
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 38P
- a. List the following esters in order of decreasing reactivity in the first slow step of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction (formation of the tetrahedral intermediate).
- b. List the same esters in order of decreasing reactivity in the second slow step of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction (collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate).
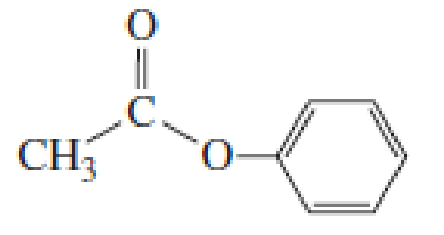
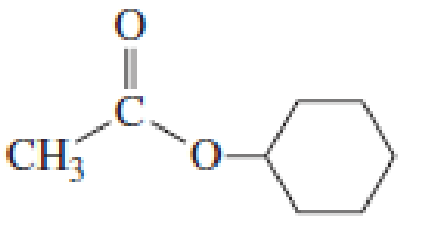
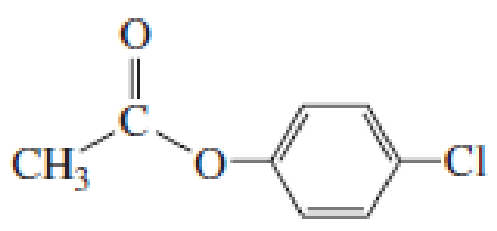
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
compared t-critical with t-calculated and 95% confidence interval to answer this question
Comparing two means. Horvat and co-workers used atomic absorption spectroscopy to determine the concentration of Hg in coal fly ash. Of particular interest to the authors was developing an appropriate procedure for digesting samples and releasing the Hg for analysis. As part of their study they tested several reagents for digesting samples. Their results using HNO3 and using a 1+3 mixture of HNO3 and HCl are shown here. All concentrations are given as ppb Hg sample.
HNO3: 161, 165, 160, 167, 166
1+3 HNO3–HCl: 159, 145, 140, 147, 143, 156
Determine whether there is a significant difference between these methods at the 95% confidence interval.
Comparison of experimental data to “known” value. Monna and co-workers used radioactive isotopes to date sediments from lakes and estuaries.21 To verify this method they analyzed a 208Po standard known to have an activity of 77.5 decays/min, obtaining the following results.
77.09, 75.37, 72.42, 76.84, 77.84, 76.69, 78.03, 74.96, 77.54, 76.09, 81.12, 75.75
Do the results differ from the expected results at the 95% confidence interval?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 11.1 - The aromas of many flowers and fruits are due to...Ch. 11.1 - Name the following compounds:Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 3PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 11.4 - a. What is the product of the reaction of acetyl...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 7PCh. 11.5 - Using the pKa values listed in Table 11.1, predict...Ch. 11.6 - Starting with acetyl chloride, what neutral...Ch. 11.6 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 11PCh. 11.8 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.8 - Using the mechanism for the acidcatalyzed...Ch. 11.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 11.8 - Prob. 16PCh. 11.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.10 - Show how each of the following esters could be...Ch. 11.11 - Which of the following reactions would lead to the...Ch. 11.12 - Prob. 22PCh. 11.12 - Prob. 23PCh. 11.13 - Prob. 24PCh. 11.13 - Prob. 25PCh. 11.14 - Prob. 26PCh. 11.14 - Prob. 27PCh. 11.14 - Prob. 28PCh. 11.15 - Prob. 29PCh. 11.15 - How would you synthesize the following compounds...Ch. 11 - Write a structure for each of the following a. N,N...Ch. 11 - Prob. 32PCh. 11 - Which ester is more reactive, methyl acetate or...Ch. 11 - What products would be formed from the reaction of...Ch. 11 - What products would be obtained from the following...Ch. 11 - Prob. 36PCh. 11 - a. Which compound would you expect to have a...Ch. 11 - a. List the following esters in order of...Ch. 11 - D. N. Kursanov, a Russian chemist, proved that the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 40PCh. 11 - Using an alcohol for one method and an alkyl...Ch. 11 - Prob. 42PCh. 11 - Prob. 44PCh. 11 - Prob. 45PCh. 11 - Prob. 46PCh. 11 - Prob. 47PCh. 11 - Prob. 48PCh. 11 - Prob. 49PCh. 11 - Show how the following compounds could be prepared...Ch. 11 - Prob. 51PCh. 11 - Prob. 52PCh. 11 - Prob. 53P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the difference between the propagated uncertainty and the standard deviation. Which number would you use to describe the uncertainty in the measurement? if the standard deviation is 0.01 and the propagated uncertainty is 0.03arrow_forwardPropagation of uncertainty. Find the absolute and percent relative uncertainty assuming the ±-values are random error. 7.65±0.04 + 5.28±0.02 – 1.12±0.01 85.6±0.9 × 50.2±0.7 ÷ 13.8±0.5 [4.88±0.07 + 3.22±0.05] / 1.53±0.02arrow_forwardExplain the difference between the propagated uncertainty and the standard deviation. Which number would you use to describe the uncertainty in the measurement?arrow_forward
- Circle the compound in each pair where the indicated bond vibrates at higher frequency. WHY IS THIS? Provide thorough explanation to tie topic.arrow_forwardHow can you distinguish between each pair of compounds below using IR? Cite a bond and frequency that can be used to distinguish. Provide thorough steps and explanation.arrow_forwardPropagation of uncertainty. Find the absolute and percent relative uncertainty assuming the ±-values are random error. 65±0.04 + 5.28±0.02 – 1.12±0.01 6±0.9 × 50.2±0.7 ÷ 13.8±0.5 [4.88±0.07 + 3.22±0.05] / 1.53±0.02arrow_forward
- Match to correct spectrum and explain the bonds and frequencies used to tell what spectrum connected to the given option. Thanks.arrow_forwardDraw the virtual orbitals for the planar and pyramidal forms of CH3 and for the linear and bent forms of CH2arrow_forwardQ2: Draw the molecules based on the provided nomenclatures below: (2R,3S)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane: (2S, 2R)-2-hydroxyl-3,6-dimethylheptane:arrow_forward
- Q3: Describes the relationship (identical, constitutional isomers, enantiomers or diastereomers) of each pair of compounds below. ག H CH3 OH OH CH3 H3C OH OH OH ////////// C CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H3C CH 3 C/III..... Physics & Astronomy www.physics.northweste COOH H нош..... H 2 OH HO CH3 HOOC H CH3 CH3 CH3 Br. H H Br and H H H Harrow_forwardQ1: For each molecule, assign each stereocenter as R or S. Circle the meso compounds. Label each compound as chiral or achiral. OH HO CI Br H CI CI Br CI CI Xf x f g Br D OH Br Br H₂N R. IN Ill I -N S OMe D II H CO₂H 1/111 DuckDuckGarrow_forwardThese are synthesis questions. You need to show how the starting material can be converted into the product(s) shown. You may use any reactions we have learned. Show all the reagents you need. Show each molecule synthesized along the way and be sure to pay attention to the regiochemistry and stereochemistry preferences for each reaction. If a racemic molecule is made along the way, you need to draw both enantiomers and label the mixture as "racemic". All of the carbon atoms of the products must come from the starting material! ? H Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Characteristic Reactions of Benzene and Phenols; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tjEqEjDd87E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
An Overview of Aldehydes and Ketones: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #27; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-fBPX-4kFlw;License: Standard Youtube License