
a.
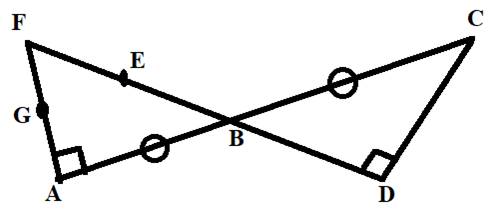
To Find: All points collinear with E and F .
a.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
B and D are points collinear with E and F .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
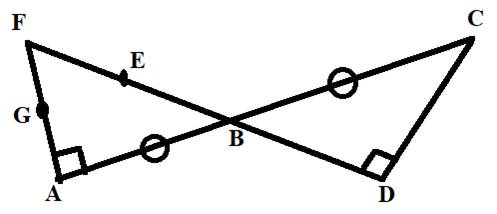
Concept Used:
Three or more points are said to be collinear if they lies on the same straight line.
Calculation:
Here, we points B and D are points collinear with E and F .
Conclusion:
B and D are points collinear with E and F .
b.
To Find: Whether points G, E and D are collinear? Whether points F and C are collinear?
b.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
No, points G, E and D are non-collinear. Also, points F and C are non-collinear.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
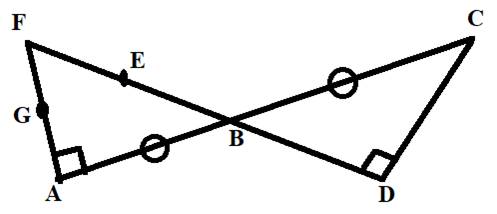
Concept Used:
Three or more points are said to be collinear if they lies on the same straight line.
Calculation:
Here, we points G, E and D are not on the same straight line, hence these points are non-collinear. Also, points F and C are not on the same straight line, hence these points are non-collinear.
Conclusion:
Points G, E and D are non-collinear. Also, points F and C are non-collinear.
c.
To Find: Which two segments are congruent?
c.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Explanation of Solution
Given:
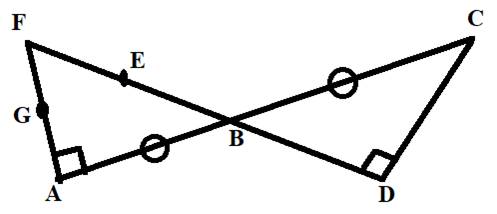
Concept Used:
Two or more line segments are said to be congruent if they are of the same measure.
Calculation:
Here, line segments AB and BC are labeled with tick marks, i.e., these line segments are of the same length.
Conclusion:
d.
To Find: Whether
d.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Yes,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
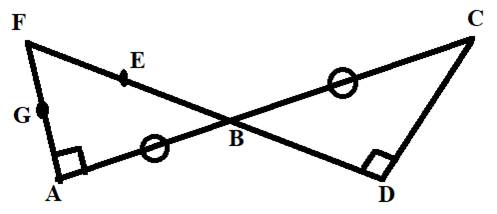
Concept Used:
Two or more
Calculation:
Here, we have
Conclusion:
e.
To Find: Whether
e.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
No,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
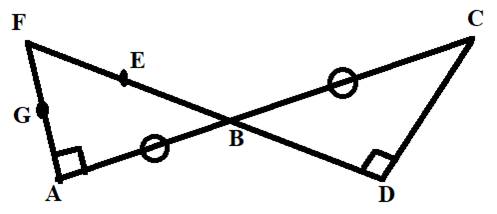
Concept Used:
Two or more angles are said to be congruent if they are of the same measure. Angles opposite to arms of equal length are equal in measure.
Calculation:
Since, it is not mention that sides AF and AB are of equal measure.
Conclusion:
f.
To Find: Where does the lines AC and FE intersects?
f.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Point B
Explanation of Solution
Given:
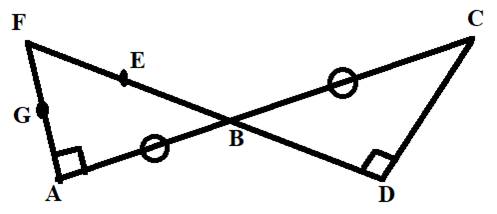
Concept Used:
Two or more lines are said to be intersecting if they cross each other at single point.
Calculation:
Since, line can move in both direction of it end points indefinitely. Here line FE when extended to point D it intersects AC at point B.
Conclusion:
Line FE when extended to point D it intersects AC at point B.
g.
To Find: The missing terms for the given blank.
g.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Explanation of Solution
Given:
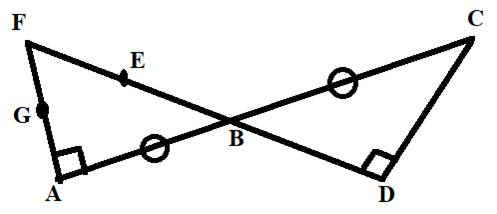
Concept Used:
Intersection of two or more line segments is the point common to both the line segments.
Calculation:
Here, point G is the point common to both the line segments AG and GF
Conclusion:
h.
To Find: The missing terms for the given blank.
h.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Explanation of Solution
Given:
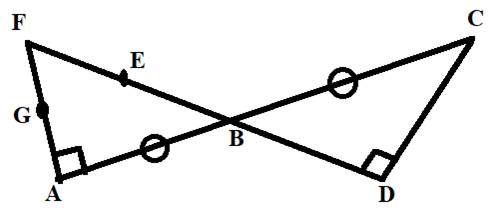
Concept Used:
Union of two or more line segments is the combination of all the line segments and get a single line whose length is the sum of all line segments taking part in union operations.
Calculation:
Here, line segments AG and GF when joined together using the point G, we get a line segment AF
Conclusion:
i.
To Find: A ray whose initial point is B and endpoint is E.
i.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept Used:
A ray is a line which has a initial point but no ending point.
Calculation:
Here, the ray
Conclusion:
j.
To Find: All points between point F and point D.
j.
Answer to Problem 3PSA
Point E and point B
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept Used:
Point is a geometrical term having no dimension, i.e., no length, breadth and thickness.
Calculation:
Here, points E and B lies between F and D.
Conclusion:
Points E and B
Chapter 1 Solutions
Geometry For Enjoyment And Challenge
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Elementary Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
- 2arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this please?arrow_forwardMariela is in her classroom and looking out of a window at a tree, which is 20 feet away. Mariela’s line of sight to the top of the tree creates a 42° angle of elevation, and her line of sight to the base of the tree creates a 31° angle of depression. What is the height of the tree, rounded to the nearest foot? Be sure to show your work to explain how you got your answer.arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

