
The oxidation of iodide ion by the hypochlorite ion in the presence of hydroxide ions
I−(aq) + ClO−(aq) → IO−(aq) + Cl−(aq)
was studied at 25 °C, and the following initial rates data (Y. Chia and R. E. Connick, Journal of
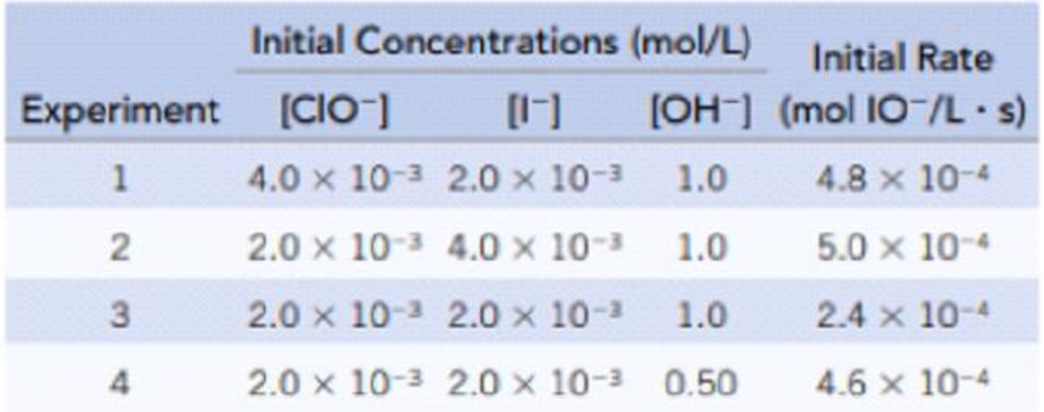
- (a) Determine the rate law for this reaction.
- (b) One mechanism that has been proposed for this reaction is the following:
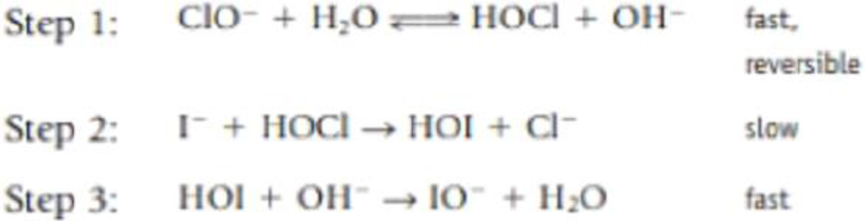
Show that the rate law predicted by this mechanism matches the experimentally determined rate law in part a. (Note that when writing the expression for K the equilibrium constant, [H2O] is not involved. See Chapter 15.)
(a)
Interpretation:
The rate law of the given reaction should be given.
Concept Introduction:
Rate law: It is generally the rate equation that consists of the reaction rate with the concentration or the pressures of the reactants and constant parameters.
Rate constant: The rate constant for a chemical reaction is the proportionality term in the chemical reaction rate law which gives the relationship between the rate and the concentration of the reactant present in the chemical reaction.
Answer to Problem 85IL
The rate law for the given reaction is as follows,
Explanation of Solution
The rate law is obtained by first determining the order of each reactant present in the given reaction. The order of each reactant is obtained by using the given set of concentration and the rate data as follows,
The order for
The order for
Similarly, the order for
The order for
Similarly the order for
Therefore, the rate law for the given reaction is as follows,
(b)
Interpretation:
The rate law predicted by the mechanism matches the experimentally determined rate law should be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Rate order: The order of each reactant in a reaction is represented by the exponential term of the respective reactant present in the rate law and the overall order of the reaction is the sum of all the exponents of all reactants present in the chemical reaction. The order of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants.
Rate law: It is generally the rate equation that consists of the reaction rate with the concentration or the pressures of the reactants and constant parameters.
Rate constant: The rate constant for a chemical reaction is the proportionality term in the chemical reaction rate law which gives the relationship between the rate and the concentration of the reactant present in the chemical reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The rate for the rate determining step is
Now,
Therefore, it clears that the rate determined from experimental data matches with the above obtained expression derived from elementary steps.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Organic Chemistry
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- So, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forwardDraw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forward
- here is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forwardDrawing of 3-fluro-2methylphenolarrow_forward
- Which compound(s) will be fully deprotonated (>99%) by reaction with one molar equivalent of sodium hydroxide? I, II, III I, || I, III I only II, III SH | H3C-C=C-H || III NH2arrow_forwardWill NBS (and heat or light) work for this reaction, or do we have to use Br2?arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





