
Concept explainers
A 32,000-Ib airplane lands on an aircraft carrier and is caught by an arresting cable. The cable is inextensible and is paid out at A and B from
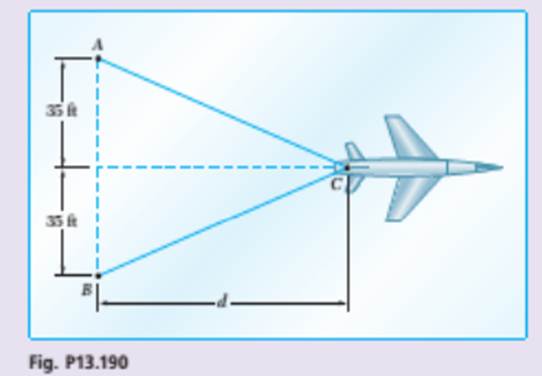
The landing speed of the airplane after it being caught by the cable.
Answer to Problem 13.190RP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of the airplane
Distance travelled
Tension in the cable =
Work of arresting cable force,
Calculation:
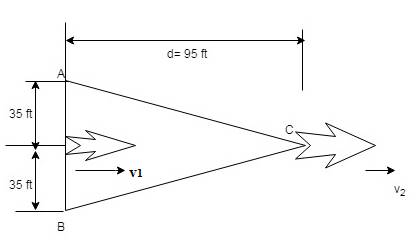
As the cable is pulled out, the cable acts parallel with the cable at the airplane hook. For a small displacement,
Here, Q is the work done by the cable force and ?l is the change in length of the cable.
Since Q is constant in both the given conditions
Now by applying Principle of work and energy:
Since,
Conclusion:
The landing speed of the airplane is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics
- For the flows in Examples 11.1 and 11.2, calculate the magnitudes of the Δ V2 / 2 terms omitted in B.E., and compare these with the magnitude of the ℱ terms.arrow_forwardCalculate ℛP.M. in Example 11.2.arrow_forwardQuestion 22: The superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical power. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 MPa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an efficiency of 90%. It is requested: Define the Power Plant Schematic Analyze the steam power system considering the steam generator system in the attached figure Determine the electrical power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant Perform an analysis on the power generated and thermal efficiency considering a variation in the steam fractions removed for regeneration ##Data: The steam generator uses biomass from coconut shells to produce 4.5 tons/h of superheated steam; The feedwater returns to the condenser at a temperature of 45°C (point A); Monitoring of the operating conditions in the steam generator indicates that the products of combustion leave the system (point B) at a temperature of 500°C;…arrow_forward
- This is an old practice exam question.arrow_forwardSteam enters the high-pressure turbine of a steam power plant that operates on the ideal reheat Rankine cycle at 700 psia and 900°F and leaves as saturated vapor. Steam is then reheated to 800°F before it expands to a pressure of 1 psia. Heat is transferred to the steam in the boiler at a rate of 6 × 104 Btu/s. Steam is cooled in the condenser by the cooling water from a nearby river, which enters the condenser at 45°F. Use steam tables. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the pressure at which reheating takes place. Use steam tables. Find: The reheat pressure is psia. (P4)Find thermal efficiencyFind m dotarrow_forwardAir at T1 = 24°C, p1 = 1 bar, 50% relative humidity enters an insulated chamber operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/min and mixes with a saturated moist air stream entering at T2 = 7°C, p2 = 1 bar. A single mixed stream exits at T3 = 17°C, p3 = 1 bar. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects Determine mass flow rate of the moist air entering at state 2, in kg/min Determine the relative humidity of the exiting stream. Determine the rate of entropy production, in kJ/min.Karrow_forward
- Air at T1 = 24°C, p1 = 1 bar, 50% relative humidity enters an insulated chamber operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/min and mixes with a saturated moist air stream entering at T2 = 7°C, p2 = 1 bar. A single mixed stream exits at T3 = 17°C, p3 = 1 bar. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects Determine mass flow rate of the moist air entering at state 2, in kg/min Determine the relative humidity of the exiting stream. Determine the rate of entropy production, in kJ/min.Karrow_forwardAir at T1 = 24°C, p1 = 1 bar, 50% relative humidity enters an insulated chamber operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 3 kg/min and mixes with a saturated moist air stream entering at T2 = 7°C, p2 = 1 bar. A single mixed stream exits at T3 = 17°C, p3 = 1 bar. Neglect kinetic and potential energy effects (a) Determine mass flow rate of the moist air entering at state 2, in kg/min (b) Determine the relative humidity of the exiting stream. (c) Determine the rate of entropy production, in kJ/min.Karrow_forwardA simple ideal Brayton cycle operates with air with minimum and maximum temperatures of 27°C and 727°C. It is designed so that the maximum cycle pressure is 2000 kPa and the minimum cycle pressure is 100 kPa. The isentropic efficiencies of the turbine and compressor are 91% and 80%, respectively, and there is a 50 kPa pressure drop across the combustion chamber. Determine the net work produced per unit mass of air each time this cycle is executed and the cycle’s thermal efficiency. Use constant specific heats at room temperature. The properties of air at room temperature are cp = 1.005 kJ/kg·K and k = 1.4. The fluid flow through the cycle is in a clockwise direction from point 1 to 4. Heat Q sub in is given to a component between points 2 and 3 of the cycle. Heat Q sub out is given out by a component between points 1 and 4. An arrow from the turbine labeled as W sub net points to the right. The net work produced per unit mass of air is kJ/kg. The thermal efficiency is %.arrow_forward
- Steam enters the high-pressure turbine of a steam power plant that operates on the ideal reheat Rankine cycle at 700 psia and 900°F and leaves as saturated vapor. Steam is then reheated to 800°F before it expands to a pressure of 1 psia. Heat is transferred to the steam in the boiler at a rate of 6 × 104 Btu/s. Steam is cooled in the condenser by the cooling water from a nearby river, which enters the condenser at 45°F. Use steam tables. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the pressure at which reheating takes place. Use steam tables. The reheat pressure is psia.Find thermal efficieny Find m dotarrow_forwardThis is an old exam practice question.arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure below, moist air at T₁ = 36°C, 1 bar, and 35% relative humidity enters a heat exchanger operating at steady state with a volumetric flow rate of 10 m³/min and is cooled at constant pressure to 22°C. Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, determine: (a) the dew point temperature at the inlet, in °C. (b) the mass flow rate of moist air at the exit, in kg/min. (c) the relative humidity at the exit. (d) the rate of heat transfer from the moist air stream, in kW. (AV)1, T1 P₁ = 1 bar 11 = 35% 120 T₂=22°C P2 = 1 bararrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





