
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given species, the complete Lewis structure is to be completed by adding multiple bonds and/or lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
In order to draw a Lewis structure for a molecule, start by counting the total number of valence electrons in a molecule. The number of valence electrons by each atom is the same as its group number. For the given skeleton of the molecule, distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs. In doing so, start with the outer atoms and work inwards. Try to achieve an octet on each atom other than hydrogen. If there is an atom with less than an octet, increase the atom’s share of electrons by converting lone pairs from neighboring atoms to bonding pairs thereby creating double or triple bonds. For an uncharged atom, carbon atoms will have a maximum of four bonds; Nitrogen will have three bonds and one lone pair, while oxygen will have two bonds and two lone pairs. Hydrogen always contributes to one bond. The number of bonds in case of halogen is one; while there will be three lone pair of electrons on halide atoms.
Answer to Problem 1.24P
The complete Lewis structure for the given species is:
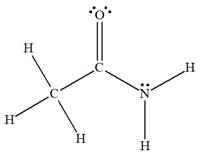
Explanation of Solution
The given species is:
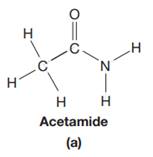
The formula for the species above is
The carbon atom on the left side has four bonds, thus, its octet is complete. The carbon atom in the middle has four bonds, hence, its octet is also complete. The nitrogen atom has three bonds, thus, its octet is not complete. There should be one lone pair of electron on nitrogen. The double bonded oxygen atom has got two bonds. Thus, in order to complete its octet, it should possess two lone pair of electrons. Thus, all the
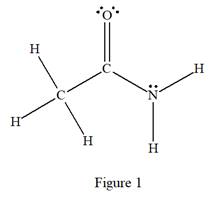
The complete Lewis structure for the given species including multiple bonds and lone pairs is shown in Figure 1 above.
(b)
Interpretation:
For given species, the complete Lewis structure is to be completed by adding multiple bonds and/or lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
In order to draw a Lewis structure for a molecule, start by counting the total number of valence electrons in a molecule. The number of valence electrons by each atom is the same as its group number. For a charged species, each negative charge increases the number of valence electrons by one while each positive charge decreases the number of valence electrons by one. For the given skeleton of the molecule, distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs. In doing so, start with the outer atoms and work inwards. Try to achieve an octet on each atom other than hydrogen. If there is an atom with less than an octet, increase the atom’s share of electrons by converting lone pairs from neighboring atoms to bonding pairs thereby creating double or triple bonds. For an uncharged atom, carbon atoms will have maximum of four bonds. Nitrogen will have three bonds and one lone pair, while oxygen will have two bonds and two lone pairs. Hydrogen always contributes to one bond. The number of bond in case of halogen is one, while there will be three lone pair of electrons on halide atoms.
Answer to Problem 1.24P
The complete Lewis structure for the given species is:
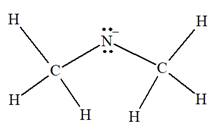
Explanation of Solution
The given species is:
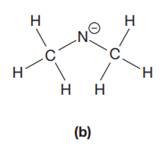
The formula for the species above is
The carbon atom on the left as well as on the right has four bonds, thus, their octets are complete. The nitrogen atom has two bonds and a negative formal charge. This suggests that the remaining four electrons should be present on the nitrogen atom so as to complete its octet and have a negative formal charge. Thus, the complete Lewis structure for the given species is:
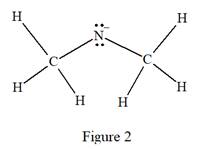
The complete Lewis structure for the given species including multiple bonds and lone pairs is shown in Figure 2 above.
(c)
Interpretation:
For given species, the complete Lewis structure is to be completed by adding multiple bonds and/or lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
In order to draw a Lewis structure for a molecule, start by counting the total number of valence electrons in a molecule. The number of valence electrons by each atom is the same as its group number. For a charged species, each negative charge increase the number of valence electrons by one while each positive charge decrease the number of valence electrons by one. For the given skeleton of the molecule, distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs. In doing so, start with the outer atoms and work inwards. Try to achieve an octet on each atom other than hydrogen. If there is an atom with less than an octet, increase the atom’s share of electrons by converting lone pairs from neighboring atoms to bonding pairs thereby creating double or triple bonds. For an uncharged atom, carbon atoms will have maximum of four bonds. Nitrogen will have three bonds and one lone pair, while oxygen will have two bonds and two lone pairs. Hydrogen always contributes to one bond. The number of bond in case of halogen is one, while there will be three lone pair of electrons on halide atoms.
Answer to Problem 1.24P
The complete Lewis structure for the given species is:
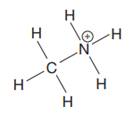
Explanation of Solution
The given species is:
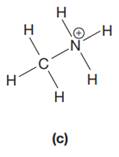
The formula for the species above is
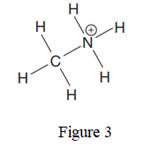
The complete Lewis structure for the given species including multiple bonds and lone pairs is shown in Figure 2 above.
(d)
Interpretation:
For given species, the complete Lewis structure is to be completed by adding multiple bonds and/or lone pairs.
Concept introduction:
In order to draw a Lewis structure for a molecule, start by counting the total number of valence electrons in a molecule. The number of valence electrons by each atom is the same as its group number. For a charged species, each negative charge increase the number of valence electrons by one while each positive charge decrease the number of valence electrons by one. For the given skeleton of the molecule, distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs. In doing so, start with the outer atoms and work inwards. Try to achieve an octet on each atom other than hydrogen. If there is an atom with less than an octet, increase the atom’s share of electrons by converting lone pairs from neighboring atoms into bonding pairs thereby creating double or triple bonds. For an uncharged atom, carbon atoms will have maximum of four bonds. Nitrogen will have three bonds and one lone pair, while oxygen will have two bonds and two lone pairs. Hydrogen always contributes to one bond. The number of bond in case of halogen is one, while there will be three lone pair of electrons on halide atoms.
Answer to Problem 1.24P
The complete Lewis structure for the given species is:
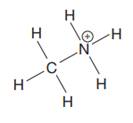
Explanation of Solution
The given species is:
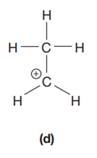
The formula for the species above is
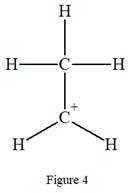
The complete Lewis structure for the given species including multiple bonds and lone pairs is shown in Figure 4 above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- reciprocal lattices rotates along with the real space lattices of the crystal. true or false?arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction vn the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ O If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Product can't be made in one step. Explanation Checkarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Larrow_forward
- > Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accesarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: O O + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. eserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center >arrow_forward(EXM 2, PRBLM 3) Here is this problem, can you explain it to me and show how its done. Thank you I need to see the work for like prbl solving.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

