
(a)
Interpretation:
Considering the acid catalyzed mechanism of ester hydrolysis reaction answer the following,
The species which can be represented by
Concept Introduction:
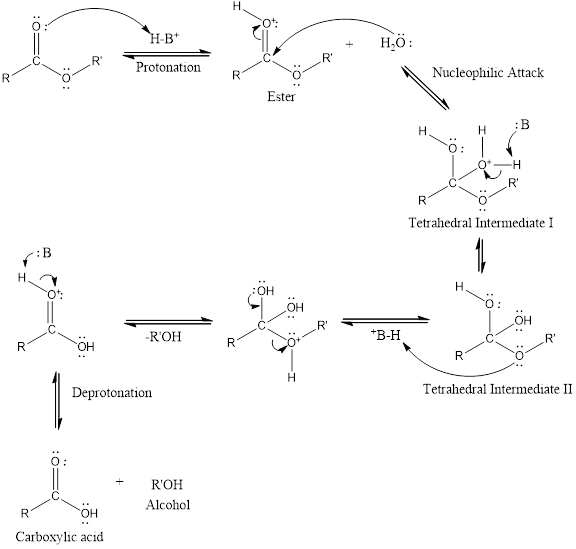
An acid catalyzed hydrolysis of ester is much faster reaction as compared to uncatalyzed hydrolysis of ester. The acid catalyzed reaction mechanism is written as,
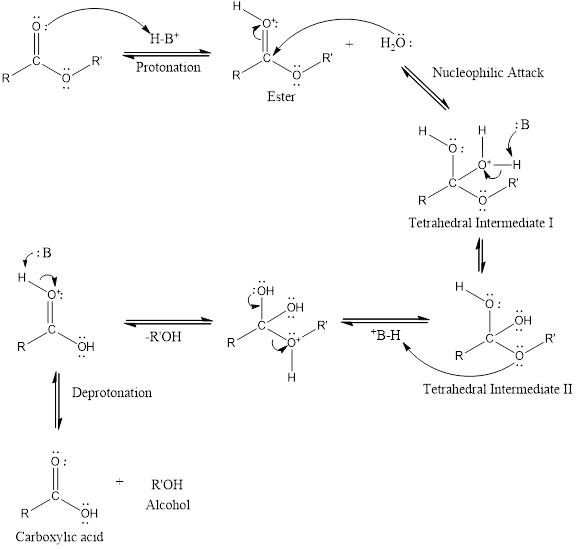
(b)
Interpretation:
Considering the acid catalyzed mechanism of ester hydrolysis reaction answer the following,
The species which can be represented by
Concept Introduction:
An acid catalyzed hydrolysis of ester is much faster reaction as compared to uncatalyzed hydrolysis of ester. The acid catalyzed reaction mechanism is written as,
(c)
Interpretation:
Considering the acid catalyzed mechanism of ester hydrolysis reaction answer the following,
The species which is mostly used as
Concept introduction:
An acid catalyzed hydrolysis of ester is much faster reaction as compared to uncatalyzed hydrolysis of ester. The acid catalyzed reaction mechanism is written as,

(d)
Interpretation:
Considering the acid catalyzed mechanism of ester hydrolysis reaction answer the following,
The species which is mostly used as
Concept Introduction:
An acid catalyzed hydrolysis of ester is much faster reaction as compared to uncatalyzed hydrolysis of ester. The acid catalyzed reaction mechanism is written as,

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Indicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward2,2-Dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Indicate the products obtained.arrow_forwardAdd conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward
- Steps on how to solve. Thank you!arrow_forward3. Name this ether correctly. H₁C H3C CH3 CH3 4. Show the best way to make the ether in #3 by a Williamson Ether Synthesis. Start from an alcohol or phenol. 5. Draw the structure of an example of a sulfide.arrow_forward1. Which one(s) of these can be oxidized with CrO3 ? (could be more than one) a) triphenylmethanol b) 2-pentanol c) Ethyl alcohol d) CH3 2. Write in all the product(s) of this reaction. Label them as "major" or "minor". 2-methyl-2-hexanol H2SO4, heatarrow_forward
- 3) Determine if the pairs are constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or mesocompounds. (4 points)arrow_forwardIn the decomposition reaction in solution B → C, only species C absorbs UV radiation, but neither B nor the solvent absorbs. If we call At the absorbance measured at any time, A0 the absorbance at the beginning of the reaction, and A∞ the absorbance at the end of the reaction, which of the expressions is valid? We assume that Beer's law is fulfilled.arrow_forward> You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: 1. ☑ CI 2. H3O+ O Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check ? DO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

