
Concept explainers
In kinetics experiments, the hydrolysis of the substrate sialic acid by neuraminidase appears to obey Michaelis—Menten kinetics. Neuraminidase activity is critical for viral infectivity; thus, this enzyme is the target of much work by pharmaceutical companies to develop a drug to treat influenza virus
infection. The drug "Tamiflu" is a competitive inhibitor of neuraminidase. Initial rate data collected at
pH = 6.15, 37 oC with 0.021 µM neuraminidase and 25.0 µM sialic acid gives a Lineweaver—Burk plot with a slope of 51.2 s.
a. Recall from Problem that the kcat for neuraminidase at pH = 6.15, 37 oC is 26.8 s-1. Calculate KM for the hydrolysis of sialic acid.
b. When the reactions in part (a) are repeated in the presence of 0.040 µM of Tamiflu, the slope of the Lineweaver—Burk plot is 198.8 s. Calculate the value of KI for Tamiflu.
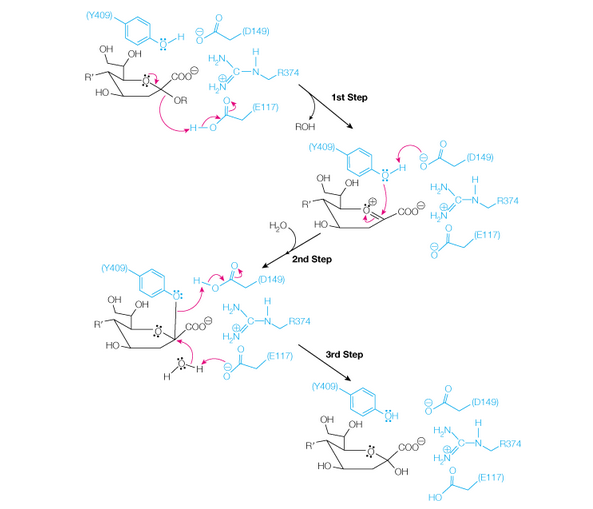
23. Shown below is a proposed mechanism for the cleavage of sialic acid by the viral enzyme
neuraminidase. The kcat for the wild-type enzyme at pH = 6.15, 37 oC is 26.8 s-1.
a. Describe the roles of the following amino acids in the catalytic mechanism: Glu117, Tyr409, and Asp149. List all of the following that apply: general acid/base catalysis (GABC), covalent catalysis, electrostatic stabilization of transition state.
b. Based on the information shown in the scheme, would you expect mutation of Glu117 to Ala to have a greater effect on KM or kcat?
c. For the R374N mutant at pH = 6.15, 37 oC, kcat is 0.020 s-1, and KM is relatively unaffected. Based on this result, it seems that R374 is more critical for catalysis than for substrate binding.
Explain how R374 stabilizes the reaction transition state more than the substrate (i.e., what feature of this reaction would explain tighter binding to the transition state vs. substrate?).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
- Biochemistry Please help. Thank you When carbamyl phosphate is joined to L-ornathine, where does the energy for the reaction come from?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you What is the function of glutamate dehydrogenase?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you How and why does a high protein diet affect the enzymes of the urea cycle?arrow_forward
- Biochemistry What is the importance of the glucose-alanine cycle?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Assuming 2.5 molecules of ATP per oxidation of NADH/(H+) and 1.5molecules of ATP per oxidation of FADH2, how many ATP are produced per molecule of pyruvate? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. How would you explain the term ‘good food’? 2. How would you define Nutrition? 3. Nutrients are generally categorised into two forms. Discuss.arrow_forward
- Biochemistry Question. Please help solve. Thank you! Based upon knowledge of oxidation of bioorganic compounds and howmuch energy is released during their oxidation, rank the following, from most to least, with respect to how much energy would be produced from each during their oxidation. Explain your placement for each one.arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question.For the metabolism of amino acids what is the first step for theirbreakdown? Why is it necessary for this breakdown product to be transported to the liver? For the catabolism of the carbon backbone of these amino acids, there are 7 entry points into the “standard” metabolic pathways. List these 7 entry points and which amino acids are metabolized to these entry points. Please help. Thank you!arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question. Please help. Thank you. You are studying pyruvate utilization in mammals for ATP production under aerobic conditions and have synthesized pyruvate with Carbon #1 labelled with radioactive C14. After only one complete cycle of the TCA cycle, which of the TCA cycle intermediates would be labeled with C14? Explain your answer. Interestingly, you find C14 being excreted in the urine. How does it get there?arrow_forward
- Biochemistry question. Please help with. Thanks in advance For each of the enzymes listed below, explain what the enzyme does including function, names (or structures) of the substrate and products and the pathway(s) (if applicable) it is/are found in. (a) ATP synthetase (b) succinate dehydrogenase (c) isocitrate lyase (d) acetyl CoA carboxylase (e) isocitrate dehydrogenase (f) malate dehydrogenasearrow_forwardDraw and name each alcohol and classify it as primary, secondary, or tertiary. Explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardDraw the product of each reaction. If there are multiple products, draw only the major product. Explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning





