
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The expanded structural formula of a continuous-chain alkane with the formula
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
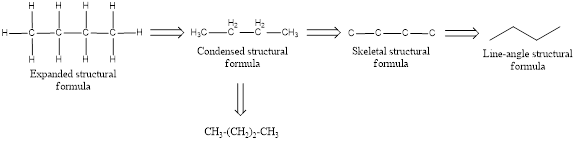
In condensed structural formula for
(b)
Interpretation:
The expanded structural formula for
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.

In condensed structural formula for alkanes, the repeating
(c)
Interpretation:
The condensed structural formula of a continuous-chain alkane with the formula
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.

In condensed structural formula for alkanes, the repeating
(d)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given alkane has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.

In condensed structural formula for alkanes, the repeating
Molecular formula of alkane can be found from condensed structural formula, by simply counting the number of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms present in the structural formula.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Which of the following compounds can be synthesized using one reaction from any alkene, as a major product? If it can be synthesized, propose a route, and you may use any other starting materials, reagents and solvents as needed. If you do not think that it can be synthesized as a major product from an alkene, explain in detail why.arrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism (with arrow pushing)arrow_forwarda) Explain why product 1 is the kinetic product and product 2 is the thermodynamic product. b) Draw the reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction pathway generating each product. c) State the Arrhenius Equation and explain the terms with their physical significance. d) State and explain which reaction pathway has a higher rate constant. What happens to the rate constant if the temperature has increased?arrow_forward
- Part 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism 1) Bakelite like polymer Using: Resorcinol + NaOH + Formalin 2) Polyester fiber Using a) pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + ethylene glycol B)pthalic anhydride + anhydrous sodium acetate + glycerol 3) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forwardUsing the table of Reactants and Products provided provide the correct letter that corresponds with the Carboxylic acid that is formed in the reaction below. 6 M NaOH Acid-workup WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES A) Pool of Reagents for Part B CI B) OH C) E) CI J) racemic F) K) OH N) OH P) G) OH D) HO H) L) M) HO Q) R) CI Aarrow_forwardIn the table below, the exact chemical structures for Methyl salicylate can be represented by the letter WRITE THE CORRECT LETTER ONLY DO NOT WRITE EXTRA WORDS OR PHRASES CI B) A) E) Cl racemic F) J) CI K) N) OH P) Pool of Reagents for Part B OH OH G) L) OH D) HO H) M) HO Q) R) CIarrow_forward
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardPart I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





