
Concept explainers
For each compound. [1] Identify the
![Chapter 11.5, Problem 11.8PP, For each compound. [1] Identify the functional group; [2] draw out the complete compound, including , example 1](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9781259883989/Chapter-11/images/html_83989-11.5-11.8pp_image001.jpg)
b.
![Chapter 11.5, Problem 11.8PP, For each compound. [1] Identify the functional group; [2] draw out the complete compound, including , example 2](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9781259883989/Chapter-11/images/html_83989-11.5-11.8pp_image002.jpg)
d.
![Chapter 11.5, Problem 11.8PP, For each compound. [1] Identify the functional group; [2] draw out the complete compound, including , example 3](http://dev-ingestion-image-output.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/9781259883989/Chapter-11/images/html_83989-11.5-11.8pp_image003.jpg)
(a)
Interpretation:
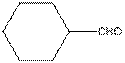
The functional group / groups should be identified and the complete structure with lone pairs on hetero-atoms of the following compound should be drawn:
Concept Introduction:
Organic molecules have some structural features in addition to
This table gives information about the compounds containing
| Type of Compound | General Structure |
| Aldehyde | 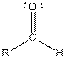 |
| Ketone | 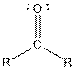 |
| Carboxylic acid | 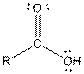 |
| Ester | 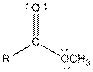 |
| Amide | 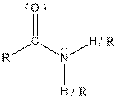 |
Here, R = any carbon backbone
Complete structural formula of a molecule represents all the atoms of molecule, types of bonds connecting atoms and how atoms are connected to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.8PP
Functional group in the given compound is '
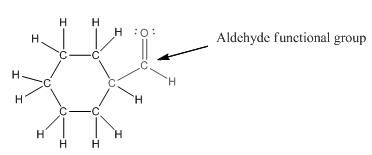
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows:
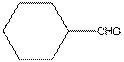
The given compound can also be drawn as:
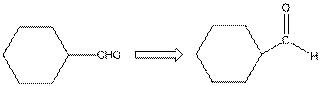
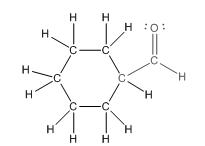
This compound contains a six membered ring and a
To draw the complete structure of the given skeletal structure, place carbon atom on each vertices and fulfill its valency with hydrogen atoms. Unlabelled vertex will represent carbon atom attached to number of hydrogen atoms required to fulfill its valency (i.e. four). Valence electron of oxygen is six. Out of six two electrons are used in making double bond with carbon atom. Then remaining four electrons will be available as lone pair.
So, complete structure of given compound is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The functional group / groups should be identified and the complete structure with lone pairs on hetero-atoms of the following compound should be drawn:
Concept Introduction:
Organic molecules have some structural features in addition to
This table gives information about the compounds containing
| Type of Compound | General Structure |
| Aldehyde | 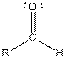 |
| Ketone | 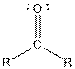 |
| Carboxylic acid | 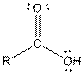 |
| Ester | 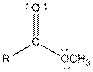 |
| Amide | 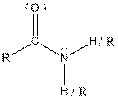 |
Here, R = any carbon backbone
Complete structural formula of a molecule represents all the atoms of molecule, types of bonds connecting atoms and how atoms are connected to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.8PP
Functional group in the given compound
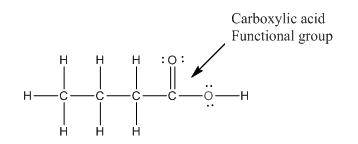
Explanation of Solution
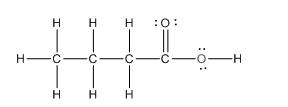
The given compound is as follows:
The above compound can be drawn as:
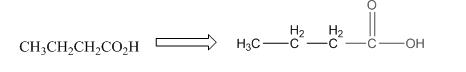
This compound contains four carbon and eight hydrogen atom with two oxygen atoms. The functional group is carboxylic acid containing an
To draw the complete structure of the given skeletal structure, place carbon atom on each vertices and fulfill its valency with hydrogen atoms. Unlabelled vertex will represent carbon atom attached to number of hydrogen atoms required to fulfill its valency (i.e. four). Valence electron of oxygen is six. Out of six two electrons of blue colored oxygen are used in making double bond with carbon atom. Then remaining four electrons will be available as lone pair.
Complete structure of the given compound is as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
The functional group / groups should be identified and the complete structure with lone pairs on hetero-atoms of the following compound should be drawn:
Concept Introduction:
Organic molecules have some structural features in addition to
This table gives information about the compounds containing
| Type of Compound | General Structure |
| Aldehyde | 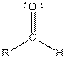 |
| Ketone | 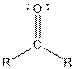 |
| Carboxylic acid | 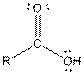 |
| Ester | 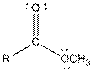 |
| Amide | 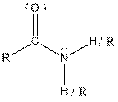 |
Here, R = any carbon backbone
Complete structural formula of a molecule represents all the atoms of molecule, types of bonds connecting atoms and how atoms are connected to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.8PP
Functional group in the given compound is 'ketone' and the complete structure of the compound is as follows:
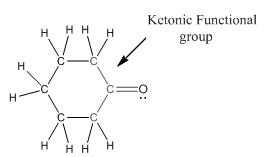
Explanation of Solution
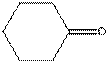
The given compound is as follows:
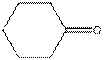
This compound contains six membered ring with one oxygen atom. The functional group is ketone containing a carbon-oxygen bond
To draw the complete structure of the given skeletal structure, place carbon atom on each vertices and fulfill its valency with hydrogen atoms. Unlabelled vertex will represent carbon atom attached to number of hydrogen atoms required to fulfill its valency (i.e. four). Valence electron of oxygen is six. Out of six two electrons of are used in making double bond with carbon atom. Then remaining four electrons will be available as lone pair.
Complete structure of the compound is as follows:
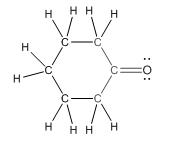
(d)
Interpretation:
The functional group / groups should be identified and the complete structure with lone pairs on hetero-atoms of the following compound should be drawn:
Concept Introduction:
Organic molecules have some structural features in addition to
This table gives information about the compounds containing
| Type of Compound | General Structure |
| Aldehyde | 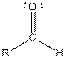 |
| Ketone | 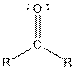 |
| Carboxylic acid | 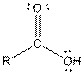 |
| Ester | 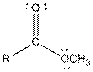 |
| Amide | 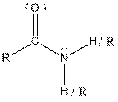 |
Here, R = any carbon backbone
Complete structural formula of a molecule represents all the atoms of molecule, types of bonds connecting atoms and how atoms are connected to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.8PP
Functional group in the given compound is 'ester' and the complete structure of the compound is as follows:
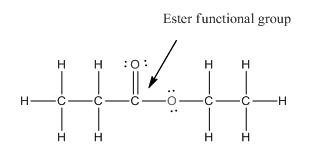
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows:
This given compound can be drawn as follows:
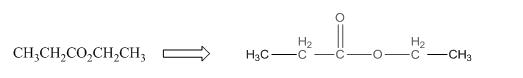
This compound contains an
To draw the complete structure of the given skeletal structure, place carbon atom on each vertices and fulfill its valency with hydrogen atoms. Unlabelled vertex will represent carbon atom attached to number of hydrogen atoms required to fulfill its valency (i.e. four).
Valence electron of oxygen is six. Out of six two electrons of blue colored oxygen are used in making double bond with carbon atom. Then remaining four electrons will be available as lone pair. For pink colored oxygen atom, one electron is used in making bond with carbonyl carbon atom and another electron is used in making bond with carbon backbone. Then remaining four will be present as lone pair.
The complete structure of the given compound is as follows:
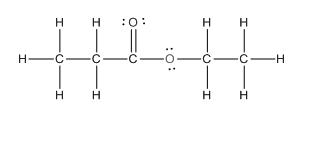
(e)
Interpretation:
The functional group / groups should be identified and the complete structure with lone pairs on hetero-atoms of the following compound should be drawn:
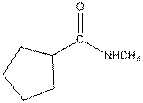
Concept Introduction:
Organic molecules have some structural features in addition to
This table gives information about the compounds containing
| Type of Compound | General Structure |
| Aldehyde | 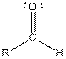 |
| Ketone | 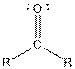 |
| Carboxylic acid | 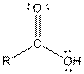 |
| Ester | 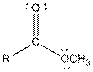 |
| Amide | 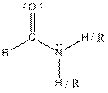 |
Here, R = any carbon backbone
Complete structural formula of a molecule represents all the atoms of molecule, types of bonds connecting atoms and how atoms are connected to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.8PP
Functional group in the given compound is an 'amide' and the complete structure of the compound is as follows:
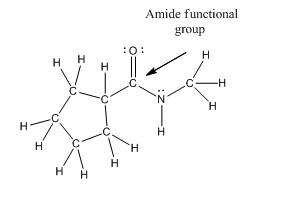
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows:
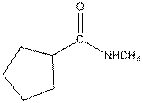
This compound contains an
To draw the complete structure of the given skeletal structure, place carbon atom on each vertices and fulfill its valency with hydrogen atoms. Unlabelled vertex will represent carbon atom attached to number of hydrogen atoms required to fulfill its valency (i.e. four).
Valence electron of oxygen is six. Out of six two electrons of oxygen atom are used in making double bond with carbon atom. Then remaining four electrons will be available as lone pair. Valence electron of nitrogen is five. Out of five, one electron is used in making bond with the carbonyl carbon atom, one electron is used in making bond with
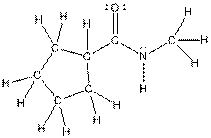
The complete structure of the given compound is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- Predict the major organic product(s), if any, of the following reactions. Assume all reagents are in excess unless otherwise indicated.arrow_forwardHow many signals would you expect to find in the 1 H NMR spectrum of each given compound? Part 1 of 2 2 Part 2 of 2 HO 5 ☑ Х IIIIII***** §arrow_forwardA carbonyl compound has a molecular ion with a m/z of 86. The mass spectra of this compound also has a base peak with a m/z of 57. Draw the correct structure of this molecule. Drawingarrow_forward
- Can you draw this using Lewis dot structures and full structures in the same way they are so that I can better visualize them and then determine resonance?arrow_forwardSynthesize the following compound from cyclohexanol, ethanol, and any other needed reagentsarrow_forwardFor a titration of 20.00 mL of 0.0500 M H2SO4 with 0.100 M KOH, calculate the pH at each of the following volume of KOH used in the titration: 1) before the titration begin; 2) 10.00 mL; 3) 20.00 mL; 4) 30.00 mL. Ka2 = 1.20×10-2 for H2SO4.arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s) Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps Problem 73 of 10 Drawing Amows ro HO Donearrow_forward12. Synthesize the following target molecules (TMs) using the specified starting materials. .CI a) HO3S SM TM b) HO- SMarrow_forwardFor a titration of 20.00 mL of 0.0500 M H2SO4 with 0.100 M KOH, calculate the pH at each of the following volume of KOH used in the titration: 1) before the titration begin; 2) 10.00 mL; 3) 20.00 mL; 4) 30.00 mL. Ka2 = 1.20×10-2 for H2SO4.arrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name show work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardA Elschboard Part of SpeechT-D Alt Leaming App app.aktiv.com Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Include all lone pairs and formal charges in the structures. Problem 45 of 10 I Select to Add Arrows N Please selarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





