
Concept explainers
The total exergy destruction for each process of an ideal dual cycle
Answer to Problem 145P
The total exergy destruction in an ideal dual cycle is
Explanation of Solution
Draw the ideal dual cycle on
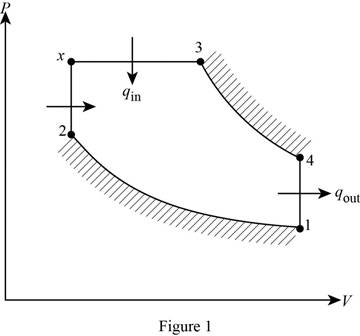
Consider, the pressure is
Write the expression of temperature and volume relation for the isentropic compression process 1-2.
Here, compression ratio is r and specific heat ratio is k.
Write the expression of pressure, and volume relation for the isentropic expansion process 1-2.
Write the expression of pressure ratio relation.
Here, pressure ratio is
Write the expression of temperature, and pressure relation for the constant volume heat addition process
Write the expression of temperature, and volume relation for the constant pressure heat addition process
Here, cutoff ratio is
Write the expression of temperature, and volume relation for the constant pressure heat addition process 3-4.
Write the expression to calculate the heat added to the cycle during process
Write the expression to calculate the heat added to the cycle during process
Here, heat input to the process
Write the expression to calculate the heat added to the cycle during process
Here, specific heat at constant pressure is
Write the expression of net heat addition to the cycle
Write the expression for exergy destruction during the process of the cycle.
Here, temperature of the surroundings is
Write the expression of entropy change for the process
Here, specific heat of air at constant volume is
Write the expression for the exergy loss for the isothermal process
Write the expression of entropy change for the isothermal process
Write the expression for the exergy loss for the process
Write the expression of entropy change for the process
Write the expression for the exergy loss for the process
Here, temperature of the sink is
Write the expression to calculate the total in an ideal dual cycle.
Conclusion:
From Table A-1E, “Molar mass, gas constant, and critical-point properties”, obtain the following properties of air at room temperature.
From Table A-2Ea, “Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases”, obtain the value for gas content
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (VII).
The exergy loss for the isothermal process 1-2
Here
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The exergy loss for the isothermal process 3-4
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
During heat rejection process the largest exergy destruction in an ideal dual cycle occur.
Substitute
Thus, the total exergy destruction in an ideal dual cycle is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS (LL)-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
- 4- In the system shown in the figure, the water velocity in the 12 in. diameter pipe is 8 ft/s. Determine the gage reading at position 1. Elevation 170 ft 1 Elevation 200 ft | 8 ft, 6-in.-diameter, 150 ft, 12-in.-diameter, f = 0.020 f = 0.020 A B Hints: the minor losses should consider the contraction loss at A and the expansion loss at B.arrow_forwardWhat is the moment of Inertia of this body? What is Ixx, Iyy, and Izzarrow_forwardConsider a glass window (Hight = 1.2 m, Width = 2 m). The room thatfaces the window are maintained at 25 o C. The average temperature ofthe inner surface of the window is 5 o C. Calculate the total heat transferrate from through the window a) IdenCfy what type(s) of convecCon is important (circle one). • external forced (Chapter 7)• internal forced (Chapter 8)• natural convecCon (Chapter 9)• boiling and condensaCon (Chapter 10)b) IdenCfy the necessary equaCon(s) needed to solve the problem. c) IdenCfy important fluid properCes you need to solve the problem. d) Calculate the total heat transferred.arrow_forward
- Water is condensing on a square plate (0.5 m x 0.5 m) placed verCcally. If the desired rate ofcondensaCon is 0.016 kJ/s, determine the necessary surface temperature of the plate at atmosphericpressure. Assume the film temperature of 90 o C for evaluaCon of fluid properCes of water and thesurface temperature of 80 o C for the evaluaCon of modified latent heat of vaporizaConarrow_forwardWater at 20 o C enters the 4 cm-diameter, 14 m-long tube at a rate of 0.8 kg/s. The surfacetemperature of the pipe is maintained at 165 o Cby condensing geothermal stream at the shellside of the heat exchanger. Use water properCesat 85 o C for all calculaCons.(a) Show that the water flow is turbulent and thermally fully developed. (b) EsCmate the heat transfer coefficient for convecCve heat transfer from the pipe to the water. For a fully developed turbulent flow within the smooth pipe, the Nu number can becalculated from the following equaCon:(c) Calculate the exit temperature of the water. (d) Share your opinion on whether the use of water properties at 85°C is appropriate. Yes or No because:arrow_forwardConsider a hot automotive engine, which can beapproximated as a 0.5-m-high, 0.40-m-wide, and 0.8-m-long rectangular block. The bottom surface of the block isat a temperature of 100°C and has an emissivity of 0.95.The ambient air is at 20°C, and the road surface is at25°C. Determine the rate of heat transfer from the bottomsurface of the engine block by convection and radiationas the car travels at a velocity of 80 km/h. Assume theflow to be turbulent over the entire surface because of theconstant agitation of the engine block. a) Calculate convective heat transfer coefficient (h). b) Calculate the total heat transfer ratearrow_forward
- 8 mm- Top view -200 mm-180 mm- D B B 12 mm Side view B -8 mm D PROBLEM 1.56 In an alternative design for the structure of Prob. 1.55, a pin of 10-mm-diameter is to be used at A. Assuming that all other specifications remain unchanged, determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired. PROBLEM 1.55 In the structure shown, an 8- mm-diameter pin is used at A, and 12-mm- diameter pins are used at B and D. Knowing that the ultimate shearing stress is 100 MPa at all connections and that the ultimate normal stress is 250 MPa in each of the two links joining B and D, determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired. 20 mm P 8 mm- 12 mm- Front viewarrow_forwardWhere on the beam below is the Maximum Deflection likely to occur? 2P A "ती Point A Point B Point C Point D Point B or Point D ८ B पarrow_forwardSign in ||! PDE 321 proje X IMB321 PDF Lecture 5 X PDF Planet Ec X PDF Planet Ec X PDF PEABWX PDF meeting x PDF GSS Quo X PDF File C:/Users/KHULEKANI/Downloads/CIVE%20281%20Ass-2.pdf Draw | | All | a | Ask Copilot + 1 of 7 | D SOLUTION B PROBLEM 12.16 Block 4 has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a mass of 8 kg. The coefficients of friction between all surfaces of contact are μ, = 0.20 H = 0.15. Knowing that P = 50 N→, determine (a) the acceleration of block B, (b) the tension in the cord. Constraint of cable: 2x + (x-x1) = x + x = constant. a+ag = 0, or aB = -a Assume that block A moves down and block B moves up. Block B: +/ΣF, = 0: NAB - WB cos 0 = 0 =ma: -T+μN + Wsin = We as g + ΣΕ We Eliminate NAB and aB- NAB B Nas HN UNA A NA -T+W(sin+μcоsе) = WB- g VD"M- g Block A: +/ΣF, = 0: NA-NAB - W₁cos + Psinė = 0 N₁ = N AB+W cose - Psin = (WB+WA)cose - Psinė ΣF=ma -T+Wsino-FAB-F + Pcos = CIVE 281 X + Ждал g Q | го || حالم ☑arrow_forward
- Where on the below beam is the Maxiumum Slope likely to occur? 120 Point A Point B Point C Point B or Point C B сarrow_forwardA very thin metallic sheet is placed between two wood plates of different thicknesses. Theplates are firmly pressed together and electricity is passed through the sheet. The exposed surfaces ofthe two plates lose heat to the ambient fluid by convection. Assume uniform heating at the interface.Neglect end effects and assume steady state.[a] Will the heat transfer through the two plates be the same? Explain.[b] Will the exposed surfaces be at the same temperature? Explainarrow_forwardDesign consideration requires that the surface of a small electronic package be maintained at atemperature not to exceed 82 o C. Noise constraints rule out the use of fans. The power dissipated inthe package is 35 watts and the surface area is 520 cm2 . The ambient temperature and surroundingwalls are assumed to be at 24 o C. The heat transfer coefficient is estimated to be 9.2 W/m2- oC andsurface emissivity is 0.7. Will the package dissipate the required power without violating designconstraints?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





