
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of predominant organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols undergo halogenation reaction to give halogenated product. Alcohols on halogenation gives halogenated product in which the hydroxyl group present in the alcohol is substituted by the halogen. Phosphorous trihalides are useful in producing
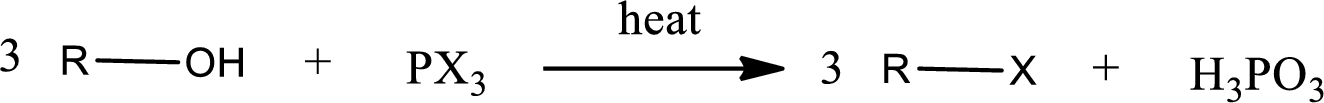
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of predominant organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction is the loss of water from a single reactant. Alcohol undergoes dehydration reaction to form
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of predominant organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols do undergo
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of predominant organic product that is formed in the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction is the loss of water from a single reactant. Alcohol undergoes dehydration reaction to form alkene. Sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst for hydration of alkene at room temperature. The same sulfuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent when treated with alcohol at high temperature. If the reaction is carried out at a lower temperature, the loss of water molecule takes place from two molecule of reactant. This results in the formation of ether. Primary alcohol when treated with sulfuric acid at lower temperature (
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning





