
Concept explainers
Scenes A-D represent atomic-scale views of different samples of substances:
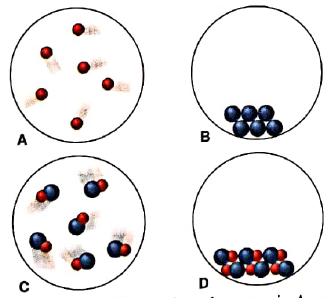
- Under one set of conditions, the substances in A and B mix, and the result is depicted in C. Does this represent a chemical or a physical change?
- Under a second set of conditions, the same substances mix, and the result is depicted in D. Does this represent a chemical or a physical change?
- Under a third set of conditions, the same substances mix, and the result is depicted in D. Does this represent a chemical or a physical change?
- After the change in part(c) has occurred, does the sample have different chemical properties? Physical properties?
a)
Interpretation: Whether combination of A and B to form C is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction: Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
Substances that are present in A and B have completely different properties than those formed in C. So when A and B are mixed to form C, it refers to chemical change.
b)
Interpretation: Whether combination of A and B to form D is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction:Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
Substances that are present in A and B have completely different properties than those formed in D. So when A and B are mixed to form D, a completely different substance is formed. Therefore combination of A and B to form D is chemical change.
c)
Interpretation: Whether conversion of C to D is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction: Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
When sample in C is converted to D, there occurs difference in arrangement of particles only while substances remain same. Therefore it is physical change.
d)
Interpretation: Whether conversion of C to D is physical or chemical change should be determined.
Concept introduction: Changes can be classified as physical and chemical changes. Physical changes are such changes that allow change of state of matter only but not formation of new substances. Reversal of such changes is possible by physical methods.
Chemical changes allow formation of new and different substances from original substances via chemical reactions. These cannot be reversed back to original state by any method.
Explanation of Solution
When sample in C is converted to D, only arrangement of particles is changed while substances remain same. Therefore it is physical change and physical properties are changed in conversion of C to D.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Principles of General Chemistry
- I have a 2 mil plastic film that degrades after 22 days at 88C and at 61C takes 153 days. What is the failure at 47C in days.arrow_forwardIf a 5 film plastic film degraded in 30 days at 35C and the same film degraded in 10 days at 55 C and 2 days at 65C what would the predicted life time be at 22C for the same film?arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- I have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- no Ai walkthroughs (product in picture is wrong btw don't submit the same thing)arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward136 PRACTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Compound 78 is a high-boiling liquid (boiling point 189° C) that contains halogen, but will not react with alkoxides to yield an halogen. ether. The Mass, IR, and 'H NMR spectra, along with 13C NMR data, are given below. Elemental Analysis: C, 35.32; H, 2.47; contains BC Spectral Data: doublet, 137.4 ppm; doublet, 130.1 ppm; doublet, 127.4 ppm; singlet, 97.3 ppm Absorbance Mass Spectrum Intensity 77 77 204 M + 128 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 m/e 200 220 280 240 260 300 Infrared Spectrum Wave Number, cm -1 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 3 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 15 Wavelength, microns 'H NMR wwwww 5 Structure: www ppm, & ©2000 Brooks/Cole Publishing Com-arrow_forward
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





