
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The equation given below has to be balanced.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given chemical equation is written as follows;
Balancing hydrogen atoms: In the above equation, there are four hydrogen atoms on left side of the equation while three hydrogen atoms are present in right side of the equation. Adding coefficient
(b)
Interpretation:
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation state of a species is the one that has a specified oxidation number. Increase in oxidation number corresponds to oxidation while decrease in oxidation number corresponds to reduction. Rules for assigning oxidation number for an element is given as follows;
- The oxidation number is zero for the element that is present in uncombined state.
- Sum of the oxidation number of the atoms that is present in it is equal to the charge on the species.
- Oxidation number of the element is the charge that is possessed when the more electronegative atom is imagined to be an ion.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
The sum of oxidation state of the individual atoms is equal to the total charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of nitrogen can be found as shown below;
Thus the oxidation state of nitrogen in
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
The sum of oxidation state of the individual atoms is equal to the total charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of nitrogen can be found as shown below;
Thus the oxidation state of nitrogen in
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
Nitrogen molecule consists only atoms of nitrogen. Oxidation number of an element that is in its free form is zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of nitrogen in
(c)
Interpretation:
Oxidizing agent and reducing agent has to be identified in the given reaction.
Concept Introduction:
In
In redox reactions, reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized by causing reduction. These agents can be ions, elements, or even compounds. In reduction, the oxidation number decreases due to gain of electrons.
(c)
Answer to Problem K.22E
Oxidizing agent and reducing agent is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is written as follows;
Oxidation number of the atoms present in the above equation is indicated as follows;
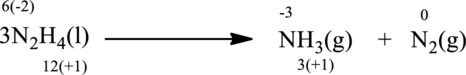
From the above equation, it is found that the oxidation state of nitrogen is increased from
The oxidation state of nitrogen decreases from
(d)
Interpretation:
Volume of nitrogen gas that will be obtained from
(d)
Answer to Problem K.22E
Volume of nitrogen is
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is written as follows;
Density of hydrazine is given as
Molar mass of hydrazine is
Considering the balanced chemical equation, it is found that three moles of hydrazine gives one mole of nitrogen. Therefore, moles of nitrogen is calculated as shown below;
It is given that
Thus the volume of nitrogen that will be produced is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
ACHIEVE/CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES ACCESS 2TERM
- a. H3C CH3 H, 1.0 equiv. Br2arrow_forwardH3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forward
- in the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forwardIs the chemical reaction CuCl42-(green) + 4H2O <==> Cu(H2O)42+(blue) + 4Cl- exothermic or endothermic?arrow_forwardIf we react tetraethoxypropane with hydrazine, what is the product obtained (explain its formula). State the reason why the corresponding dialdehyde is not used.arrow_forward
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward+ Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





