
The reaction
Answer to Problem 152P
The reaction
The reaction
The reaction
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Let, choose reaction
Show the free body diagram of the beam in below Figure 1.
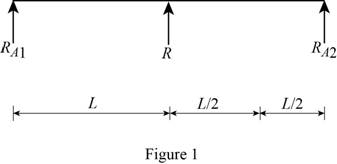
Calculate the vertical reaction
Calculate the vertical reaction
Show the free body diagram of the beam in below Figure 2.
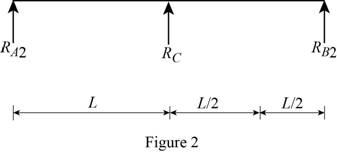
Calculate the vertical reaction
Calculate the vertical reaction
Calculate the moment
Calculate the
Substitute
Show the
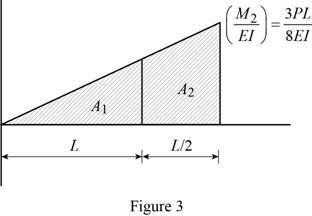
Calculate the area
Substitute
Calculate the area
Substitute
Calculate the moment
Substitute
Calculate the
Substitute
Show the
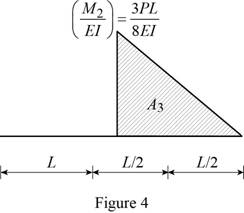
Calculate the area
Substitute
Calculate the moment
Calculate the
Substitute
Show the
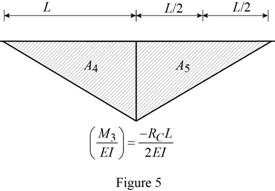
Calculate the area
Substitute
Calculate the area
Substitute
Calculate the tangential deviation of A with respect to B using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate the tangential deviation of C with respect to A using the relation:
Substitute
Express the deflection
Express the deflection
Substitute
Calculate the reaction
Substitute
Calculate the reaction
Substitute
Calculate the reaction
Substitute
Thus, the reaction
Thus, the reaction
Thus, the reaction
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- USE MATLAB ONLY provide typed code solve for velocity triangle and dont provide copied answer Turbomachienery . GIven: vx = 185 m/s, flow angle = 60 degrees, R = 0.5, U = 150 m/s, b2 = -a3, a2 = -b3 Find: velocity triangle , a. magnitude of abs vel leaving rotor (m/s) b. flow absolute angles (a1, a2, a3) 3. flow rel angles (b2, b3) d. specific work done e. use code to draw vel. diagram Use this code for plot % plots Velocity Tri. in Ch4 function plotveltri(al1,al2,al3,b2,b3) S1L = [0 1]; V1x = [0 0]; V1s = [0 1*tand(al3)]; S2L = [2 3]; V2x = [0 0]; V2s = [0 1*tand(al2)]; W2s = [0 1*tand(b2)]; U2x = [3 3]; U2y = [1*tand(b2) 1*tand(al2)]; S3L = [4 5]; V3x = [0 0]; V3r = [0 1*tand(al3)]; W3r = [0 1*tand(b3)]; U3x = [5 5]; U3y = [1*tand(b3) 1*tand(al3)]; plot(S1L,V1x,'k',S1L,V1s,'r',... S2L,V2x,'k',S2L,V2s,'r',S2L,W2s,'b',U2x,U2y,'g',... S3L,V3x,'k',S3L,V3r,'r',S3L,W3r,'b',U3x,U3y,'g',...... 'LineWidth',2,'MarkerSize',10),... axis([-1 6 -4 4]), ...…arrow_forwardThe answer should equal to 1157. Please sent me the solution. Thank you!arrow_forwardBONUS: If the volume of the 8cm x 6.5cm x 6cm Block of Aluminum was 312cm3 before machining, find how much material was removed when the fixture below was machined. +2 2.00 cm 6.00 cm 2.50 cm 6.50 cm 1.00 cm 2.50 cm 11.00 cm 8.00 cm 30 CP 9411 FL.4) (m² 1157 Area of triangle = 1/2*B*H Area of circle = лR² Circumference of a circle = 2πR 6.00 cm 6.50 cm 1.50 cm Radius 1.50 cm 1.00 cmarrow_forward
- Consider a 5m by 5m wet concret patio with an average water film thickness of .2mm. Now wind at 50 km/h is blowing over the surface. If the air is at 1 atm, 15oC and 35 percent relative humidity, determine how long it will take for the patio to completely dry.arrow_forward70. Compute the number of cubic centimeters of iron required for the cast-iron plate shown. The plate is 3.50 centimeters thick. Round the answer to the nearest cubic centimeter. 50.0 cm 40.0 cm Radius 150° 115.0 cm- 81.0 cmarrow_forwardLaw of Sines Solve the following problems using the Law of Sin 7. Find side x. All dimensions are in inches. -°-67°-37° 81° x Sin A 8.820 X 67°00' 32°00' a sin A b C sin B sin Carrow_forward
- 35. a. Determine B. b. Determine side b. c. Determine side c. 5.330 in.- ZB 73°30'arrow_forwardConsider a 12 cm internal diameter, 14 m long circular duct whose interior surface is wet. The duct is to be dried by forcing dry air at 1 atm and 15 degrees C throught it at an average velocity of 3m/s. The duct passes through a chilled roo, and it remains at an average temp of 15 degrees C at all time. Determine the mass transfer coeeficient in the duct.arrow_forwardnote n=number of link(dont include the ground link (fixed))arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





