
Concept explainers
12-42 Complete these equations.
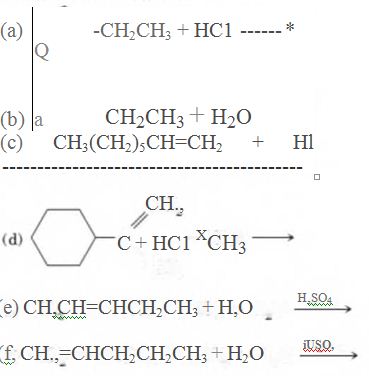
(a)
Interpretation:
Complete the below equation:
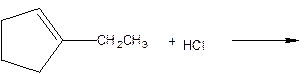
Concept introduction:
During the hydration of alkene the unsaturated alkene converted into saturated alkane with the addition of H+ and Cl- ions. This reaction is carried out in the presence of acid therefore it is called acid catalyzed hydration of alkene.
Answer to Problem 12.42P
Explanation of Solution
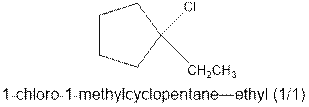
As per the given equation, the reactant is a cyclic alkene to which HCl is added. And the characteristics reactions given by the alkenes are addition reactions in which the addition takes place at the double bond. The addition follows the Markovnikov’s rule.
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it. Here, the positive part is H+ and the halogen part is Cl-. On numbering the carbon atoms, the structure is.
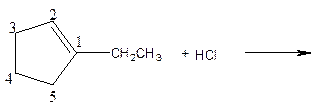
Now as per the rule, the hydrogen in the above equation attaches to carbon 2 as carbon 2 of the double bond has one hydrogen attached to it. The Cl- will attached to carbon 1 as it has no carbon attached to it. Thus, the complete reaction is:
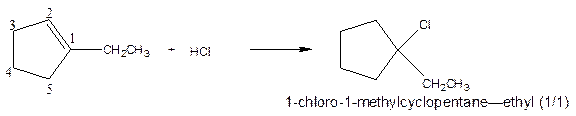
(b)
Interpretation:
Complete the below equation:
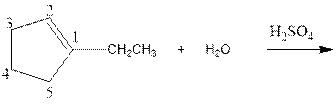
Concept introduction:
During the hydration of alkene the unsaturated alkene converted into saturated alkane with the addition of H+ and OH- ions in the presence of H2 SO4. This reaction is carried out in the presence of acid therefore it is called acid catalyzed hydration of alkene.
Answer to Problem 12.42P
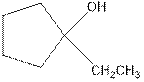
Explanation of Solution
As per the given equation, the reactant is a cyclic alkene to which H2 O is added. And the characteristics reactions given by the alkenes are addition reactions in which the addition takes place at the double bond. The addition follows the Markovnikov’s rule.
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it. Here, the positive part is H+ and the halogen part is OH-. On numbering the carbon atoms, the structure is.
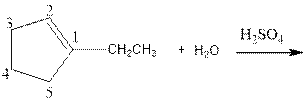
Now as per the rule, the hydrogen in the above equation attaches to carbon 2 as carbon 2 of the double bond has one hydrogen attached to it. The OH- will attached to carbon 1 as it has no carbon attached to it. Thus, the complete reaction is:
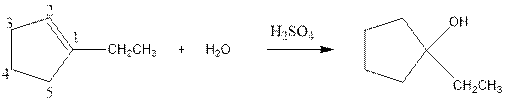
(c)
Interpretation:
Complete the below equation:
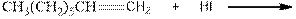
Concept introduction:
During the hydration of alkene the unsaturated alkene converted into saturated alkane with the addition of H+ and I- ions.
Answer to Problem 12.42P
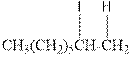
Explanation of Solution
As per the above equation, the reactant is an alkene to which HI is added. We also know that the characteristics reactions given by alkenes are addition reactions in which the addition takes place at the double bond. This addition follows the Markovnikov’s rule.
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it. Here, the positive part is H+ and the halogen part is I-. On numbering the double bonded carbons of the alkene, the structure is.
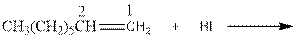
Now as per the rule, the hydrogen in the above equation attaches to carbon 1 as carbon 1 of the double bond has two hydrogen attached to it. The I- will attached to carbon 2 as it has only one carbon attached to it. Thus, the complete reaction is:
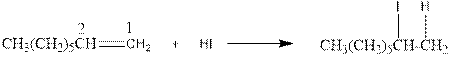
(d)
Interpretation:
Complete the below equation:

Concept introduction:
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it.
Answer to Problem 12.42P
Explanation of Solution
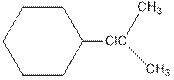
As per the above equation, the reactant is an alkene to which HCl is added. We also know that the characteristics reactions given by alkenes are addition reactions in which the addition takes place at the double bond. This addition follows the Markovnikov’s rule.
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it. Here, the positive part is H+ and the halogen part is Cl-. On numbering the double bonded carbons of the alkene, the structure is.
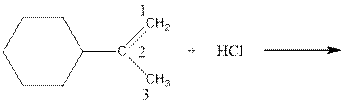
Now as per the rule, the hydrogen in the above equation attaches to carbon 1 as carbon 1 of the double bond has two hydrogen attached to it. The Cl- will attached to carbon 2 as it has only no carbon attached to it. Thus, the complete reaction is:

(e)
Interpretation:
Complete the below equation:
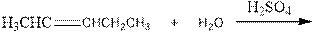
Concept introduction:
During the hydration of alkene the unsaturated alkene converted into saturated alkane with the addition of H+ and OH- ions in the presence of H2 SO4. This reaction is carried out in the presence of acid therefore it is called acid catalyzed hydration of alkene.
Answer to Problem 12.42P
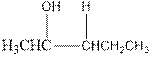
Explanation of Solution
As per the above equation, the reactant is an alkene to which H2 O is added. We also know that the characteristics reactions given by alkenes are addition reactions in which the addition takes place at the double bond. This addition follows the Markovnikov’s rule.
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it. Here, the positive part is H+ and the halogen part is OH-. On numbering the alkene, the structure is.
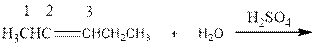
Now the below product will form where hydrogen will attach to the 2nd carbon to form more suitable product:
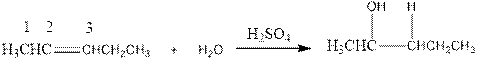
(f)
Interpretation:
Complete the below equation:
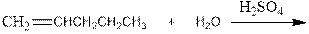
Concept introduction:
During the hydration of alkene the unsaturated alkene converted into saturated alkane with the addition of H+ and OH- ions in the presence of H2 SO4. This reaction is carried out in the presence of acid therefore it is called acid catalyzed hydration of alkene.
Answer to Problem 12.42P
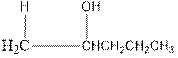
Explanation of Solution
As per the above equation, the reactant is an alkene to which H2 O is added. We also know that the characteristics reactions given by alkenes are addition reactions in which the addition takes place at the double bond. This addition follows the Markovnikov’s rule.
As per the Markovnikov’s rule, the hydrogen acid is added to the carbon of a double bond containing higher number of hydrogens in it. The halogen part is added to the carbon in the double bond containing fewer number of hydrogens in it. Here, the positive part is H+ and the halogen part is OH-. On numbering the alkene, the structure is.
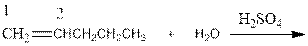
Now as per the rule, the hydrogen in the above equation attaches to carbon 1 as carbon 1 of the double bond has two hydrogen attached to it. The OH- will attached to carbon 2 as it has only one carbon attached to it. Thus, the complete reaction is:
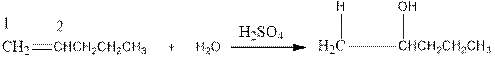
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: F structure Br LL Br Br الحمد name ☐ ☐arrow_forwardDraw an appropriate reactant on the left-hand side of this organic reaction. Also, if any additional major products will be formed, add them to the right-hand side of the reaction. + + Х ง C 1. MCPBA Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. NaOH, H₂O Explanation Check OI... OH ol OH 18 Ar © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardCalculate the atomic packing factor of quartz, knowing that the number of Si atoms per cm3 is 2.66·1022 and that the atomic radii of silicon and oxygen are, respectively, 0.038 and 0.117 nm.arrow_forward
- 3. a. Use the periodic table to add up the molecular weight of thionyl chloride (SOCl2) and show your work. b. The actual value obtained for the molecular ion on a high resolution mass spectrometer is 117.9041. Explain the discrepancy. c. Show the calculations that correctly result in the exact mass of 117.9041 for SOC₁₂. Use Table 11.2 or Appendix E in your calculations.arrow_forward6. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B₂2+ B22+, B2, C22, B22- and N22+ Molecular Orbital Diagram B2 C22- B22- N22+ Which molecule is paramagnetic?arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- EXERCISES: Complete the following exercises. You must show all work to receive full credit. 1. How many molecular orbitals can be built from the valence shell orbitals in O2? 2. Give the ground state electron configuration (e.g., 02s² 0*2s² П 2p²) for these molecules and deduce its bond order. Ground State Configuration Bond Order H2+ 02 N2arrow_forward7. Draw the Lewis structures and molecular orbital diagrams for CO and NO. What are their bond orders? Are the molecular orbital diagrams similar to their Lewis structures? Explain. CO Lewis Structure NO Lewis Structure CO Bond Order NO Bond Order CO Molecular Orbital Diagram NO Molecular Orbital Diagramarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



