
Concept explainers
The parameters of the transistors in the circuit in Figure P10.68 are
The currents
Answer to Problem 10.68P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
The given circuit is,
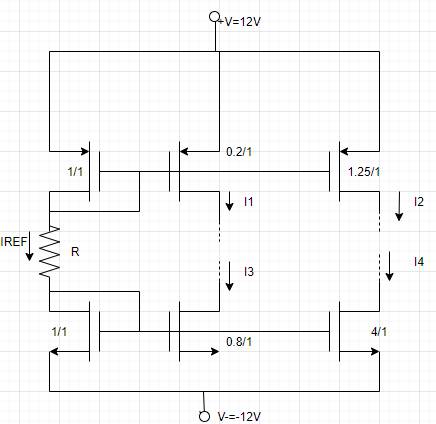
According to the circuit reference current
And
Now substitute the given values in equation (1) and equation (2),
On comparing equation (3) and equation (4),
Now reference current expression is,
Now compare equation (3) and equation (6)
Solve the above expression by quadratic degree method,
Consider
Calculate reference current,
Now calculate current
Conclusion:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- Q1: Write a VHDL code to implement the finite state machine described in the state diagram shown below. Clk D 0 CIK Q D 0 Cik Q =arrow_forwardQ1: Consider the finite state machine logic implementation in Fig. shown below: Construct the state diagram. Repeat the circuit design using j-k flip flop. r" Clk Y D' Y, Clk Q D Clk 10 0 22 3'2arrow_forwardQ: Write a VHDL code to implement the finite state machine described in the state diagram shown below. T 2 Clk Q Clk T₂ 0 la Clk T3 Q Cik 0arrow_forward
- Do you happen to know what is the complete circuit?arrow_forwardb) Draw the magnitude and phase bode plot c) Given Cdb=0.02pF, how will the frequency response change, draw the resulting magnitude and phase bode plotplz help me to solve part b and c.arrow_forwardMedium 1 is a lossless dielectric (ε₁, μ₁ = μo, σ₁ = 0) Medium 2 is a perfect electric conductor (PEC) ( 2 = 0, μ2 = μo, σ₂ = ∞) [ Moσ = 0] [ε0 μ₁ σ₂ = ∞ ] (J=σE is finite, E = 0) E(z) Exe² +Пe₁²] 1. For the case εr] = λι = = E2(z)-0 - 1 (vacuum), E₁x 1 V/m and a frequency f = 500 MHz determine: n₁ = 12= 2. Determine: r = T= 3. Using this I show that the total electric field E₁0(z) in region 1 can be written as: E(z) = -2jE, sin(2лz/λ)✰ 4. The magnitude E10(z) will show an interference pattern. The SWR (standing wave ratio) is the Emax/Emin ratio of the magnitude of the total electric field in region 1. What is the SWR? E (z) = 2|E|sin(2лz/2₁)| E" (z) SWR A Imax E(z) Imin 1+r 1-|| tot 5. Roughly SKETCH the magnitude of E10(z) and E20(z) on the graph below. E₁tot(z) tot E20(z) -0.40 -0.30 -0.ło z=0 +0.1b +0.20arrow_forward
- would anyone be able to tell me the amount of wire needed for this electrical plan in this house? and if possible would anyone be able to tell me the amount of any other materials needed (wire sizes, box sizes/styles)arrow_forwardPlease show all stepsarrow_forwardA plane wave propagating in the +z direction in medium 1 is normally incident to medium 2 located at the z=0 plane as below. Both mediums are general, characterized by ( ε i, Mi, Ơi ). tot = [ ει μη σ] [ε, μη σε ] Ex Ex tot E₁₂ (z) = Ee Ex z=0 From conservation of energy: P₁AV'(z=0) + Piav'(z=0) = P2av²(z=0). Using the above show for lossless media that: ( 1 - ||²) = (1/M2 )|T|² .arrow_forward
- A plane wave propagating in the +z direction in medium 1 is normally incident to medium 2 located at the z=0 plane as below. Both mediums are general, characterized by ( ε i, Hi, σ¡ ). [ ει μη σ] Ex [ ει μη ση ] Ex tot E₁₂ (z) = E'₁e¹² -122 E(z) = Ee+ E₁₁₁² E₁x z=0 1. Specify the electric field reflection coefficient г and transmission coefficient T: E ΓΔ E E TA EL 2. Show that T=1+г. Can the transmitted electric field amplitude in region 2 be LARGER than the incident electric field amplitude? 3. Determine expressions for P₁AV'(z), PIAV'(z) and P2AV'(z) (note the sign for the reflected power direction should be (-z).arrow_forward2) In the ideal transformer circuit shown below find Vo and the complex power supplied by the source. 292 www b 1:4 16 Ω ww + + 240/0° V rms -12492arrow_forward3) In the ideal autotransformer circuit shown below find 11, 12 and lo. Find the average power delivered to the load. (hint: write KVL for both sides) 20/30° V(+ 2-1602 200 turns V₂ 10 + j40 Ω 80 turns V₁arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





