs Consider the...Ch. 14.5 - Divergence and flux from graphs Consider the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a rotational field Consider the following...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a rotational field Consider the following...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a rotational field Consider the following...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a rotational field Consider the following...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Curl of a vector field Compute the curl of the...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 35ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 36ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 37ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 38ECh. 14.5 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.5 - Another derivative combination Let F = (f, g, h)...Ch. 14.5 - Does it make sense? Are the following expressions...Ch. 14.5 - Zero divergence of the rotation field Show that...Ch. 14.5 - General rotation fields a.Let a = (0, 1, 0), r =...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 44ECh. 14.5 - Curl of the rotation field For the general...Ch. 14.5 - Inward to outward Find the exact points on the...Ch. 14.5 - Maximum divergence Within the cube {(x, y, z): |x|...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 48ECh. 14.5 - Zero component of the curl For what vectors n is...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 50ECh. 14.5 - Find a vector Field Find a vector field F with the...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 52ECh. 14.5 - Paddle wheel in a vector field Let F = z, 0, 0 and...Ch. 14.5 - Angular speed Consider the rotational velocity...Ch. 14.5 - Angular speed Consider the rotational velocity...Ch. 14.5 - Heat flux Suppose a solid object in 3 has a...Ch. 14.5 - Heat flux Suppose a solid object in 3 has a...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 58ECh. 14.5 - Gravitational potential The potential function for...Ch. 14.5 - Electric potential The potential function for the...Ch. 14.5 - Navier-Stokes equation The Navier-Stokes equation...Ch. 14.5 - Stream function and vorticity The rotation of a...Ch. 14.5 - Amperes Law One of Maxwells equations for...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 64ECh. 14.5 - Properties of div and curl Prove the following...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 66ECh. 14.5 - Identities Prove the following identities. Assume...Ch. 14.5 - Identities Prove the following identities. Assume...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 69ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 70ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 71ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 72ECh. 14.5 - Prob. 73ECh. 14.5 - Gradients and radial fields Prove that for a real...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 75ECh. 14.6 - Give a parametric description for a cylinder with...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 2ECh. 14.6 - Give a parametric description for a sphere with...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 4ECh. 14.6 - Explain how to compute the surface integral of a...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 6ECh. 14.6 - Prob. 7ECh. 14.6 - Explain what it means for a surface to be...Ch. 14.6 - Describe the usual orientation of a closed surface...Ch. 14.6 - Why is the upward flux of a vertical vector field...Ch. 14.6 - Parametric descriptions Give a parametric...Ch. 14.6 - Parametric descriptions Give a parametric...Ch. 14.6 - Parametric descriptions Give a parametric...Ch. 14.6 - Parametric descriptions Give a parametric...Ch. 14.6 - Parametric descriptions Give a parametric...Ch. 14.6 - Parametric descriptions Give a parametric...Ch. 14.6 - Identify the surface Describe the surface with the...Ch. 14.6 - Identify the surface Describe the surface with the...Ch. 14.6 - Identify the surface Describe the surface with the...Ch. 14.6 - Identify the surface Describe the surface with the...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using a parametric description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using a parametric description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using a parametric description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using a parametric description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using a parametric description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using a parametric description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals using a parametric description...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals using a parametric description...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals using a parametric description...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals using a parametric description...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using an explicit description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area using an explicit description Find...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 33ECh. 14.6 - Prob. 34ECh. 14.6 - Surface integrals using an explicit description...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 36ECh. 14.6 - Surface integrals using an explicit description...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals using an explicit description...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 39ECh. 14.6 - Average values 40.Find the average squared...Ch. 14.6 - Average values 41.Find the average value of the...Ch. 14.6 - Average values 42.Find the average value of the...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals of vector fields Find the flux...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals of vector fields Find the flux...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals of vector fields Find the flux...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals of vector fields Find the flux...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals of vector fields Find the flux...Ch. 14.6 - Surface integrals of vector fields Find the flux...Ch. 14.6 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.6 - Miscellaneous surface integrals Evaluate the...Ch. 14.6 - Miscellaneous surface integrals Evaluate the...Ch. 14.6 - Miscellaneous surface integrals Evaluate the...Ch. 14.6 - Miscellaneous surface integrals Evaluate the...Ch. 14.6 - Cone and sphere The cone z2 = x2 + y2 for z 0,...Ch. 14.6 - Cylinder and sphere Consider the sphere x2 + y2 +...Ch. 14.6 - Flux on a tetrahedron Find the upward flux of the...Ch. 14.6 - Flux across a cone Consider the field F = x, y, z...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area formula for cones Find the general...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area formula for spherical cap A sphere of...Ch. 14.6 - Radial fields and spheres Consider the radial...Ch. 14.6 - Heat flux The heat flow vector field for...Ch. 14.6 - Heat flux The heat flow vector field for...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 63ECh. 14.6 - Flux across a cylinder Let S be the cylinder x2 +...Ch. 14.6 - Flux across concentric spheres Consider the radial...Ch. 14.6 - Mass and center of mass Let S be a surface that...Ch. 14.6 - Mass and center of mass Let S be a surface that...Ch. 14.6 - Mass and center of mass Let S be a surface that...Ch. 14.6 - Mass and center of mass Let S be a surface that...Ch. 14.6 - Outward normal to a sphere Show that...Ch. 14.6 - Special case of surface integrals of scalar-valued...Ch. 14.6 - Surfaces of revolution Suppose y = f(x) is a...Ch. 14.6 - Rain on roofs Let z = s(x, y) define a surface...Ch. 14.6 - Surface area of a torus a.Show that a torus with...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 75ECh. 14.7 - Explain the meaning of the integral S(F)ndS in...Ch. 14.7 - Explain the meaning of the integral S(F)ndS in...Ch. 14.7 - Explain the meaning of Stokes Theorem.Ch. 14.7 - Why does a conservative vector field produce zero...Ch. 14.7 - Verifying Stokes Theorem Verify that the line...Ch. 14.7 - Verifying Stokes Theorem Verify that the line...Ch. 14.7 - Verifying Stokes Theorem Verify that the line...Ch. 14.7 - Verifying Stokes Theorem Verify that the line...Ch. 14.7 - Verifying Stokes Theorem Verify that the line...Ch. 14.7 - Verifying Stokes Theorem Verify that the line...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating line integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating line integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating line integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating line integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating line integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating line integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating surface integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating surface integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating surface integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem for evaluating surface integrals...Ch. 14.7 - Interpreting and graphing the curl For the...Ch. 14.7 - Interpreting and graphing the curl For the...Ch. 14.7 - Interpreting and graphing the curl For the...Ch. 14.7 - Interpreting and graphing the curl For the...Ch. 14.7 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.7 - Conservative fields Use Stokes Theorem to find the...Ch. 14.7 - Conservative fields Use Stokes Theorem to find the...Ch. 14.7 - Conservative fields Use Stokes Theorem to find the...Ch. 14.7 - Conservative fields Use Stokes Theorem to find the...Ch. 14.7 - Tilted disks Let S be the disk enclosed by the...Ch. 14.7 - Tilted disks Let S be the disk enclosed by the...Ch. 14.7 - Tilted disks Let S be the disk enclosed by the...Ch. 14.7 - Tilted disks Let S be the disk enclosed by the...Ch. 14.7 - Prob. 34ECh. 14.7 - Circulation in a plane A circle C in the plane x +...Ch. 14.7 - No integrals Let F = (2z, z, 2y + x) and let S be...Ch. 14.7 - Compound surface and boundary Begin with the...Ch. 14.7 - Ampres Law The French physicist AndrMarie Ampre...Ch. 14.7 - Maximum surface integral Let S be the paraboloid z...Ch. 14.7 - Area of a region in a plane Let R be a region in a...Ch. 14.7 - Choosing a more convenient surface The goal is to...Ch. 14.7 - Radial fields and zero circulation Consider the...Ch. 14.7 - Zero curl Consider the vector field...Ch. 14.7 - Average circulation Let S be a small circular disk...Ch. 14.7 - Proof of Stokes Theorem Confirm the following step...Ch. 14.7 - Stokes Theorem on closed surfaces Prove that if F...Ch. 14.7 - Rotated Greens Theorem Use Stokes Theorem to write...Ch. 14.8 - Review Questions 1.Explain the meaning of the...Ch. 14.8 - Interpret the volume integral in the Divergence...Ch. 14.8 - Explain the meaning of the Divergence Theorem.Ch. 14.8 - What is the net outward flux of the rotation field...Ch. 14.8 - What is the net outward flux of the radial field F...Ch. 14.8 - What is the divergence of an inverse square vector...Ch. 14.8 - Suppose div F = 0 in a region enclosed by two...Ch. 14.8 - If div F 0 in a region enclosed by a small cube,...Ch. 14.8 - Verifying the Divergence Theorem Evaluate both...Ch. 14.8 - F = x, y, z; D = {(x, y, z): |x| 1, |y| 1, |z| ...Ch. 14.8 - Basic Skills 912.Verifying the Divergence Theorem...Ch. 14.8 - F = x2, y2, z2; D = {(x, y, z): |x| 1, |y| 2,...Ch. 14.8 - Rotation fields 13.Find the net outward flux of...Ch. 14.8 - Rotation fields 14.Find the net outward flux of...Ch. 14.8 - Find the net outward flux of the field F = bz cy,...Ch. 14.8 - Rotation fields 16.Find the net outward flux of F...Ch. 14.8 - Computing flux Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14.8 - Computing flux Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14.8 - F = x, 2y, z; S is the boundary of the tetrahedron...Ch. 14.8 - Computing flux Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14.8 - F = y 2x, x3 y, y2 z; S is the sphere {(x, y,...Ch. 14.8 - Computing flux Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14.8 - Computing flux Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14.8 - Computing flux Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14.8 - Divergence Theorem for more general regions Use...Ch. 14.8 - Divergence Theorem for more general regions Use...Ch. 14.8 - Divergence Theorem for more general regions Use...Ch. 14.8 - Divergence Theorem for more general regions Use...Ch. 14.8 - F = x2, y2, z2); D is the region in the first...Ch. 14.8 - Divergence Theorem for more general regions Use...Ch. 14.8 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14.8 - Flux across a sphere Consider the radial field F =...Ch. 14.8 - Flux integrals Compute the outward flux of the...Ch. 14.8 - Flux integrals Compute the outward flux of the...Ch. 14.8 - Flux integrals Compute the outward flux of the...Ch. 14.8 - Prob. 36ECh. 14.8 - Singular radial field Consider the radial field...Ch. 14.8 - Logarithmic potential Consider the potential...Ch. 14.8 - Gauss Law for electric fields The electric field...Ch. 14.8 - Gauss Law for gravitation The gravitational force...Ch. 14.8 - Heat transfer Fouriers Law of heat transfer (or...Ch. 14.8 - Heat transfer Fouriers Law of heat transfer (or...Ch. 14.8 - Heat transfer Fouriers Law of heat transfer (or...Ch. 14.8 - Heat transfer Fouriers Law of heat transfer (or...Ch. 14.8 - Heat transfer Fouriers Law of heat transfer (or...Ch. 14.8 - Inverse square fields are special Let F be a...Ch. 14.8 - A beautiful flux integral Consider the potential...Ch. 14.8 - Integration by parts (Gauss' Formula) Recall the...Ch. 14.8 - Prob. 49ECh. 14.8 - Prob. 50ECh. 14.8 - Greens Second Identity Prose Greens Second...Ch. 14.8 - Prob. 52ECh. 14.8 - Prob. 53ECh. 14.8 - Prob. 54ECh. 14 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 14 - Matching vector fields Match vector fields a-f...Ch. 14 - Gradient fields in 2 Find the vector field F = ...Ch. 14 - Gradient fields in 2 Find the vector field F = ...Ch. 14 - Gradient fields in 3 Find the vector field F = ...Ch. 14 - Gradient fields in 3 Find the vector field F = ...Ch. 14 - Normal component Let C be the circle of radius 2...Ch. 14 - Line integrals Evaluate the following line...Ch. 14 - Prob. 9RECh. 14 - Line integrals Evaluate the following line...Ch. 14 - Two parameterizations Verify that C(x2y+3z)ds has...Ch. 14 - Work integral Find the work done in moving an...Ch. 14 - Work integrals in R3 Given the following force...Ch. 14 - Work integrals in 3 Given the following force...Ch. 14 - Circulation and flux Find the circulation and the...Ch. 14 - Circulation and flux Find the circulation and the...Ch. 14 - Circulation and flux Find the circulation and the...Ch. 14 - Circulation and flux Find the circulation and the...Ch. 14 - Flux in channel flow Consider the flow of water in...Ch. 14 - Conservative vector fields and potentials...Ch. 14 - Conservative vector fields and potentials...Ch. 14 - Conservative vector fields and potentials...Ch. 14 - Conservative vector fields and potentials...Ch. 14 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14 - Evaluating line integrals Evaluate the line...Ch. 14 - Radial fields in R2 are conservative Prove that...Ch. 14 - Greens Theorem for line integrals Use either form...Ch. 14 - Greens Theorem for line integrals Use either form...Ch. 14 - Greens Theorem for line integrals Use either form...Ch. 14 - Greens Theorem for line integrals Use either form...Ch. 14 - Areas of plane regions Find the area of the...Ch. 14 - Areas of plane regions Find the area of the...Ch. 14 - Circulation and flux Consider the following vector...Ch. 14 - Circulation and flux Consider the following vector...Ch. 14 - Parameters Let F = ax + by, cx + dy, where a, b,...Ch. 14 - Divergence and curl Compute the divergence and...Ch. 14 - Divergence and curl Compute the divergence and...Ch. 14 - Divergence and curl Compute the divergence and...Ch. 14 - Divergence and curl Compute the divergence and...Ch. 14 - Identities Prove that (1|r|4)=4r|r|6 and use the...Ch. 14 - Prob. 43RECh. 14 - Paddle wheel in a vector field Let F = 0, 2x, 0...Ch. 14 - Surface areas Use a surface integral to find the...Ch. 14 - Surface areas Use a surface integral to find the...Ch. 14 - Surface areas Use a surface integral to find the...Ch. 14 - Surface areas Use a surface integral to find the...Ch. 14 - Surface integrals Evaluate the following surface...Ch. 14 - Surface integrals Evaluate the following surface...Ch. 14 - Surface integrals Evaluate the following surface...Ch. 14 - Flux integrals Find the flux of the following...Ch. 14 - Flux integrals Find the flux of the following...Ch. 14 - Three methods Find the surface area of the...Ch. 14 - Flux across hemispheres and paraboloids Let S be...Ch. 14 - Surface area of an ellipsoid Consider the...Ch. 14 - Stokes Theorem for line integrals Evaluate the...Ch. 14 - Stokes Theorem for line integrals Evaluate the...Ch. 14 - Stokes Theorem for surface integrals Use Stokes...Ch. 14 - Stokes Theorem for surface integrals Use Stokes...Ch. 14 - Conservative fields Use Stokes Theorem to find the...Ch. 14 - Computing fluxes Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14 - Computing fluxes Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14 - Computing fluxes Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14 - General regions Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14 - General regions Use the Divergence Theorem to...Ch. 14 - Flux integrals Compute the outward flux of the...Ch. 14 - Stokes Theorem on a compound surface Consider the...
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
If n is a counting number, bn, read______, indicates that there are n factors of b. The number b is called the_...
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Two fair dice are rolled. What is the conditional probability that at least one lands on 6 given that the dice ...
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Children of First Ladies This list represents the number of children for the first six “first ladies” of the Un...
Introductory Statistics
For a population containing N=902 individual, what code number would you assign for a. the first person on the ...
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
3. Voluntary Response Sample What is a voluntary response sample, and why is such a sample generally not suitab...
Elementary Statistics
1. How many solutions are there to ax + b = 0 with ?
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let E be the region bounded cone z = √√/6 - (x² + y²) and the sphere z = x² + y² + z² . Provide an answer accurate to at least 4 significant digits. Find the volume of E. Triple Integral Spherical Coordinates Cutout of sphere is for visual purposes 0.8- 0.6 z 04 0.2- 0- -0.4 -0.2 04 0 0.2 0.2 x -0.2 04 -0.4 Note: The graph is an example. The scale and equation parameters may not be the same for your particular problem. Round your answer to 4 decimal places. Hint: Solve the cone equation for phi. * Oops - try again.arrow_forwardThe temperature at a point (x,y,z) of a solid E bounded by the coordinate planes and the plane 9.x+y+z = 1 is T(x, y, z) = (xy + 8z +20) degrees Celcius. Find the average temperature over the solid. (Answer to 4 decimal places). Average Value of a function using 3 variables z 1- y Hint: y = -a·x+1 * Oops - try again. xarrow_forwardFind the saddle pointsarrow_forward
- For the curve defined by r(t) = (e** cos(t), et sin(t)) find the unit tangent vector, unit normal vector, normal acceleration, and tangential acceleration at t = πT 3 T (1) N Ň (1) 133 | aN = 53 ar = = =arrow_forwardFind the tangential and normal components of the acceleration vector for the curve - F(t) = (2t, −3t³, −3+¹) at the point t = 1 - ā(1) = T + Ñ Give your answers to two decimal placesarrow_forwardFind the unit tangent vector to the curve defined by (t)=(-2t,-4t, √√49 - t²) at t = −6. T(−6) =arrow_forward
- An airplane flies due west at an airspeed of 428 mph. The wind blows in the direction of 41° south of west at 50 mph. What is the ground speed of the airplane? What is the bearing of the airplane? 428 mph 41° 50 mph a. The ground speed of the airplane is b. The bearing of the airplane is mph. south of west.arrow_forwardRylee's car is stuck in the mud. Roman and Shanice come along in a truck to help pull her out. They attach one end of a tow strap to the front of the car and the other end to the truck's trailer hitch, and the truck starts to pull. Meanwhile, Roman and Shanice get behind the car and push. The truck generates a horizontal force of 377 lb on the car. Roman and Shanice are pushing at a slight upward angle and generate a force of 119 lb on the car. These forces can be represented by vectors, as shown in the figure below. The angle between these vectors is 20.2°. Find the resultant force (the vector sum), then give its magnitude and its direction angle from the positive x-axis. 119 lb 20.2° 377 lb a. The resultant force is (Tip: omit degree notations from your answers; e.g. enter cos(45) instead of cos(45°)) b. It's magnitude is lb. c. It's angle from the positive x-axis isarrow_forwardFind a plane containing the point (3, -3, 1) and the line of intersection of the planes 2x + 3y - 3z = 14 and -3x - y + z = −21. The equation of the plane is:arrow_forward
- Determine whether the lines L₁ : F(t) = (−2, 3, −1)t + (0,2,-3) and L2 : ƒ(s) = (2, −3, 1)s + (−10, 17, -8) intersect. If they do, find the point of intersection. ● They intersect at the point They are skew lines They are parallel or equalarrow_forwardAnswer questions 2arrow_forwardHow does a fourier transform works?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL  Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 1 | Geometric Idea + Chain Rule Example; Author: Dr. Trefor Bazett;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hAfpl8jLFOs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY