
Concept explainers
The
Answer to Problem 19E
The
The
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equation
Concept Used:
The
The
Calculation:
The equation
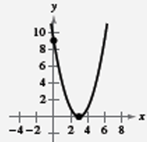
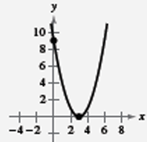
Since, the graph intersects
Therefore,
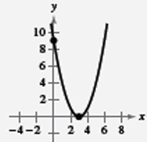
Since, the graph intersects
Therefore,
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- a -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forwardEvaluate F. dr where F(x, y, z) = (2yz cos(xyz), 2xzcos(xyz), 2xy cos(xyz)) and C is the line π 1 1 segment starting at the point (8, ' and ending at the point (3, 2 3'6arrow_forward
- I need help in ensuring that I explain it propleryy in the simplifest way as possiblearrow_forwardI need help making sure that I explain this part accutartly.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction decompostion on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forward
- Please help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forwardEvaluate F³ - dr where ♬ = (4z, -4y, x), and C' is given by (t) = (sin(t), t, cos(t)), 0≤t≤ñ .arrow_forwardMid-Term Review Find the formula for (f + g)(x). f(x) = x² - 10x + 25 and g(x) = x² - 10x + 24 (f + g) (x) = [ 2 ]x² X + DELL Skip Sarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





