
(a) Interpretation:
The balanced equation for the reaction catalyzed by PFK-2 should be written.
Concept Introduction:
PFK-2 is an enzyme that indirectly regulates the glycolysis rate in the cells. It is known to be a bifunctional enzyme due to its structure. The two domains independently act as functional enzymes because both are located on one protein honodimer.
In mammals, different PFK-2 isoforms are encoded by genetic mechanisms to accommodate tissue specific needs. General function of PFK-2 remains the same. Slight differences in enzymatic properties are featured by isoforms which are then controlled by different methods of regulation.
(b) Interpretation:
The balanced equation for the conversion of 2 moles of oxaloacetate to glucose should be written.
Concept Introduction:
Gluconeogenesis is a
(c) Interpretation:
The balanced equation for the conversion of glucose to UDP-Glc should be written.
Concept Introduction:
ATP to ADP conversion is reduction reaction. Energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP, this energy is used in cellular processes. Also, ADP can combined with a phosphate to form ATP, the reaction is as follows:
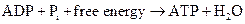
(d) Interpretation:
The balanced equation for the conversion of 2 moles of glycerol to glucose should be written.
Concept Introduction:
ATP to ADP conversion is reduction reaction. Energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP, this energy is used in cellular processes. Also, ADP can combine with a phosphate to form ATP, the reaction is as follows:
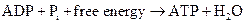
Also, NAD+ is an oxidizing agent as it accepts electrons from other molecules to get reduced to NADH. Here, NADH can act as a reducing agent to donate electrons. Thus, the main function of NAD is electron transfer reaction.
(e) Interpretation:
The balanced equation for the conversion of 2 moles of malate to glucose-6-phosphate should be written.
Concept Introduction:
ATP to ADP conversion is reduction reaction. Energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP, this energy is used in cellular processes. Also, ADP can combine with a phosphate to form ATP, the reaction is as follows:
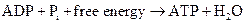
Similarly, the conversion of GTP to GDP is also a reduction reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
- Show the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose.arrow_forwardImagine that aldolase can react with the seven carbon molecule Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (below). Use the mechanism to predict the two products generated.arrow_forwardShow the mechanisms of PGK and PFK-1. How are they different?arrow_forward
- Show the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP.arrow_forwardSodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a potent inhibitor of aldolase. It is known to ONLY inhibit theenzyme when it is complexed with substrate. Treatment of the enzyme alone has no effect.What is the mechanism for this inhibition?arrow_forwardA non-hydrolysable ATP (AMPPNP - below) is ingested by a graduate student on a dare. Whateffects would you anticipate on his metabolism?arrow_forward
- Show the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of an [α-1,6] glycosidic linkagebetween two molecules of α-D-glucopyranose. Please sketch the structure and use arrows showing electron flow!arrow_forwardI am a Biochemistry student and I am confused on how to analyze FRAP Analysis using Excel Spread Sheets. The following spread sheet has my 0 minute data listed at top and the 4 minute data listed on the bottom. Sheet: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EXjrCizWiXRPmpittqZA12IB8EkB5eE8iaRqj_iun-IAtg?rtime=Wo9zPHFY3Ug The formula for FRAP Analysis is: FRAP value = A (4 min sample) - A (0 min sample) over A (4 min 30 uM ascorbic acid) - A (0 min 30 uM ascorbic acid) multiplied by 30 uM and the dilution factor of 1/10arrow_forwardHO Fill in the missing boxes. ON 800 NO NO Glucose ATP NADH Hexokinase 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate Mg2+ ADP NAD+, Pi Phosphoglucose Isomerase Glucose-6-Phosphate ON 沁 Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate HO حلمة ADP ADP Phospho Mg2+ glycerate Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate ATP kinase ATP Phosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate Mutase H₁₂O Fructose-6-Phosphate ATP Mg2+ ADP Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate 2-phosphoglycerate H₂O Phosphoenolpyruvate ADP Mg2+ ATP Pyruvatearrow_forward
- In a diffraction experiment of a native crystal, intensity of reflection (-1 0 6) is equivalent to the intensity of reflection (1 0 -6). true or false?arrow_forwardin an x-ray diffraction experiment, moving the detector farther away from the crystal will allow collection of reflection of reflections with high Miller indices. true or false?arrow_forwardShow the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed formation of an [α-1,6] glycosidic linkagebetween two molecules of α-D-glucopyranose.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





