
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 95SCQ
Examine the reaction coordinate diagram given here.
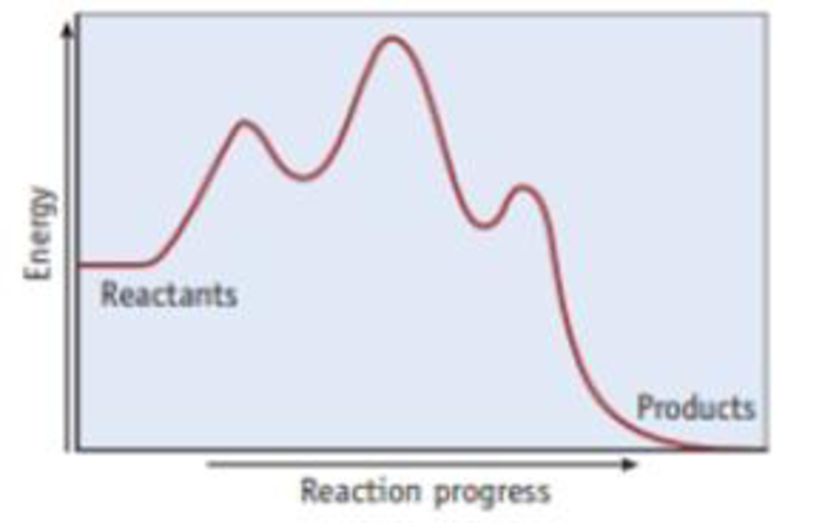
- (a) How many steps are in the mechanism for the reaction described by this diagram?
- (b) Is the reaction overall exothermic or endothermic?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Basic strength of organic bases.
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? What is the name of the intermediate complex? *See image
Predict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor” *see attached
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Ch. 14.1 - Sucrose decomposes to fructose and glucose in acid...Ch. 14.1 - What are the relative rates of appearance or...Ch. 14.1 - Prob. 1RCCh. 14.1 - 2. Use the graph provided in Example 14.1 to...Ch. 14.2 - 1. Which of the following will not usually...Ch. 14.3 - The initial rate ( [NO]/ t] of the reaction of...Ch. 14.3 - The rate constant, k, at 25 C is 0.27/h for the...Ch. 14.3 - The reaction NO(g) + 1/2 Cl2(g) NOCl(g) is...Ch. 14.4 - Sucrose, a sugar, decomposes in acid solution to...Ch. 14.4 - Gaseous azomethane (CH3N2CH3) decomposes to ethane...
Ch. 14.4 - Prob. 3CYUCh. 14.4 - The catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide...Ch. 14.4 - Americium is used in smoke detectors and in...Ch. 14.4 - The decomposition of N2O5 is a first-order...Ch. 14.4 - Which of the following will confirm that the...Ch. 14.4 - 3. The equation for the decomposition of NO2(g) at...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 1CYUCh. 14.5 - The colorless gas N2O4, decomposes to the brown...Ch. 14.5 - Prob. 1RCCh. 14.5 - Prob. 2RCCh. 14.6 - Nitrogen monoxide is reduced by hydrogen to give...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 2CYUCh. 14.6 - One possible mechanism for the decomposition of...Ch. 14.6 - The rate equation for a reaction A + B C was...Ch. 14.6 - A reaction is believed to occur by the following...Ch. 14.6 - Prob. 1QCh. 14.6 - Prob. 2QCh. 14.6 - Prob. 3QCh. 14.6 - Prob. 4QCh. 14.6 - Prob. 5QCh. 14.6 - Determine the activation energy for the reaction...Ch. 14 - Give the relative rates of disappearance of...Ch. 14 - Give the relative rates of disappearance of...Ch. 14 - In the reaction 2 O3(g) 3 O2(g), the rate of...Ch. 14 - In the synthesis of ammonia, if [H2]/t = 4.5 104...Ch. 14 - Experimental data are listed here for the reaction...Ch. 14 - 6. Phenyl acetate, an ester, reacts with water...Ch. 14 - Using the rate equation Rate = k[A]2[B], define...Ch. 14 - A reaction has the experimental rate equation Rate...Ch. 14 - The reaction between ozone and nitrogen dioxide at...Ch. 14 - Nitrosyl bromide, NOBr, is formed from NO and Br2:...Ch. 14 - The data in the table are for the reaction of NO...Ch. 14 - The reaction 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) N2(g) + 2 H2O(g)...Ch. 14 - Data for the reaction NO(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) are...Ch. 14 - Data for the following reaction are given in the...Ch. 14 - The rate equation for the hydrolysis of sucrose to...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of N2O5 in CCl4 is a first-order...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of SO2Cl2 is a first-order...Ch. 14 - The conversion of cyclopropane to propene (Example...Ch. 14 - Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2(aq), decomposes to H2O()...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of nitrogen dioxide at a high...Ch. 14 - At 573 K, gaseous NO2(g) decomposes, forming NO(g)...Ch. 14 - The dimerization of butadiene, C4H6, to form...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of ammonia on a metal surface to...Ch. 14 - Hydrogen iodide decomposes when heated, forming...Ch. 14 - The rate equation for the decomposition of N2O5...Ch. 14 - Gaseous azomethane, CH3N=NCH3, decomposes in a...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of SO2Cl2 SO2Cl2(g) SO2(g) +...Ch. 14 - The compound Xe(CF3)2 decomposes in a first-order...Ch. 14 - The radioactive isotope 64Cu is used in the form...Ch. 14 - Radioactive gold-198 is used in the diagnosis of...Ch. 14 - Prob. 31PSCh. 14 - Ammonia decomposes when heated according to the...Ch. 14 - Gaseous NO2 decomposes at 573 K. NO2(g) NO(g) + ...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of HOF occurs at 25 C. HOF(g) ...Ch. 14 - Prob. 35PSCh. 14 - Prob. 36PSCh. 14 - Calculate the activation energy, Ea, for the...Ch. 14 - If the rate constant for a reaction triples when...Ch. 14 - When healed lo a high temperature, cyclobutane,...Ch. 14 - When heated, cyclopropane is converted to propene...Ch. 14 - The reaction of H2 molecules with F atoms H2(g) +...Ch. 14 - Prob. 42PSCh. 14 - What is the rate law for each of the following...Ch. 14 - What is the rate law for each of the following...Ch. 14 - Ozone, O3, in the Earths upper atmosphere...Ch. 14 - The reaction of NO2(g) and CO(g) is thought to...Ch. 14 - A proposed mechanism for the reaction of NO2 and...Ch. 14 - The mechanism for the reaction of CH3OH and HBr is...Ch. 14 - A reaction has the following experimental rate...Ch. 14 - For a first-order reaction, what fraction of...Ch. 14 - Prob. 51GQCh. 14 - Data for the following reaction are given in the...Ch. 14 - Formic acid decomposes at 550 C according to the...Ch. 14 - Isomerization of CH3NC occurs slowly when CH3NC is...Ch. 14 - When heated, tetrafluoroethylene dimerizes to form...Ch. 14 - Data in the table were collected at 540 K for the...Ch. 14 - Ammonium cyanate, NH4NCO, rearranges in water to...Ch. 14 - Prob. 58GQCh. 14 - At temperatures below 500 K, the reaction between...Ch. 14 - Nitryl fluoride can be made by treating nitrogen...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of dinitrogen pentaoxide N2O5(g)...Ch. 14 - The data in the table give the temperature...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of gaseous dimethyl ether at...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of phosphine, PH3, proceeds...Ch. 14 - The thermal decomposition of diacetylene, C4H2,...Ch. 14 - Prob. 66GQCh. 14 - The ozone in the Earths ozone layer decomposes...Ch. 14 - Hundreds of different reactions occur in the...Ch. 14 - Data for the reaction [Mn(CO)5(CH3CN)]+ + NC5H5 ...Ch. 14 - The gas-phase reaction 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + O2(g)...Ch. 14 - Prob. 71GQCh. 14 - The decomposition of SO2Cl2 to SO2 and Cl2 is...Ch. 14 - The decomposition of nitrogen dioxide at a high...Ch. 14 - Prob. 74GQCh. 14 - Egg protein albumin is precipitated when an egg is...Ch. 14 - A The compound 1,3-butadiene (C4H6) forms...Ch. 14 - Hypofluorous acid, HOF, is very unstable,...Ch. 14 - We know that the decomposition of SO2Cl2 is...Ch. 14 - Nitramide, NO2NH2, decomposes slowly in aqueous...Ch. 14 - Prob. 80GQCh. 14 - Prob. 83ILCh. 14 - Prob. 84ILCh. 14 - The oxidation of iodide ion by the hypochlorite...Ch. 14 - The acid-catalyzed iodination of acetone...Ch. 14 - Prob. 87SCQCh. 14 - The following statements relate to the reaction...Ch. 14 - Chlorine atoms contribute to the destruction of...Ch. 14 - Prob. 91SCQCh. 14 - Prob. 92SCQCh. 14 - The reaction cyclopropane propene occurs on a...Ch. 14 - Prob. 94SCQCh. 14 - Examine the reaction coordinate diagram given...Ch. 14 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for an...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Some people consider Pasteur or Koch to be the Father of Microbiology, rather than Leeuwenhoek. Why might they ...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
11. In the early 1800s, French naturalist Jean Baptiste Lamarck suggested that the best explanation for the rel...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
The validity of a scientific law.
Physical Universe
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardThe answer here says that F and K have a singlet and a doublet. The singlet and doublet are referring to the H's 1 carbon away from the carbon attached to the OH. Why don't the H's two carbons away, the ones on the cyclohexane ring, cause more peaks on the signal?arrow_forward
- Draw the Birch Reduction for this aromatic compound and include electron withdrawing groups and electron donating groups. *See attachedarrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see imagearrow_forward
- Elimination-Addition: What molecule was determined to be an intermediate based on a “trapping experiment”? *please solve and see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor”. **see attachedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Kinetics: Initial Rates and Integrated Rate Laws; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wYqQCojggyM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY