
(a)
Interpretation:
The given line-angle structural formula has to be converted to skeletal structural formula.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
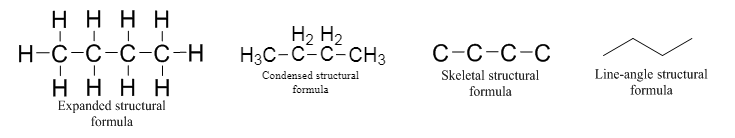
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given line-angle structural formula has to be converted to skeletal structural formula.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.

(c)
Interpretation:
The given line-angle structural formula has to be converted to skeletal structural formula.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.

(d)
Interpretation:
The given line-angle structural formula has to be converted to skeletal structural formula.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Can the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forwardAll of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forward
- A student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forwardCalculate the density of 21.12 g of an object that displaces 0.0250 L of water.arrow_forward
- Draw the expected reactant R28. Cu(II) CO₂Mearrow_forwardPpplllleeeaaasssseeee helllppp wiithhh thisss Organic chemistryyyyyy I talked like this because AI is very annoyingarrow_forwardName the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward
- 1b. Br LOHarrow_forwardI would like my graphs checked please. Do they look right? Do I have iodine and persulfate on the right axis ?arrow_forwardReaction Fill-ins Part 2! Predict the product(s) OR starting material of the following reactions. Remember, Hydride shifts are possible if/when a more stable carbocation can exist (depending on reaction mechanism)! Put your answers in the indicated boxes d. d. ง HCIarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





