
Concept explainers
Draw the products of each reaction, and indicate the stereochemistry where appropriate.
a. 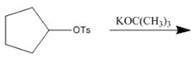 f
f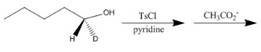
b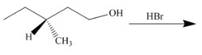 g.
g. 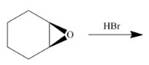
c. 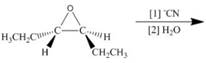 h.
h. 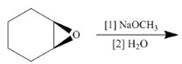
d. ![]() i.
i. 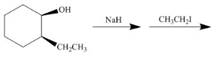
e. 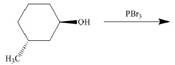 j.
j. 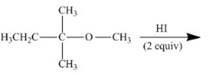
(a)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: Alkyl tosylates undergo elimination reaction when they are allowed to react with strong nucleophilic base. The mechanism of the elimination reaction is
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
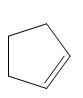
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of alkyl tosylate with
Alkyl tosylates undergo elimination reaction when they are allowed to react with strong nucleophilic base. The mechanism of the reaction is
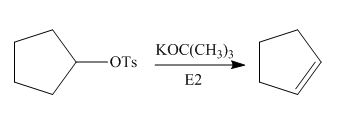
Figure 1
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 2
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: The reaction of alcohols with halogen acids
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
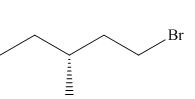
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of an alcohol with
The reaction of alcohols with halogen acids
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
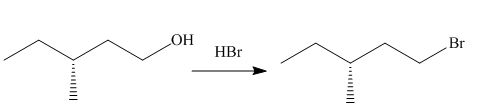
Figure 3
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 4
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
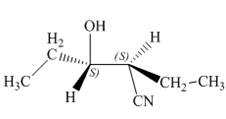
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of epoxide ring with cyanide ion.
In the given reaction,
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
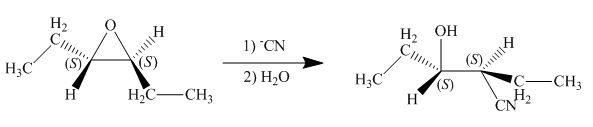
Figure 5
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 6
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: The
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
Figure 8
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of alkyl tosylate with
The
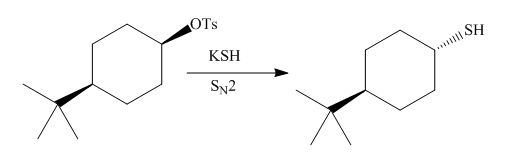
Figure 7
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 8
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: Alkyl bromides are obtained by the reaction of
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
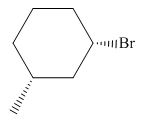
Figure 10
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of secondary alcohol with
Alkyl bromides are obtained by the reaction of
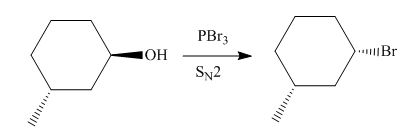
Figure 9
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 10
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: Alcohols are converted into alkyl tosylates by treatment with
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
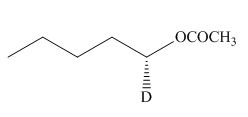
Figure 12
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of an alcohol with
Alcohols are converted into alkyl tosylates by treatment with
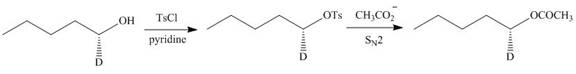 Figure 11
Figure 11
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 12
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
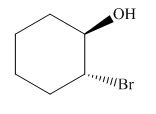
Figure 14
Explanation of Solution
The give reaction involves treatment of an epoxide with halogen acid
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
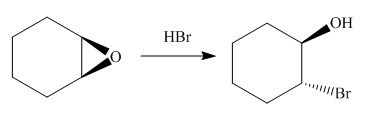
Figure 13
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 14
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
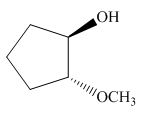
Figure 16
Explanation of Solution
The give reaction involves treatment of an epoxide with
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
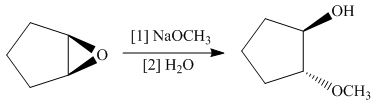
Figure 15
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 16
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: Ethers are the most common organic products of nucleophilic substitution reaction. They are prepared from alkyl halides and strong nucleophiles. The reaction proceeds through
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
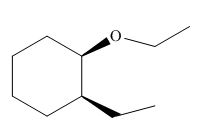
Figure 18
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of a
The alkoxide salts are prepared from alcohols through the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction. In this reaction,
The obtained alkoxide from this reaction contains
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
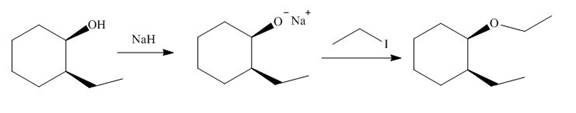
Figure 17
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,
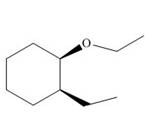
Figure 18
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 18.
(j)
Interpretation: The product of the given reaction is to be drawn including stereochemistry if appropriate.
Concept introduction: Ethers react with strong acids, (only
In this reaction, both
Answer to Problem 9.71P
The product of the given reaction is,
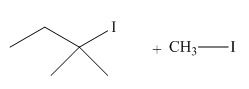
Figure 20
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves treatment of an ether with two equivalents of
Ethers react with strong acids, (only
In this reaction, both
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
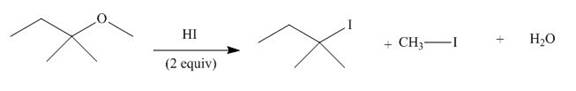
Figure 19
Thus, the product of the given reaction is,

Figure 20
The product of the given reaction is drawn in Figure 20.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
