
Concept explainers
Methyl salicylate is responsible for the characteristic odor of the oil Wintergreen.
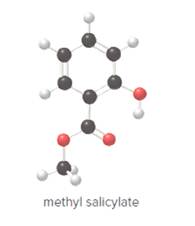
- Give the molecular formula for methyl salicylate.
- Draw in all lone pairs on heteroatoms using a skeletal structure.
- How many trigonal planar carbons does methyl salicylate contain?
- Predict the water solubility of methyl salicylate.
- Label all polar bonds.
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the molecular formula of methyl salicylate from the ball and stick model.
Concept Introduction:
In ball and stick model, black color ball represents carbon atom, white color ball represents hydrogen atom, red color ball represents oxygen atom and blue color ball represents nitrogen atom. To determine the molecular formula, convert the ball and stick model to complete structure.
Answer to Problem 82P
Molecular formula of methyl salicylate is
Explanation of Solution
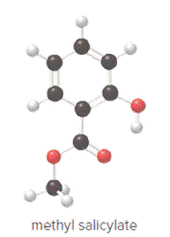
Ball and stick model of methyl salicylate is as follows:
Convert ball and stick model to normal structure. Replace black balls by carbon atoms, red balls by oxygen atoms and white balls by hydrogen atom. But all the bonds between atoms are same.
In methyl salicylate, eight carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms and three oxygen atoms present. Hence, molecular formula of methyl salicylate is
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw all lone pairs on heteroatoms of methyl salicylate using a skeletal structure.
Concept Introduction:
Heteroatoms are those atoms in an organic compound other than carbon and hydrogen atom like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. Lone pairs are pair of electrons available on an atom after bond formation.
Answer to Problem 82P
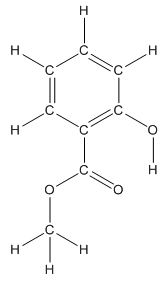
The structure having all lone pairs on heteroatoms is represented as follows:
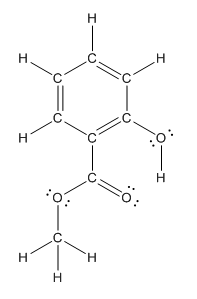
Explanation of Solution
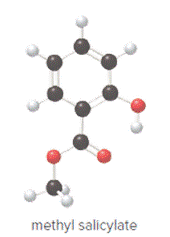
Structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
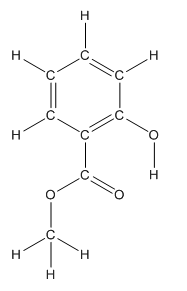
The heteroatoms present in benzocaine are oxygen atoms. Oxygen has six valence electrons. In double bonded oxygen atom, two electrons are used for making double bond. Remaining four electrons present as two lone pairs. Both the single bonded oxygen atom has two bonds. So, remaining four electrons present as two lone pairs in both the oxygen atom. So, the structure having all lone pairs on heteroatoms is represented as follows:
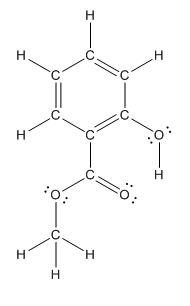
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the number of carbon atoms having trigonal planar shape in methyl salicylate.
Concept Introduction:
The following table should be used while determining shape around an atom.
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
If an atom is surrounded by three groups, then the shape around that particular atom is trigonal planar.
Answer to Problem 82P
Seven carbon atoms in methyl salicylate have trigonal planar structure.
Explanation of Solution
If an atom is surrounded by three groups, then the shape around that particular atom is trigonal planar.
Structure ofmethyl salicylate is as follows:
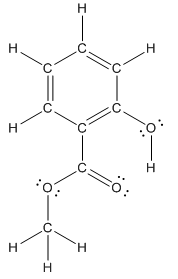
To find the number of carbon atoms having trigonal planar shape in methyl salicylate, observe the carbon atoms and find which carbon atom has three groups surround it.
All the carbon atoms in the benzene ring have three atoms around them also the carbon bonded to the benzene ring has three groups surround it. So, seven carbon atoms in methyl salicylatehave trigonal planar structure represented as follows:
The bold carbon atoms in the above structure have trigonal planar structure.
(d)
Interpretation:
To predict the solubility of methyl salicyate in water.
Concept Introduction:
Water is a polar solvent. To dissolve in water the compound must be polar. Polar compound is that compound in which polar bonds are present. The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 82P
Methyl salicylate is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
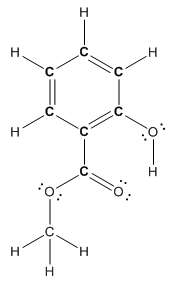
Structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
In methyl salicylate, three heteroatoms present that is, three oxygen atoms. These heteroatoms can form hydrogen bond with water. The presence of heteroatoms make the compound polar and a polar compound will dissolve in polar compound. So, methyl salicylate is soluble in water.
(e)
Interpretation:
To label all the polar bonds in methyl salicylate.
Concept Introduction:
The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 82P
The structure of methyl salicylate with all polar bonds labeled is as follows:
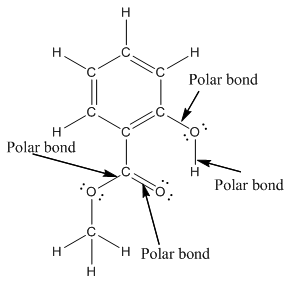
Explanation of Solution
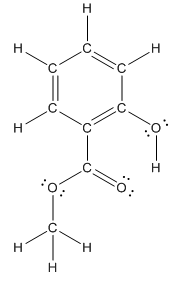
Structure of methyl salicylate is as follows:
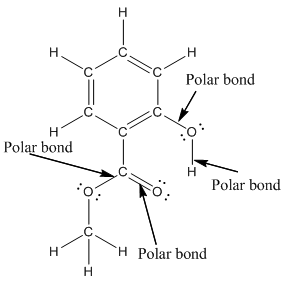
In organic compound, most of the polar bonds formed between carbon and heteroatoms like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. In methyl salicylate, four polar bonds present that is, three polar bond between carbon and oxygen (oxygen is more electronegative than carbon) and one polar bond between oxygen and hydrogen (oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- Nonearrow_forwardA complete tensile test was performed on a magnesium specimen of 12 mm diameter and 30 mm length, until breaking. The specimen is assumed to maintain a constant volume. Calculate the approximate value of the actual stress at breaking. TABLE. The tensile force F and the length of the specimen are represented for each L until breaking. F/N L/mm 0 30,0000 30,0296 5000 10000 30,0592 15000 30,0888 20000 30,15 25000 30,51 26500 30,90 27000 31,50 26500 32,10 25000 32,79arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Differentiate between plastic deformation, elastic deformation, viscoelastic deformation and viscoplastic deformation.arrow_forward1.57 Draw all reasonable resonance structures for the following cation. Then draw the resonance hybrid.arrow_forwardFor the two questions below, draw the mechanism and form the major product.arrow_forward
- Indicate similarities and differences between natural, exchanged and pillared clays.arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardIn intercalation compounds, their sheets can be neutral or have a negative or positive charge, depending on the nature of the incorporated species and its structure. Is this statement correct?arrow_forward
- This thermodynamic cycle describes the formation of an ionic compound MX2 from a metal element M and nonmetal element X in their standard states. What is the lattice enthalpy of MX2 ? What is the enthalpy formation of MX2 ? Suppose both the heat of sublimation of M and the ionization enthalpy of M were smaller. Would MX2 be more stable? Or less? or impossible to tell without more information?arrow_forward7. Draw the mechanism to describe the following transformation: Note: This is a base catalyzed reaction. So, the last steps must make [OH]- OH [OH]¯ OH Heat Oarrow_forwardShow work with explanation...don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER




