
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780100257061
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 164RP
The cantilever beam BC is attached to the steel cable AB as shown. Knowing that the cable is initially taut, determine the tension in the cable caused by the distributed load shown. Use E = 200 GPa.
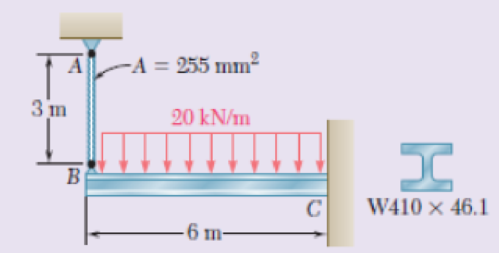
Fig. P9.164
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An unpressurized cylindrical tank with a 100-foot diameter holds a 40-foot column of water. What is total force acting against the bottom of the tank?
7. In the following problems check to see if the set S is a vector subspace of the corresponding
R. If it is not, explain why not. If it is, then find a basis and the dimension.
(a) S
=
(b) S =
{[],+,"}
X1
x12x2 = x3
CR³
{[1], 4+4 = 1} CR³
X2
AAA
Show laplace transform on 1; (+) to L (y(+)) : SY(s) = x (0)
Y(s) = £ [lx (+)] = 5 x(+) · est de
2
-St
L [ y (^) ] = So KG) et de
D
2
D
D
AA
Y(A) → Y(s)
Ŷ (+) → s Y(s)
-y
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 9.2 - In the following problems assume that the flexural...Ch. 9.2 - In the following problems assume that the flexural...Ch. 9.2 - In the following problems assume that the flexural...Ch. 9.2 - 9.1 through 9.4 For the loading shown, determine...Ch. 9.2 - 9.5 and 9.6 For the cantilever beam and loading...Ch. 9.2 - 9.5 and 9.6 For the cantilever beam and loading...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.2 - Knowing that beam .AB is a W10 33 rolled shape...Ch. 9.2 - Knowing that beam AB is an S200 34 roiled shape...
Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, (a) express the...Ch. 9.2 - (a) Determine the location and magnitude of the...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 9.2 - Knowing that beam AE is a W360 101 rolled shape...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, knowing that a = 2...Ch. 9.2 - Knowing that beam AE is an S200 27.4 rolled shape...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.2 - 9.19 through 9.22 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.2 - 9.19 through 9.22 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.2 - 9.19 through 9.22 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.2 - 9.19 through 9.22 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam shown, determine the reaction at the...Ch. 9.2 - For the beam shown, determine the reaction at the...Ch. 9.2 - 9.25 through 9.28 Determine the reaction at the...Ch. 9.2 - 9.25 through 9.28 Determine the reaction at the...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 9.2 - 9.25 through 9.28 Determine the reaction at the...Ch. 9.2 - 9.29 and 9.30 Determine the reaction at the roller...Ch. 9.2 - 9.29 and 9.30 Determine the reaction at the roller...Ch. 9.2 - 9.37 and 9.32 Determine the reaction at the roller...Ch. 9.2 - 9.31 and 9.32 Determine the reaction at the roller...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 33PCh. 9.2 - 9.33 and 9.34 determine the reaction at A and draw...Ch. 9.3 - 9.35 and 9.36 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.35 and 9.36 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.37 and 9.38 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.37 and 9.38 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.39 and 9.40 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.39 and 9.40 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.41 and 9.42 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.41 and 9.42 For the beam and loading shown (a)...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - For the timber beam and loading shown, determine...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - 9.49 and 9.50 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.49 and 9.50 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.51 and 9.52 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.49 and 9.50 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam shown, and knowing that P = 40 kN,...Ch. 9.3 - 9.55 and 9.56 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 9.3 - 9.55 and 9.56 For the beam and loading shown, (a)...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 59PCh. 9.3 - 9.59 through 9.62 For the beam and loading...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 61PCh. 9.3 - 9.59 through 9.62 For the beam and loading...Ch. 9.3 - The rigid bars BF and DH are welded to the...Ch. 9.3 - The rigid bar DEF is welded at point D to the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 84PCh. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.4 - Use the method of superposition to solve the...Ch. 9.5 - 9.95 through 9.98 For the uniform cantilever beam...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 96PCh. 9.5 - 9.95 through 9.98 For the uniform cantilever beam...Ch. 9.5 - 9.95 through 9.98 For the uniform cantilever beam...Ch. 9.5 - 9.99 and 9.100 For the uniform cantilever beam and...Ch. 9.5 - 9.99 and 9.100 For the uniform cantilever beam and...Ch. 9.5 - For the cantilever beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 102PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 103PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 104PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 105PCh. 9.5 - For the cantilever beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.5 - Two cover plates are welded to the rolled-steel...Ch. 9.5 - Two cover plates are welded to the rolled-steel...Ch. 9.5 - 9.109 through 9.114 For the prismatic beam and...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 110PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 111PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 112PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 113PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 114PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 115PCh. 9.5 - 9.115 and 9.116 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 117PCh. 9.5 - 9.118 and 9.119 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 119PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 120PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 121PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 122PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 123PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 124PCh. 9.6 - 9.125 through 9.128 For the prismatic beam and...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 126PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 127PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 128PCh. 9.6 - 9.129 and 9.130 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 130PCh. 9.6 - For the timber beam and loading shown, determine...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 132PCh. 9.6 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 134PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 135PCh. 9.6 - Knowing that the beam AD is made of a solid steel...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 137PCh. 9.6 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 139PCh. 9.6 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 141PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 142PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 143PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 144PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 145PCh. 9.6 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 147PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 148PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 149PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 150PCh. 9.6 - 9.151 and 9.152 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 152PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 153PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 154PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 155PCh. 9.6 - Fig. P9.155 and P9.156 9.156 For the beam and...Ch. 9 - For the loading shown, determine (a) the equation...Ch. 9 - Prob. 158RPCh. 9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the reaction at A and draw the bending...Ch. 9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9 - Beam CE rests on beam AB as shown. Knowing that a...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam BC is attached to the steel...Ch. 9 - For the cantilever beam and loading shown,...Ch. 9 - Knowing that P = 4 kips, determine (a) the slope...Ch. 9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the reaction at the roller support and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1) In each of the following scenarios, based on the plane of impact (shown with an (n, t)) and the motion of mass 1, draw the direction of motion of mass 2 after the impact. Note that in all scenarios, mass 2 is initially at rest. What can you say about the nature of the motion of mass 2 regardless of the scenario? m1 15 <+ m2 2) y "L χ m1 m2 m1 בז m2 Farrow_forward8. In the following check to see if the set S is a vector subspace of the corresponding Rn. If it is not, explain why not. If it is, then find a basis and the dimension. X1 (a) S = X2 {[2], n ≤ n } c X1 X2 CR² X1 (b) S X2 = X3 X4 x1 + x2 x3 = 0arrow_forward2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities V₁ and V₂, respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact, mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution. m1 m2 8 m1 ↑ บา m2 ñ Вarrow_forward
- The fallowing question is from a reeds book on applied heat i am studying. Although the answer is provided, im struggling to understand the whole answer and the formulas and the steps theyre using. Also where some ov the values such as Hg and Hf come from in part i for example. Please explain step per step in detail thanks In an NH, refrigerator, the ammonia leaves the evaporatorand enters the cornpressor as dry saturated vapour at 2.68 bar,it leaves the compressor and enters the condenser at 8.57 bar with50" of superheat. it is condensed at constant pressure and leavesthe condenser as saturated liquid. If the rate of flow of the refrigerantthrough the circuit is 0.45 kglmin calculate (i) the compressorpower, (ii) the heat rejected to the condenser cooling water in kJ/s,an (iii) the refrigerating effect in kJ/s. From tables page 12, NH,:2.68 bar, hg= 1430.58.57 bar, hf = 275.1 h supht 50" = 1597.2Mass flow of refrigerant--- - - 0.0075 kgls 60Enthalpy gain per kg of refrigerant in…arrow_forwardstate the formulas for calculating work done by gasarrow_forwardExercises Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) y" + y = 3x² 3) "+2y+3y=27x 5) y"+y=6sin(x) 7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x) 9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x) 11) y"+y=x²+x 13) y"-2y+y=e* 15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³ 2) y"+2y' + y = x² 4) "+y=-30 sin(4x) 6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x) 8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x) 10) y+y-2y=3e* 12) y"-y=e* 14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x² 16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)arrow_forward
- The state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi, Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T = -14.00 kpsi. Determine the principal stresses. The principal normal stress σ₁ is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ2 is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ3 is determined to be kpsi. kpsi. The principal shear stress 71/2 is determined to be [ The principal shear stress 7½ is determined to be [ The principal shear stress T₁/, is determined to be [ kpsi. kpsi. kpsi. kpsi.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotatingand transmitting a torque of 150 N * m from the left bearing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile keyseat at the middle under the load. (I want to understand this problem)arrow_forwardProb 2. The material distorts into the dashed position shown. Determine the average normal strains &x, Ey and the shear strain Yxy at A, and the average normal strain along line BE. 50 mm B 200 mm 15 mm 30 mm D ΕΙ 50 mm x A 150 mm Farrow_forward
- Prob 3. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the shear strain, Yxy, at A. Prob 4. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain & along the x axis. Prob 5. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain &x along the x' axis. x' 45° 800 mm 45° 45% 800 mm 5 mmarrow_forwardAn airplane lands on the straight runaway, originally travelling at 110 ft/s when s = 0. If it is subjected to the decelerations shown, determine the time t' needed to stop the plane and construct the s -t graph for the motion. draw a graph and show all work step by steparrow_forwarddny dn-1y dn-1u dn-24 +a1 + + Any = bi +b₂- + +bnu. dtn dtn-1 dtn-1 dtn-2 a) Let be a root of the characteristic equation 1 sn+a1sn- + +an = : 0. Show that if u(t) = 0, the differential equation has the solution y(t) = e\t. b) Let к be a zero of the polynomial b(s) = b₁s-1+b2sn−2+ Show that if the input is u(t) equation that is identically zero. = .. +bn. ekt, then there is a solution to the differentialarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license