
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
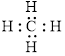
The structural formula for
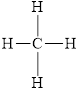
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
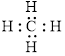
Figure 1
All electron pair are involved in bonding. Therefore, there is no lone pair. The structural formula for
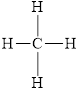
Figure 2
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
![]()
The structural formula for
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
![]()
Figure 3
Out of ten electron pairs, only two electron pairs are involved in bonding. Therefore, there are eight lone pairs. The structural formula for
![]()
Figure 4
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
![]()
The structural formula for
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
![]()
Figure 5
Out of seven electron pairs, three electron pairs are involved in bonding. Therefore, there are four lone pairs. The structural formula for
![]()
Figure 6
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
(d)
Interpretation:
The electron dot formula and structural formula for
Concept introduction:
The electron dot formula shows the valence electrons which form the bond between the atoms in a molecule. The electron pairs that are shared by the atoms are known as bonding electrons. The other electrons that are present in order to complete the octet are known as non-bonding electrons. The electron dot formula is also known as the Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 37E
The electron dot formula for
![]()
The structural formula for
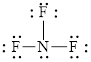
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electron in
![]()
Figure 7
Out of thirteen electron pairs, only three electron pairs are involved in bonding. Therefore, there are ten lone pairs. The structural formula for
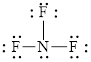
Figure 8
The electron dot formula for
The structural formula for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (8th Edition)
- Draw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
- 11. Use the equation below to answer the following questions: 2 Al(s) + 3 Cd(NO3)2 (aq) → 2 Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 Cd(s) a. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction? b. Which species is a spectator ion in this reaction? Define a spectator ion. c. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax


