
To prove: In quadrilateral ABCD , the sum of the square of the sides AB , BC , CD and DA is equal to the sum of the square of the diagonals AC and BD plus four times the square of the segment MN joining the midpoints of the diagonals AC and BD .
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In quadrilateral ABCD, AB , BC , CD and DA are sides.
AC and BD are diagonals. MN is the segment joining the midpoints of the diagonals AC and BD .
Formula used:
The distance between two points by using the distance formula, which is an application of the Pythagoras theorem.
D
Proof:
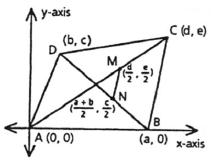
The distance AB , BC, CD , DA , AC , BD and MN can be calculated by applying distance formula.
Distance AB :
Distance BC :
Distance CD :
Distance DA :
Distance AC :
Distance BD :
Distance MN :
Adding squares of all sides of quadrilateral ABCD , we get
Adding sum of the square of the diagonals AC and BD plus four times the square of the segment MN joining the midpoints of the diagonals AC and BD , we get
Chapter 9 Solutions
Geometry For Enjoyment And Challenge
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- To approximate the length of a marsh, a surveyor walks x = 400 meters from point A to point B. Then, the surveyor turns 75° and walks 220 meters to point C (see figure). Approximate the length AC of the marsh. (Round your answer to one decimal place.) m C B 75° 220 m x marrow_forward. The students who attend Memorial High School have a wide variety of extra-curricular activities to choose from in the after-school program. Students are 38% likely to join the dance team; 18% likely to participate in the school play; 42% likely to join the yearbook club; and 64% likely to join the marching band. Many students choose to participate in multiple activities. Students have equal probabilities of being freshmen, sophomores, juniors, or seniors.What is the probability of the union of being either a freshman or senior? 0.07 0.44 0.50 0.25arrow_forwardWhich angles are complementary to each other? Select all that apply. 3 2 4 in 5 1 Z1 and 23 Z1 and 25 22 and 23 Z2 and 25 Submitarrow_forward
- Which angles are adjacent to each other? Select all that apply. 3 2 4 67 5 8 11 10 12 12 9 27 and 28 Z9 and 12 Z3 and 24 Z10 and Z11arrow_forwardIf the arc length of NMP is 11π, what is the length of MNP expressed in terms of πT? M N 5 44% ○ A. 54π OB. 108π P О с. 103 18 O D. 108arrow_forwardGiven: Circle J 2 What is the value of y? A. 38 C. 68 B. 50 D. 92arrow_forward
- Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. yd2arrow_forward5:00 PM Sat May 3 deltamath.com DeltaMath Given: ABBC and D is the midpoint of AC. Prove: ABD ≈ ACBD. ← Back to Home Deltamath Regents Review Week 3 Due: May 9 at 8:00 PM Grade: 97% Step Statement AB ≈ BC Reason 1 Given D is the midpoint of AC 2 BD BD 3 ADDC Calculating Volume (Mixed) Volume of Oblique Solids Volume, Density, and Unit 5 4 AABC is an isosceles triangle ZAZC Conversions (Level 1) Triangle Congruence Criteria try ZAD =/ DC Basic Triangle Proofs (Congruence Only - No CPCTC) Triangle Proofs (Reasons Only) Calculator Aseret Martinez Domi... Log Out Reflexive Property A midpoint divides a segment into two congruent segments The triangle has two congruent sides In a triangle, angles opposite of congruent sides are congruent An angle bisector divides an angle into two congruent angles B * A Ꭰ Note: the segment AC is a straight segment. 86%arrow_forwardLANDMARKS Stonehenge is a British landmark made of huge stones arranged in a circular pattern that reflects the movements of Earth and the moon. The diagram shows that the angle formed by the north/south axis and the line aligned from the station stone to the northmost moonrise position measures 23.5°. a. Find measure of arc BC. b. Is arc ABC semicircle? Explain. c. If the circle measures about 100 feet across, approximately how far would you walk around the circle from point B to point sarsen circle B station stone trilithons horseshoe 71° 23.5° farthest north moonrise Sarrow_forward
- find the value of each variablearrow_forwardName: Date: Bell: Unit 11: Volume & Surface Area Homework 2: Area of Sectors Directions: Find the area of each shaded sector. Round to the hundredths place. 1. GH 11 in 2. KL 20 ft H F 64 G L 119 M K 3. BA 6.5 cm 4. YZ 14.2 m B 23 X 87° Y Z 5. KL = 27.1 mm J 32 L X:360-32.1 K A-3 360 7. BD 18 cm E 136 B X=32.8 127.0 (271) A: 069.13 Amm² 19=2102.13 A-136 360.16912 A:300cm² A=96.13 6. PQ = 2.8 in P R 311° 8. WZ 5.3 km V = Z 108 W D 9. HK = 25 ft G H KO 26 X 10. SR 26 m = S 73 T R Gina Wilson (All Things Algebarrow_forward538 Chapter 13 12. Given: Points E(-4, 1), F(2, 3), G(4, 9), and H(-2, 7) a. Show that EFGH is a rhombus. b. Use slopes to verify that the diagonals are perpendicular. 13. Given: Points R(-4, 5), S(-1, 9), T(7, 3) and U(4, -1) a. Show that RSTU is a rectangle. b. Use the distance formula to verify that the diagonals are congruent. 14. Given: Points N(-1, -5), O(0, 0), P(3, 2), and 2(8, 1) a. Show that NOPQ is an isosceles trapezoid. b. Show that the diagonals are congruent. Decide what special type of quadrilateral HIJK is. Then prove that your answer is correct. 15. H(0, 0) 16. H(0, 1) 17. H(7, 5) 18. H(-3, -3) I(5, 0) I(2,-3) 1(8, 3) I(-5, -6) J(7, 9) K(1, 9) J(-2, -1) K(-4, 3) J(0, -1) K(-1, 1) J(4, -5) K(6,-2) 19. Point N(3, - 4) lies on the circle x² + y² = 25. What is the slope of the (Hint: Recall Theorem 9-1.) - line that is tangent to the circle at N? 20. Point P(6, 7) lies on the circle (x + 2)² + (y − 1)² = 100. What is the slope of the line that is tangent to the circle at…arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

