
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305856745
Author: DECOSTE
Publisher: CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 13, Problem 68E
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: The Lewis structure including resonance forms for PAN needs to be determined if the skeletal arrangement is as given below.
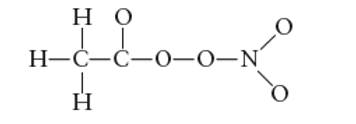
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that exist on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu
Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee
Please sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu
Chapter 13 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
Ch. 13 - Explain the electronegativity trends across a row...Ch. 13 - Prob. 2DQCh. 13 - Prob. 3DQCh. 13 - Prob. 4DQCh. 13 - Prob. 5DQCh. 13 - Prob. 6DQCh. 13 - Prob. 7DQCh. 13 - Prob. 8DQCh. 13 - Prob. 9DQCh. 13 - Arrange the following molecules from most to least...
Ch. 13 - Prob. 11DQCh. 13 - Prob. 12DQCh. 13 - Prob. 13ECh. 13 - Prob. 14ECh. 13 - An alternative definition of electronegativity...Ch. 13 - Prob. 16ECh. 13 - Without using Fig. 13.3, predict the order of...Ch. 13 - Without using Fig. 13.3, predict which bond in...Ch. 13 - Prob. 19ECh. 13 - Prob. 20ECh. 13 - Indicate the bond polarity (show the partial...Ch. 13 - Prob. 22ECh. 13 - Prob. 23ECh. 13 - Prob. 24ECh. 13 - Prob. 25ECh. 13 - Prob. 26ECh. 13 - Prob. 27ECh. 13 - Prob. 28ECh. 13 - Prob. 29ECh. 13 - Prob. 30ECh. 13 - Prob. 31ECh. 13 - Give an example of an ionic compound where both...Ch. 13 - What noble gas has the same electron configuration...Ch. 13 - Which of the following ions have noble gas...Ch. 13 - Give three ions that are isoelectronic with...Ch. 13 - Prob. 36ECh. 13 - Predict the empirical formulas of the ionic...Ch. 13 - Which compound in each of the following pairs of...Ch. 13 - Use the following data to estimate Hf for...Ch. 13 - Use the following data to estimate Hf for...Ch. 13 - Consider the following:...Ch. 13 - In general, the higher the charge on the ions in...Ch. 13 - Consider the following energy changes: a....Ch. 13 - Prob. 44ECh. 13 - Prob. 45ECh. 13 - The lattice energies of FeCl3,FeCl2,andFe2O3 are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 47ECh. 13 - Prob. 48ECh. 13 - Prob. 49ECh. 13 - Prob. 50ECh. 13 - Prob. 51ECh. 13 - Prob. 52ECh. 13 - Prob. 53ECh. 13 - Prob. 54ECh. 13 - Prob. 55ECh. 13 - Prob. 56ECh. 13 - Prob. 57ECh. 13 - Prob. 58ECh. 13 - Prob. 59ECh. 13 - Prob. 60ECh. 13 - Prob. 61ECh. 13 - Prob. 62ECh. 13 - Prob. 63ECh. 13 - Prob. 64ECh. 13 - Prob. 65ECh. 13 - Prob. 66ECh. 13 - Prob. 67ECh. 13 - Prob. 68ECh. 13 - Prob. 69ECh. 13 - Prob. 70ECh. 13 - Prob. 71ECh. 13 - Prob. 72ECh. 13 - Prob. 73ECh. 13 - Prob. 74ECh. 13 - Prob. 75ECh. 13 - Prob. 76ECh. 13 - Prob. 77ECh. 13 - Prob. 78ECh. 13 - Prob. 79ECh. 13 - Prob. 80ECh. 13 - Prob. 81ECh. 13 - Prob. 82ECh. 13 - Prob. 83ECh. 13 - Prob. 84ECh. 13 - Prob. 85ECh. 13 - Prob. 86ECh. 13 - Prob. 87ECh. 13 - Prob. 88ECh. 13 - Prob. 89ECh. 13 - Prob. 90ECh. 13 - Prob. 91ECh. 13 - Prob. 92ECh. 13 - Prob. 93ECh. 13 - Prob. 94ECh. 13 - Prob. 95ECh. 13 - Predict the molecular structure and the bond...Ch. 13 - Prob. 97ECh. 13 - Two variations of the octahedral geometry are...Ch. 13 - Prob. 99ECh. 13 - Predict the molecular structure and the bond...Ch. 13 - Which of the molecules in Exercise 96 have net...Ch. 13 - Prob. 102ECh. 13 - Give two requirements that should be satisfied for...Ch. 13 - What do each of the following sets of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 105ECh. 13 - Consider the following Lewis structure, where E is...Ch. 13 - Consider the following Lewis structure, where E is...Ch. 13 - Prob. 108ECh. 13 - Prob. 109ECh. 13 - Which of the following molecules have net dipole...Ch. 13 - Prob. 111AECh. 13 - Prob. 112AECh. 13 - Prob. 113AECh. 13 - Prob. 114AECh. 13 - Prob. 115AECh. 13 - There are two possible structures of XeF2Cl2 ,...Ch. 13 - Prob. 117AECh. 13 - Prob. 118AECh. 13 - Prob. 119AECh. 13 - Prob. 120AECh. 13 - Prob. 121AECh. 13 - Prob. 122AECh. 13 - Prob. 123AECh. 13 - Prob. 124AECh. 13 - Prob. 125AECh. 13 - Prob. 126AECh. 13 - Prob. 127AECh. 13 - Prob. 128AECh. 13 - Prob. 129AECh. 13 - Prob. 130AECh. 13 - Prob. 131AECh. 13 - Prob. 132AECh. 13 - Prob. 133CPCh. 13 - Prob. 134CPCh. 13 - Given the following information: Heat of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 136CPCh. 13 - A promising new material with great potential as...Ch. 13 - Think of forming an ionic compound as three steps...Ch. 13 - Prob. 139CPCh. 13 - Prob. 140CPCh. 13 - Calculate the standard heat of formation of the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 142CPCh. 13 - Prob. 143MP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardIII O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward
- 3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forward
- Use the reaction coordinate diagram to answer the below questions. Type your answers into the answer box for each question. (Watch your spelling) Energy A B C D Reaction coordinate E A) Is the reaction step going from D to F endothermic or exothermic? A F G B) Does point D represent a reactant, product, intermediate or transition state? A/ C) Which step (step 1 or step 2) is the rate determining step? Aarrow_forward1. Using radii from Resource section 1 (p.901) and Born-Lande equation, calculate the lattice energy for PbS, which crystallizes in the NaCl structure. Then, use the Born-Haber cycle to obtain the value of lattice energy for PbS. You will need the following data following data: AH Pb(g) = 196 kJ/mol; AHƒ PbS = −98 kJ/mol; electron affinities for S(g)→S¯(g) is -201 kJ/mol; S¯(g) (g) is 640kJ/mol. Ionization energies for Pb are listed in Resource section 2, p.903. Remember that enthalpies of formation are calculated beginning with the elements in their standard states (S8 for sulfur). The formation of S2, AHF: S2 (g) = 535 kJ/mol. Compare the two values, and explain the difference. (8 points)arrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Liquids: Crash Course Chemistry #26; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BqQJPCdmIp8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Chemistry of Group 16 elements; Author: Ch-11 Chemical Engg, Chemistry and others;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5B1F0aDgL6s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY