
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are shown. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
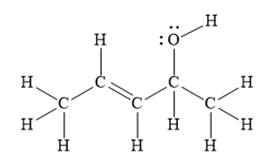
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
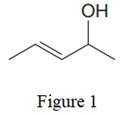
In the given line structure, there is a five carbon chain, with a carbon-carbon double bond and a hydroxyl group. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all. The hydroxyl group is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the chain. There should be two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom so as to complete its octet. Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
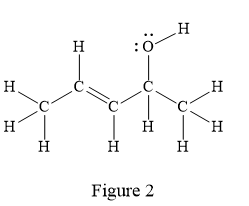
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 2 above.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
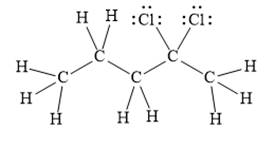
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
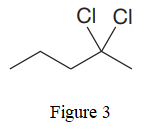
In the given line structure, there is a five carbon chain with two chlorine atoms attached to one of the carbon atoms in the chain. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all. Two chlorine atoms are attached to one of the carbon atoms of the chain. There must be three lone pairs of electrons on each chlorine atom so that its octet is complete. Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
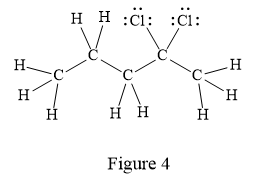
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 4 above.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
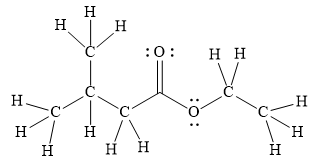
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
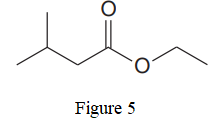
In the given line structure, there is a chain of four carbon atoms on the left side of a singly bonded oxygen. An ethyl fragment is present at the right side of the singly bonded oxygen atom. The structure has two oxygen atoms, a doubly bonded and a singly bonded, so, each of the oxygen must carry two lone pairs so that their octet is complete. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all.
Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
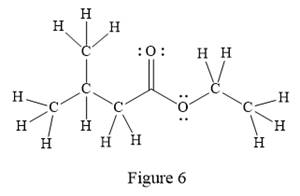
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 6 above.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
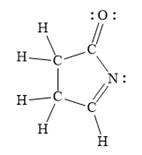
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
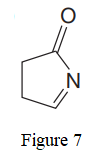
In the given line structure, a five membered ring containing a nitrogen atom is present. One of the carbon atoms in the ring forms a double bond with the oxygen atom. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all. Nitrogen atom should have a lone pair of electrons so as to complete its octet while oxygen atom needs two lone pairs of electrons on it.
Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
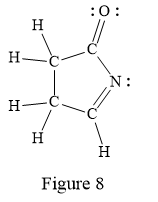
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 8 above.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
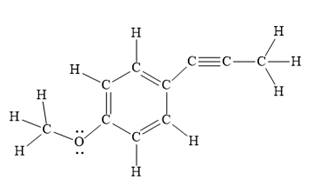
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
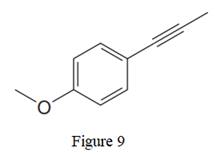
In the above line structure, the disubstituted benzene ring is present. One substituent of the benzene ring is a three carbon chain with an internal triple bond. The other substituent is a methoxy group,
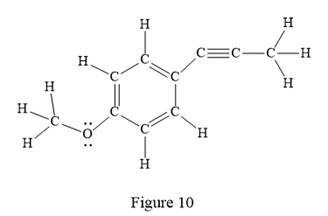
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 10 above.
(f)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
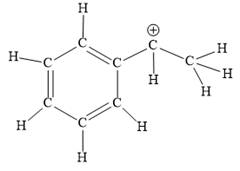
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
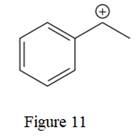
The above line structure is a structure for a cation. A carbocation is a carbon bearing a positive formal charge which is explicitly shown in the Lewis structure. A six membered carbon ring with alternate double and single bonds is present. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all. The carbon bearing a positive charge must possess three bonds.
Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
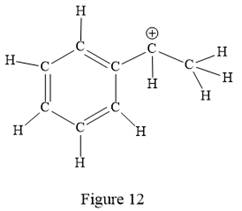
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 12 above.
(g)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
The above line structure is a structure for an anion. A six membered carbon ring with single bonds is present. The negatively charged carbon atom must possess three bonds and one lone pair of electrons. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all.
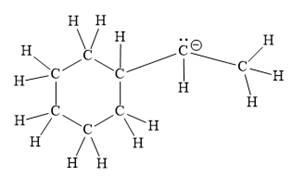
Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
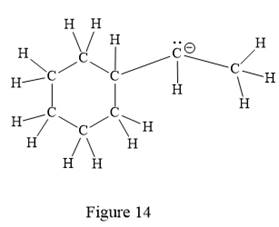
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 14 above.
(h)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
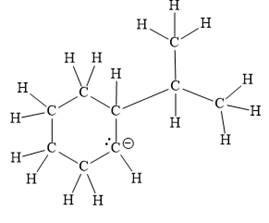
Explanation of Solution
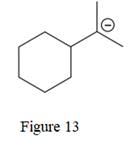
The given line structure is:
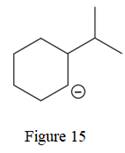
The above line structure is a six membered ring with a negative charge on one of the carbon atoms of the ring. The ring is monosubstituted with an isopropyl group. The negatively charged carbon atom must possess three bonds and one lone pair of electrons. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all.
Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
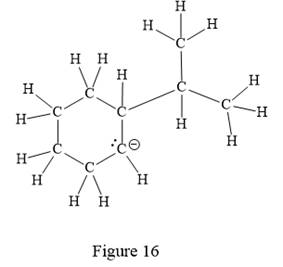
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 16 above.
(i)
Interpretation:
For the given line structure, a Lewis structure is to be drawn including all the lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
Line structures are compact like condensed structures. When drawing line structures, carbon atoms and the hydrogen atoms attached to them are not drawn explicitly. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are drawn. Non-bonding electrons are usually not shown unless they are important to emphasize an aspect of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.63P
For the given line structure, the structure with all lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is:
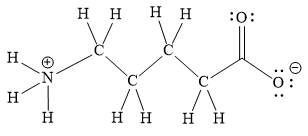
Explanation of Solution
The given line structure is:
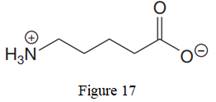
The above line structure is a chain of five carbon atoms. One end of the chain has carboxylate ion, in which the oxygen carries a negative charge. The other end of the chain has a nitrogen atom with three hydrogen atoms directly attached to it and carrying a positive charge. A carbon atom is implied at the intersection of two bonds and at the end of each bond. The hydrogen atoms are attached to each carbon atom such that each carbon atom forms four bonds in all. A singly bonded oxygen with a negative charge must have three lone pairs on it while the doubly bonded oxygen atom should possess two lone pairs.
Thus, the structure with all carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and lone pairs is as shown below:
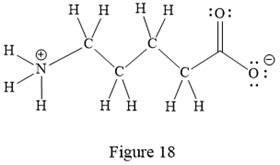
The Lewis structure for the given line structure including lone pairs and hydrogen atoms is shown in Figure 18 above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





